Abstract
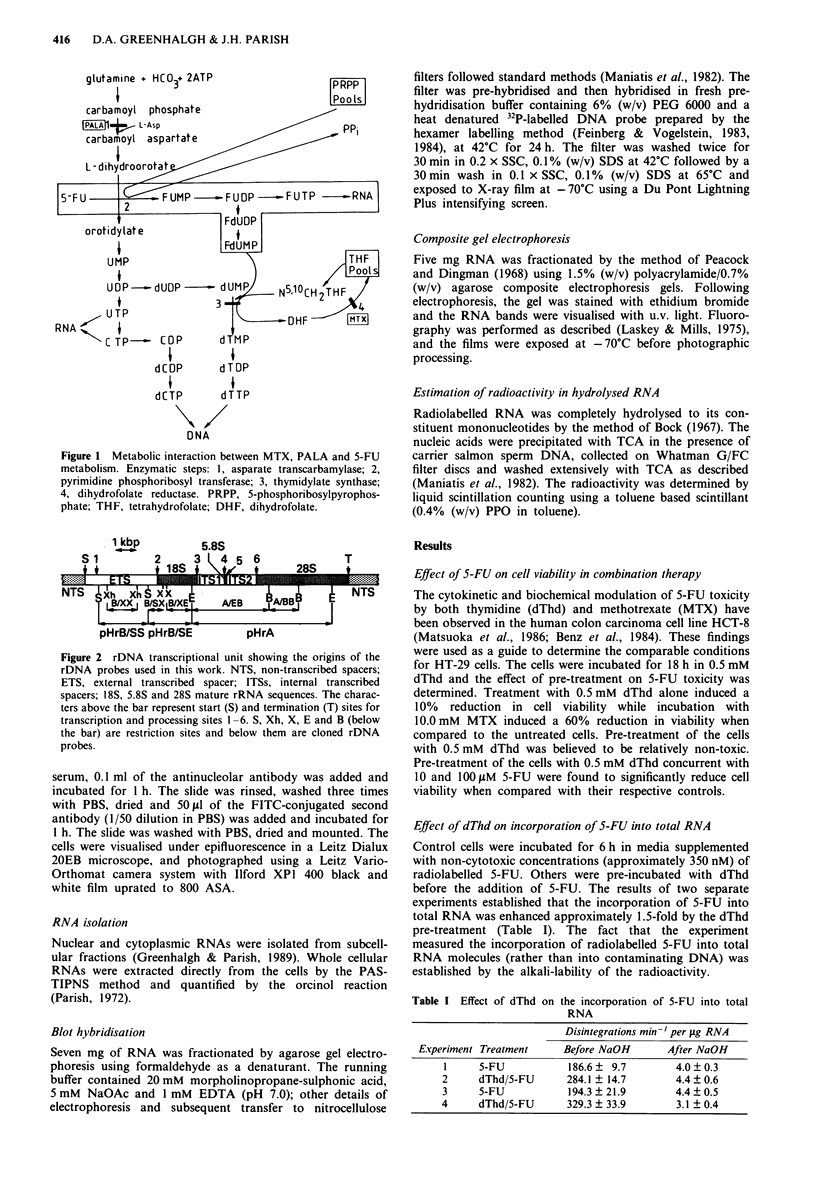
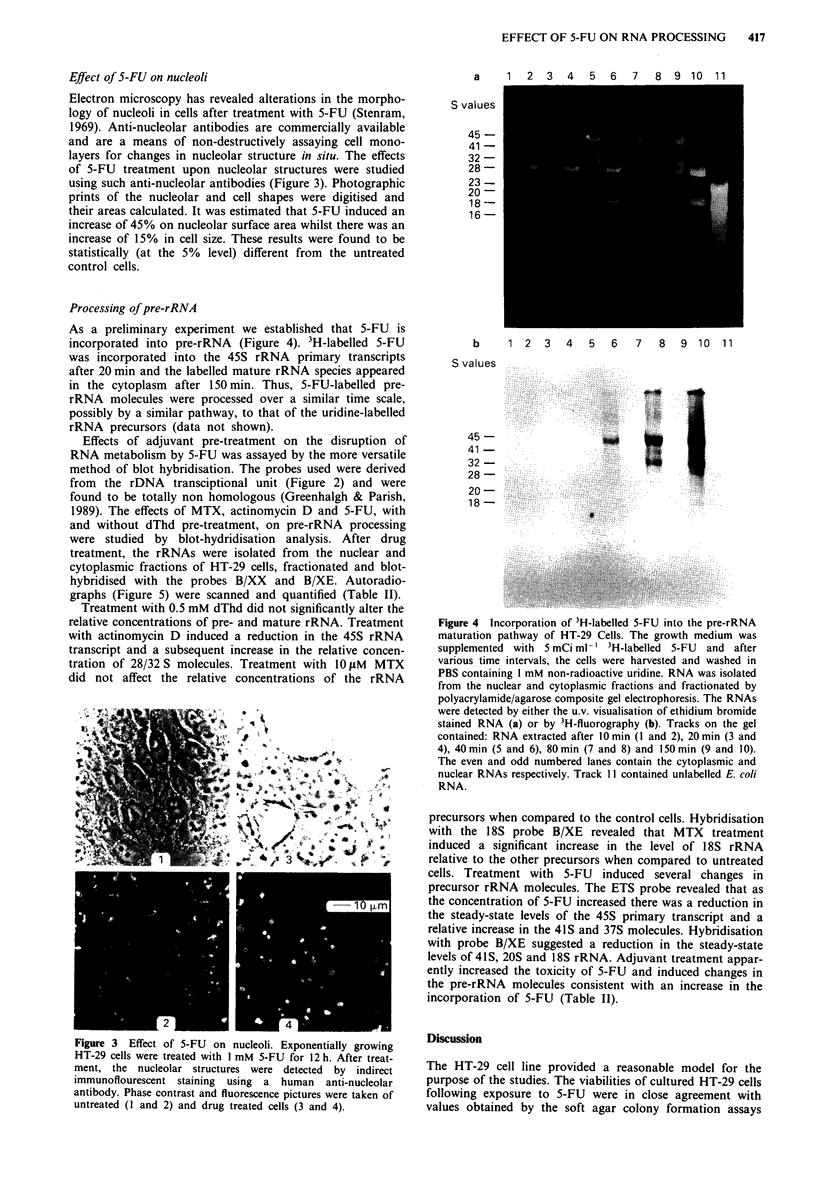
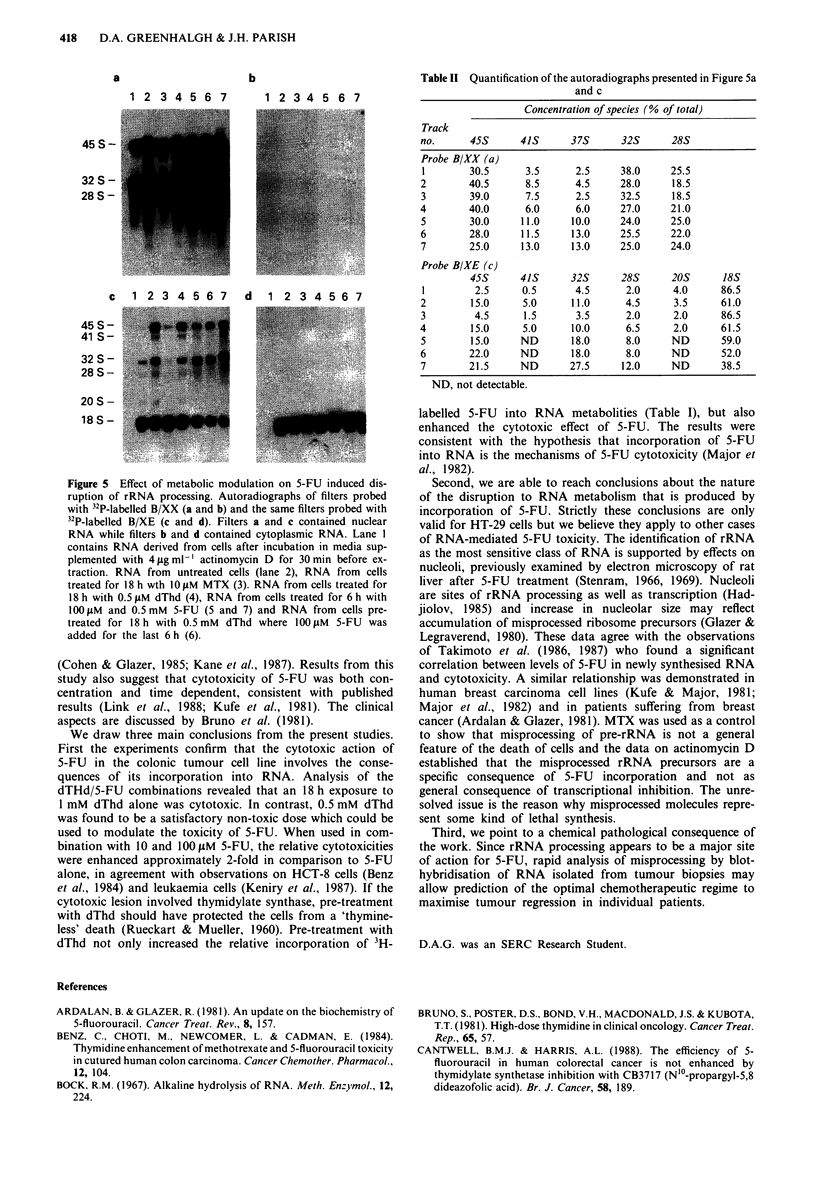
We have evaluated the RNA-directed cytotoxicity of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in human colonic carcinoma cells. The mode of action of 5-FU and its effects on human pre-rRNA processing were then examined. From these data, possible reasons why the disruption of pre-rRNA maturation could induce cytotoxic effects are considered. The results imply that inhibition of thymidylate synthase is not the sole primary cytotoxic lesion in this cell line. First, exogenous thymidine (dTHd) enchanced cytotoxicity. Second, addition of dThd to the cells was found to enhance incorporation of 5-FU into total cellular RNA. Third, 5-FU disrupted rRNA processing by a different mechanism from actinomycin D and methotrexate (MTX), suggesting that the inhibition was not just a consequence of cell death. Finally, the addition of dThd was found to enhance the disruption of rRNA processing consistent with an increase in concentration of 5-FU. These data are discussed in the light of literature reports and their potential for optimising 5-FU protocols.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ardalan B., Glazer R. An update on the biochemistry of 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Treat Rev. 1981 Sep;8(3):157–167. doi: 10.1016/s0305-7372(81)80014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz C., Choti M., Newcomer L., Cadman E. Thymidine enhancement of methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil toxicity in cultured human colon carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1984;12(2):104–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00254600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruno S., Poster D. S., Bono V. H., Jr, Macdonald J. S., Kubota T. T. "High-dose" thymidine in clinical oncology. Cancer Treat Rep. 1981 Jan-Feb;65(1-2):57–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantwell B. M., Harris A. L. The efficacy of 5-fluorouracil in human colorectal cancer is not enhanced by thymidylate synthetase inhibition with CB3717 (N10-propargyl-5,8 dideazafolic acid). Br J Cancer. 