Abstract
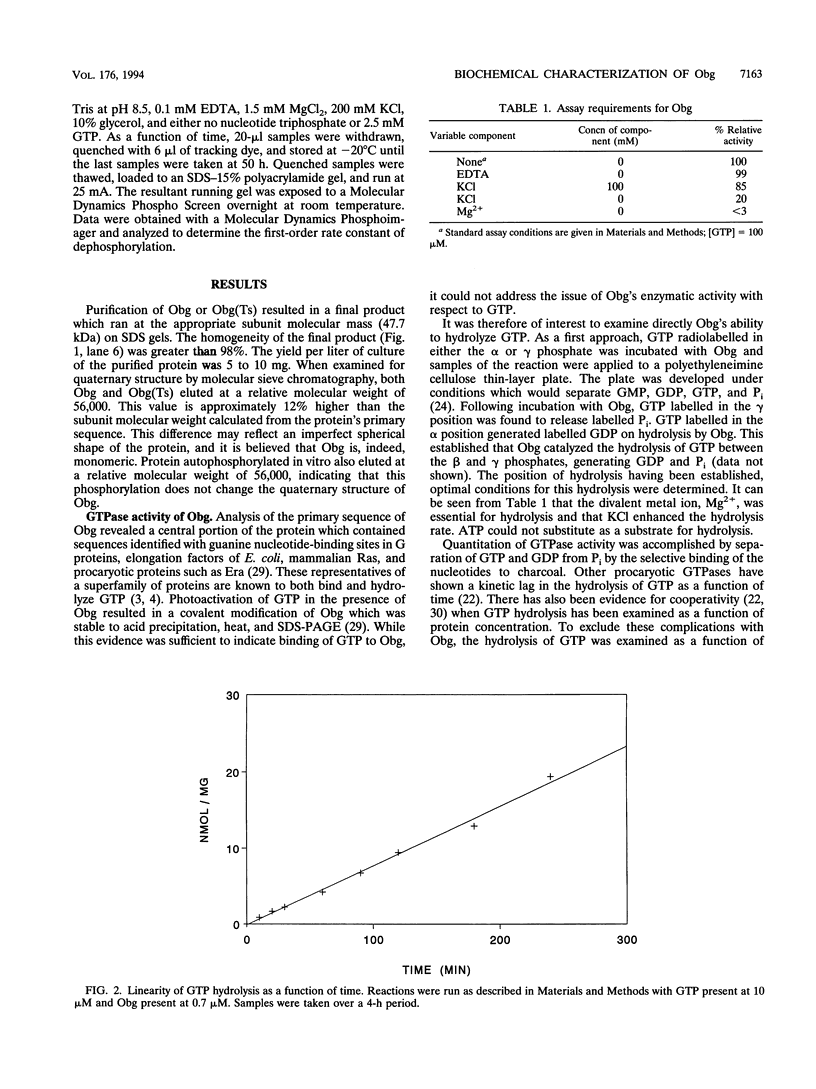
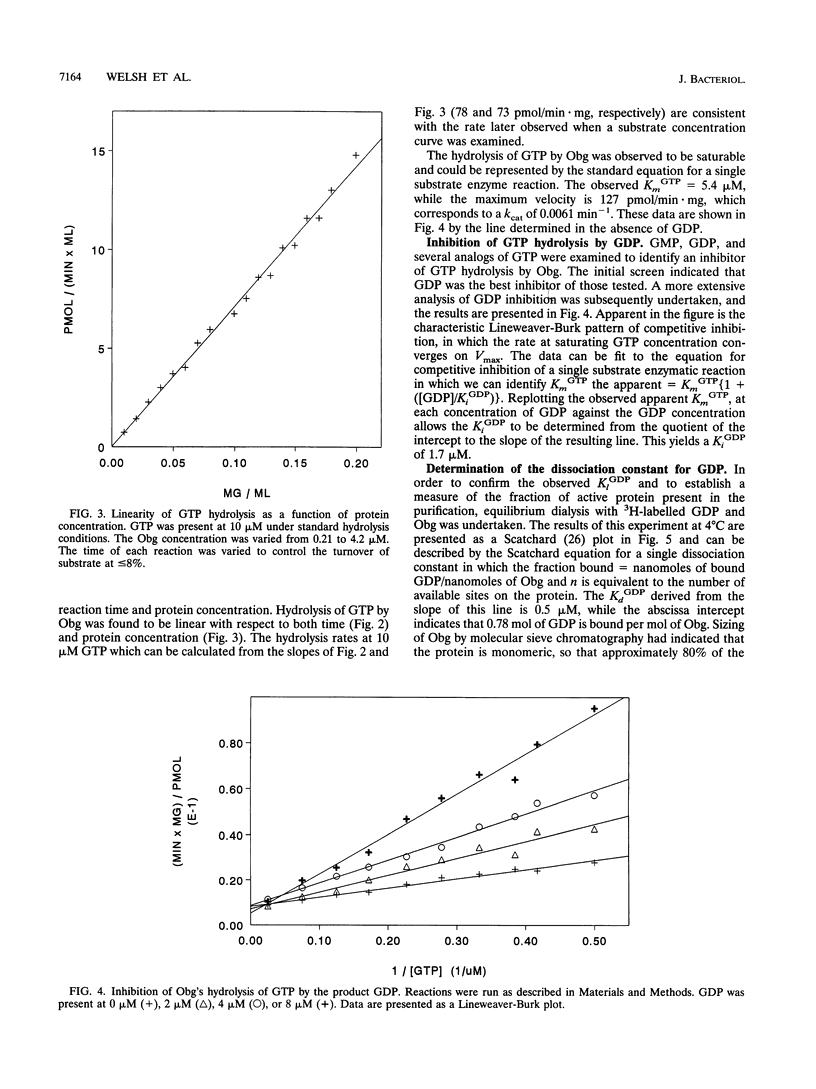
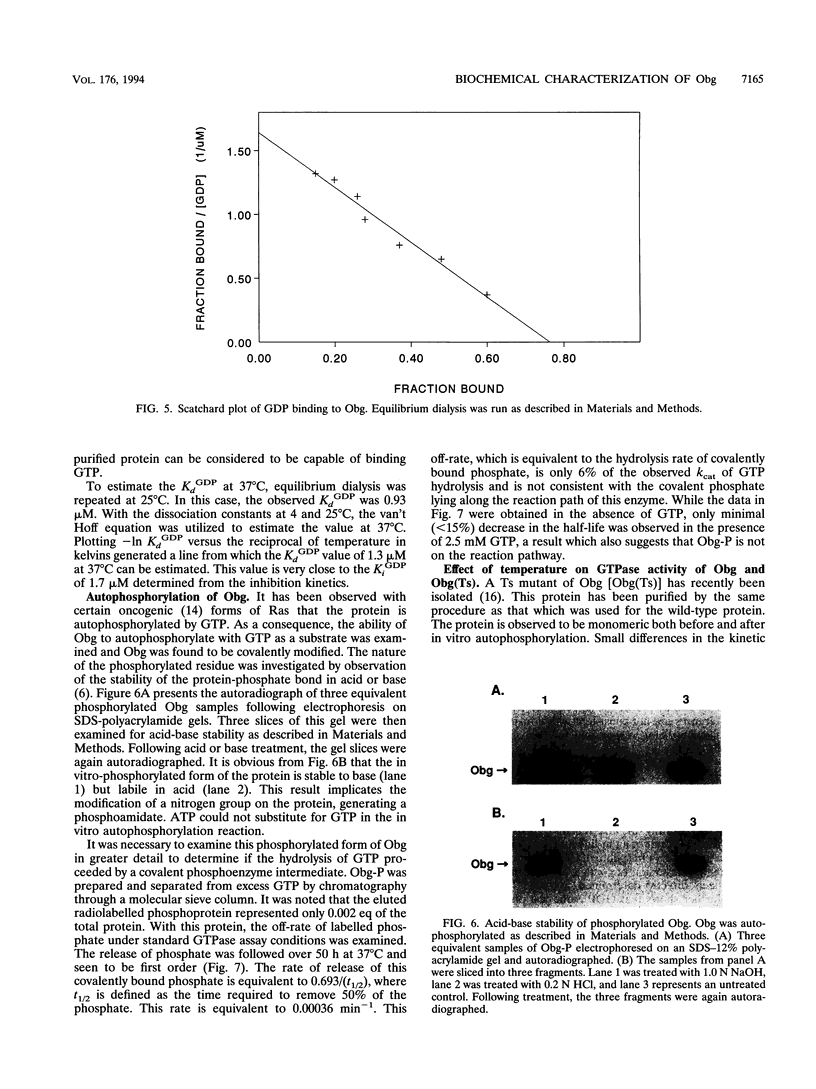
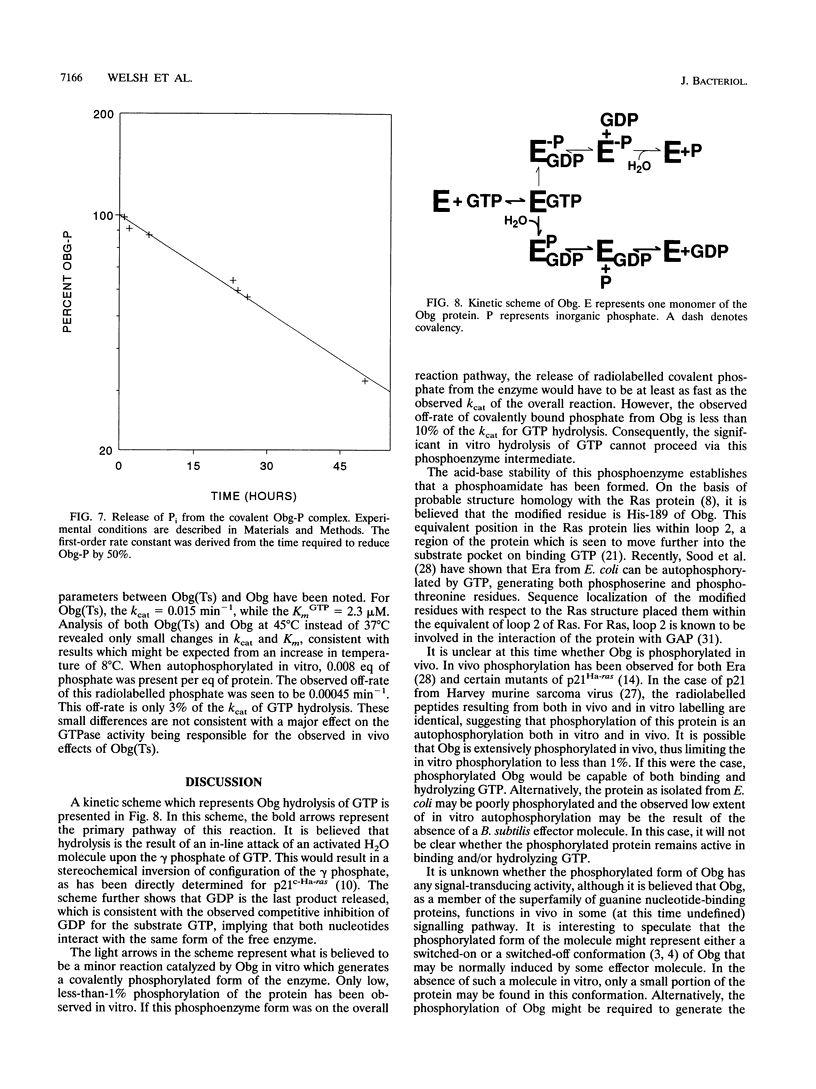
An essential guanine nucleotide-binding protein, Obg, of Bacillus subtilis has been characterized with respect to its enzymatic activity for GTP. The protein was seen to hydrolyze GTP with a Km of 5.4 microM and a kcat of 0.0061 min-1 at 37 degrees C. GDP was a competitive inhibitor of this hydrolysis, with an inhibition constant of 1.7 microM at 37 degrees C. The dissociation constant for GDP from the Obg protein was 0.5 microM at 4 degrees C and was estimated to be 1.3 microM at 37 degrees C. Approximately 80% of the purified protein was capable of binding GDP. In addition to hydrolysis of GTP, Obg was seen to autophosphorylate with this substrate. Subsequent release of the covalent phosphate proceeds at too slow a rate to account for the overall rate of GTP hydrolysis, indicating that in vitro hydrolysis does not proceed via the observed phosphoamidate intermediate. It was speculated that the phosphorylated form of the enzyme may represent either a switched-on or a switched-off configuration, either of which may be normally induced by an effector molecule. This enzyme from a temperature-sensitive mutant of Obg did not show significantly altered GTPase activity at the nonpermissive temperature.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnn J., March P. E., Takiff H. E., Inouye M. A GTP-binding protein of Escherichia coli has homology to yeast RAS proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8849–8853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Der C. J. Emerging concepts in the Ras superfamily of GTP-binding proteins. FASEB J. 1993 Jun;7(9):750–759. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.9.8330683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbulys D., Trach K. A., Hoch J. A. Initiation of sporulation in B. subtilis is controlled by a multicomponent phosphorelay. