Abstract
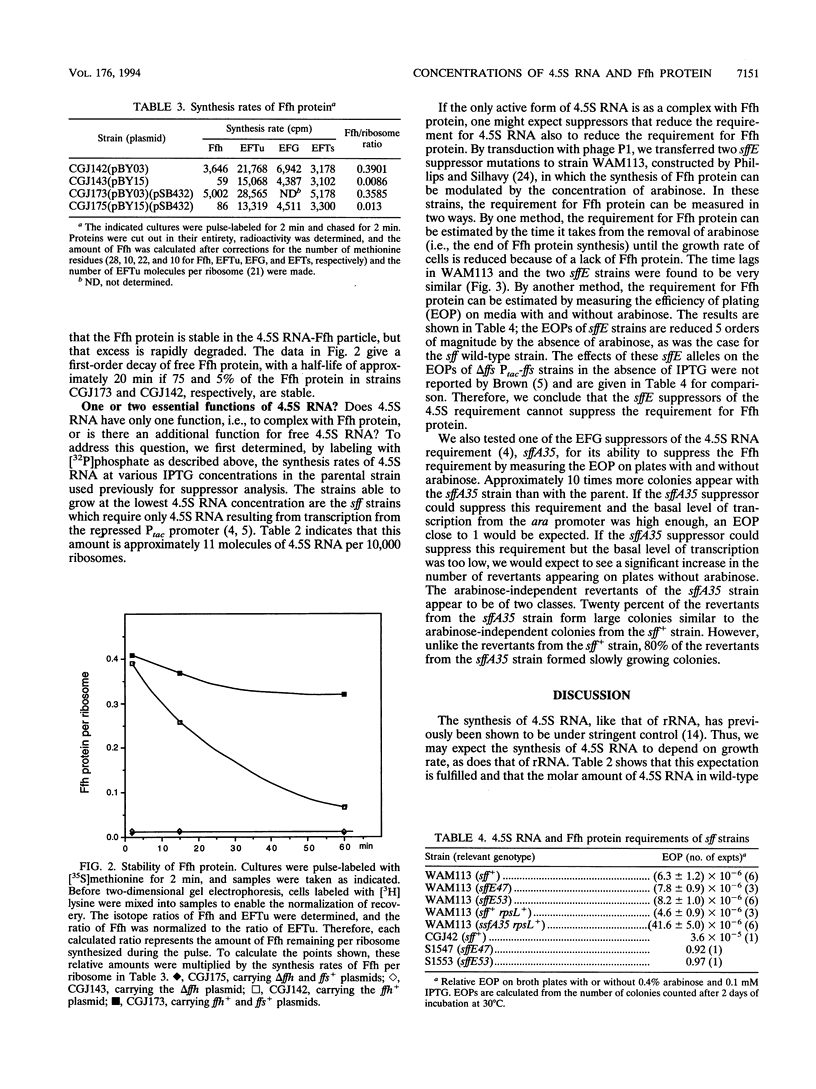
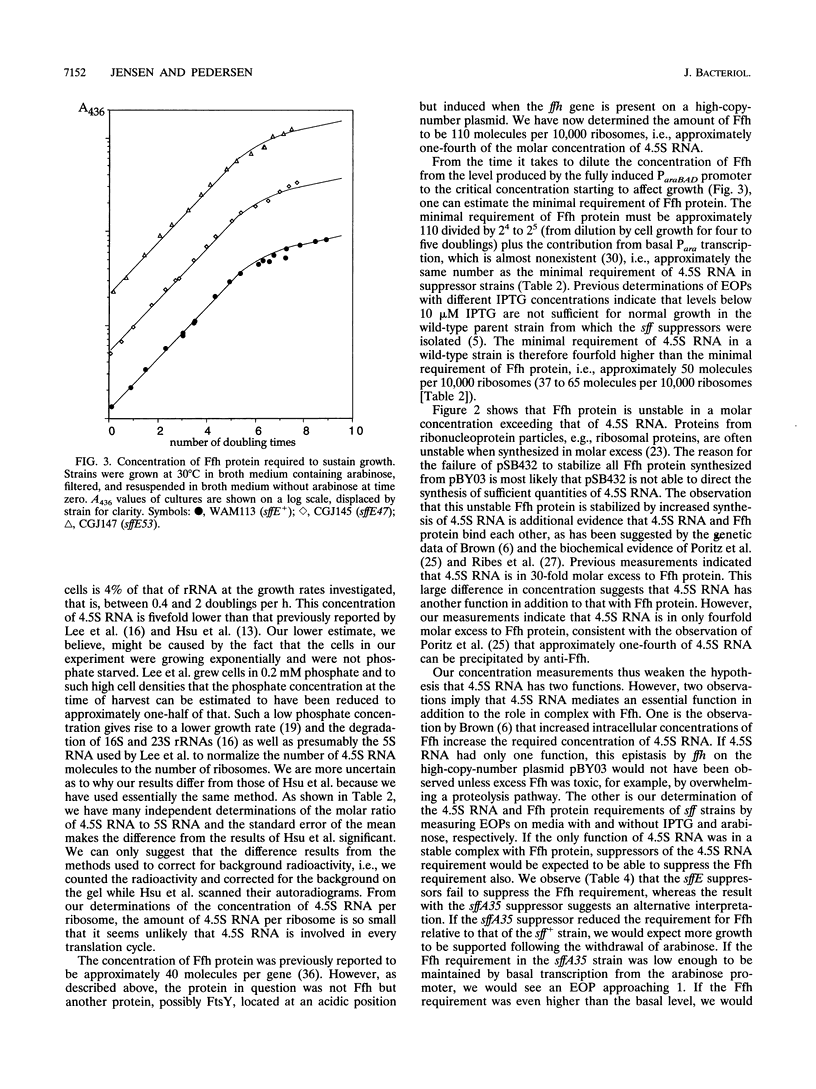
We measured the concentrations of both 4.5S RNA and Ffh protein under a variety of growth conditions and found that there were 400 molecules of 4.5S RNA per 10,000 ribosomes in wild-type cells and that the concentration of Ffh protein was one-fourth of that. This difference in concentration is 1 order of magnitude less than that previously reported but still significant. Pulse-chase labeling experiments indicated that Ffh protein is unstable in cells carrying ffh on high-copy-number plasmids and that simultaneous overproduction of 4.5S RNA stabilizes Ffh protein. Our analyses show that free Ffh protein is degraded with a half-life of approximately 20 min. We also tested whether three previously isolated suppressors of 4.5S RNA deficiency could reduce the requirement for Ffh protein. Since the two sffE suppressors do not suppress the Ffh requirement, we suggest that 4.5S RNA either acts in a sequential reaction with Ffh or has two functions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein H. D., Poritz M. A., Strub K., Hoben P. J., Brenner S., Walter P. Model for signal sequence recognition from amino-acid sequence of 54K subunit of signal recognition particle. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):482–486. doi: 10.1038/340482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgaize D. B., Phillips T. A., VanBogelen R. A., Jones P. G., Neidhardt F. C., Fournier M. J. Loss of 4.5S RNA induces the heat shock response and lambda prophage in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1151–1154. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1151-1154.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Holy A. Regulation of ribosomal RNA promoters with a synthetic lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6929–6933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. 4.5S RNA: does form predict function? New Biol. 1991 May;3(5):430–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S., Fournier M. J. The 4.5 S RNA gene of Escherichia coli is essential for cell growth. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 25;178(3):533–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. Mutations in the gene for EF-G reduce the requirement for 4.5S RNA in the growth of E. coli. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):825–833. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90620-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. Time of action of 4.5 S RNA in Escherichia coli translation. J Mol Biol. 1989 Sep 5;209(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Sanger F., Barrell B. G. Nucleotide sequence of 5S-ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli. Nature. 