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):545–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90238-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. M., Takiff H. E., Barber A. M., Dubois G. C., Bardwell J. C., Court D. L. Expression and characterization of RNase III and Era proteins. Products of the rnc operon of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2888–2895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari F. A., Trach K., Hoch J. A. Sequence analysis of the spo0B locus reveals a polycistronic transcription unit. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):556–562. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.556-562.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein J., Goody R. S., Webb M. R. The mechanism of guanosine nucleotide hydrolysis by p21 c-Ha-ras. The stereochemical course of the GTPase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6188–6190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda K., Nakamura K., Nishiguchi M., Yamane K. Cloning and characterization of a Bacillus subtilis gene encoding a homolog of the 54-kilodalton subunit of mammalian signal recognition particle and Escherichia coli Ffh. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(15):4885–4894. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.15.4885-4894.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. D., Young P. G. Sequence of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe gtp1 gene and identification of a novel family of putative GTP-binding proteins. Gene. 1993 Mar 30;125(2):191–193. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90327-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inada T., Kawakami K., Chen S. M., Takiff H. E., Court D. L., Nakamura Y. Temperature-sensitive lethal mutant of era, a G protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5017–5024. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5017-5024.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J., Frech M., Wittinghofer A. Biochemical properties of Ha-ras encoded p21 mutants and mechanism of the autophosphorylation reaction. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11792–11799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nakafuku M., Satoh T. Structure and function of signal-transducing GTP-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:349–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok J., Trach K. A., Hoch J. A. Effects on Bacillus subtilis of a conditional lethal mutation in the essential GTP-binding protein Obg. J Bacteriol. 1994 Dec;176(23):7155–7160. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.23.7155-7160.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner C. G., Sood P., Ahnn J., Inouye M. Cold-sensitive growth and decreased GTP-hydrolytic activity from substitution of Pro17 for Val in Era, an essential Escherichia coli GTPase. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Aug 15;74(2-3):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90419-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutkenhaus J. FtsZ ring in bacterial cytokinesis. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(3):403–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March P. E., Lerner C. G., Ahnn J., Cui X., Inouye M. The Escherichia coli Ras-like protein (Era) has GTPase activity and is essential for cell growth. Oncogene. 1988 Jun;2(6):539–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Tong L., deVos A. M., Brünger A., Yamaizumi Z., Nishimura S., Kim S. H. Molecular switch for signal transduction: structural differences between active and inactive forms of protooncogenic ras proteins. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):939–945. doi: 10.1126/science.2406906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee A., Dai K., Lutkenhaus J. Escherichia coli cell division protein FtsZ is a guanine nucleotide binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1053–1057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble J. A., Innis M. A., Koonin E. V., Rudd K. E., Banuett F., Herskowitz I. The Escherichia coli hflA locus encodes a putative GTP-binding