1967 Aug 12;215(5102):735–736. doi: 10.1038/215735a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byström A. S., Björk G. R. Chromosomal location and cloning of the gene (trmD) responsible for the synthesis of tRNA (m1G) methyltransferase in Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(3):440–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00330046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byström A. S., Björk G. R. The structural gene (trmD) for the tRNA(m1G)methyltransferase is part of a four polypeptide operon in Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(3):447–454. doi: 10.1007/BF00330047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. R., Hatfull G. F., Salmond G. P. A new cell division operon in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):134–145. doi: 10.1007/BF02428043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. M., Zagorski J., Fournier M. J. Cloning and sequence analysis of the Escherichia coli 4.5 S RNA gene. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 25;178(3):509–531. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Dahlberg J. E. Small ribonucleic acids of Escherichia coli. II. Noncoordinate accumulation during stringent control. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):5033–5041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen C. G., Brown S., Pedersen S. Effect of 4.5S RNA depletion on Escherichia coli protein synthesis and secretion. J Bacteriol. 1994 May;176(9):2502–2506. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.9.2502-2506.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Bailey S. C., Apirion D. Small stable RNAs from Escherichia coli: evidence for the existence of new molecules and for a new ribonucleoprotein particle containing 6S RNA. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):1015–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.1015-1023.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. D., Bernstein H. D., Walter P. Interaction of E. coli Ffh/4.5S ribonucleoprotein and FtsY mimics that of mammalian signal recognition particle and its receptor. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):657–659. doi: 10.1038/367657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S., Bloch P. L., Reeh S., Neidhardt F. C. Patterns of protein synthesis in E. coli: a catalog of the amount of 140 individual proteins at different growth rates. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S., Reeh S. V. Analysis of the proteins synthesized in ultraviolet light-irradiated Escherichia coli following infection with the bacteriophages lambdadrifd 18 and lambdadfus-3. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Mar 30;144(3):339–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00341733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen C. Escherichia coli ribosomal protein L10 is rapidly degraded when synthesized in excess of ribosomal protein L7/L12. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):431–436. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.431-436.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. J., Silhavy T. J. The E. coli ffh gene is necessary for viability and efficient protein export. Nature. 