protein and two membrane proteins, one of which contains a protease-like domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10866–10870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römisch K., Webb J., Herz J., Prehn S., Frank R., Vingron M., Dobberstein B. Homology of 54K protein of signal-recognition particle, docking protein and two E. coli proteins with putative GTP-binding domains. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):478–482. doi: 10.1038/340478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Stokes P. E., Smythers G. W., Dhar R., Oroszlan S. Characterization of the phosphorylation sites and the surrounding amino acid sequences of the p21 transforming proteins coded for by the Harvey and Kirsten strains of murine sarcoma viruses. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11767–11773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood P., Lerner C. G., Shimamoto T., Lu Q., Inouye M. Characterization of the autophosphorylation of Era, an essential Escherichia coli GTPase. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Apr;12(2):201–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trach K., Hoch J. A. The Bacillus subtilis spo0B stage 0 sporulation operon encodes an essential GTP-binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1362–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1362-1371.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Lutkenhaus J. The FtsZ protein of Bacillus subtilis is localized at the division site and has GTPase activity that is dependent upon FtsZ concentration. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(3):435–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Tong L., Milburn M. V., Matias P. M., Jancarik J., Noguchi S., Nishimura S., Miura K., Ohtsuka E., Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structure of an oncogene protein: catalytic domain of human c-H-ras p21. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):888–893. doi: 10.1126/science.2448879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]