1992 Oct 22;359(6397):744–746. doi: 10.1038/359744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Bernstein H. D., Strub K., Zopf D., Wilhelm H., Walter P. An E. coli ribonucleoprotein containing 4.5S RNA resembles mammalian signal recognition particle. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1111–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.1701272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Strub K., Walter P. Human SRP RNA and E. coli 4.5S RNA contain a highly homologous structural domain. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):4–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribes V., Römisch K., Giner A., Dobberstein B., Tollervey D. E. coli 4.5S RNA is part of a ribonucleoprotein particle that has properties related to signal recognition particle. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):591–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90454-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römisch K., Webb J., Herz J., Prehn S., Frank R., Vingron M., Dobberstein B. Homology of 54K protein of signal-recognition particle, docking protein and two E. coli proteins with putative GTP-binding domains. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):478–482. doi: 10.1038/340478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:215–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steen R., Jemiolo D. K., Skinner R. H., Dunn J. J., Dahlberg A. E. Expression of plasmid-coded mutant ribosomal RNA in E. coli: choice of plasmid vectors and gene expression systems. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1986;33:1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita S., Sato M., Toba M., Masahashi W., Hashimoto-Gotoh T. High-copy-number and low-copy-number plasmid vectors for lacZ alpha-complementation and chloramphenicol- or kanamycin-resistance selection. Gene. 1987;61(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90365-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Disassembly and reconstitution of signal recognition particle. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):525–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Purification of a membrane-associated protein complex required for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7112–7116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström P. M., Björk G. R. Noncoordinate translation-level regulation of ribosomal and nonribosomal protein genes in the Escherichia coli trmD operon. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3025–3031. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3025-3031.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Belasco J. G., Schottel J. L., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Decay of mRNA in Escherichia coli: investigation of the fate of specific segments of transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