1988 Aug;58(2):189–190. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantwell B. M., Macaulay V., Harris A. L., Kaye S. B., Smith I. E., Milsted R. A., Calvert A. H. Phase II study of the antifolate N10-propargyl-5,8-dideazafolic acid (CB 3717) in advanced breast cancer. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1988 Apr;24(4):733–736. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(88)90307-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. R. In situ detection of mycoplasma contamination in cell cultures by fluorescent Hoechst 33258 stain. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Feb;104(2):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. B., Glazer R. I. Cytotoxicity and the inhibition of ribosomal RNA processing in human colon carcinoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;27(2):308–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer R. I., Legraverend M. The effect of 5-fluorouridine 5'-triphosphate on RNA transcribed in isolated nuclei in vitro. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;17(2):279–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenhalgh D. A., Parish J. H. Effects of 5-fluorouracil on cytotoxicity and RNA metabolism in human colonic carcinoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1989;25(1):37–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00694336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding M. J., Cantwell B. M., Milstead R. A., Harris A. L., Kaye S. B. Phase II study of the thymidylate synthetase inhibitor CB3717 (N10-propargyl-5,8-dideazafolic acid) in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 1988 Jun;57(6):628–629. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane M. A., Roth E., Raptis G., Schreiber C., Waxman S. Effect of intracellular folate concentration on the modulation of 5-fluorouracil cytotoxicity by the elevation of phosphoribosylpyrophosphate in cultured human KB cells. Cancer Res. 1987 Dec 15;47(24 Pt 1):6444–6450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keniry M., Benz C., Shafer R. H., James T. L. Noninvasive spectroscopic analysis of fluoropyrimidine metabolism in cultured tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1986 Apr;46(4 Pt 1):1754–1758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kufe D. W., Egan E. M. Enhancement of 5-fluorouracil incorporation into human lymphoblast ribonucleic acid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 15;30(2):129–133. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90183-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kufe D. W., Major P. P. 5-Fluorouracil incorporation into human breast carcinoma RNA correlates with cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9802–9805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kufe D. W., Major P. P., Egan E. M., Loh E. 5-Fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine incorporation in L1210 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8885–8888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link K. H., Aigner K. R., Peschau K., Warthona M., Schwemmle K., Danenberg P. V. Concentration and time dependence of the toxicity of fluorinated pyrimidines to HT 29 colorectal carcinoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1988;22(1):58–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00254182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Major P. P., Egan E. M., Sargent L., Kufe D. W. Modulation of 5-FU metabolism in human MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1982;8(1):87–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00292877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka H., Masuda H., Maehara Y., Sugimachi K., Inokuchi K. Intratumoral injection of thymidine: enhancement of the antitumor activity and incorporation of 5-fluorouracil into tumor RNA in a murine tumor system. Cancer Treat Rep. 1986 Jul;70(7):851–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUECKERT R. R., MUELLER G. C. Studies on unbalanced growth in tissue culture. I. Induction and consequences of thymidine deficiency. Cancer Res. 1960 Dec;20:1584–1591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman S., Nayak R., Sawyer R., Stolfi R., Martin D. Potentiation of the anti-tumor activity of 5FU by thymidine and its correlation with the formation of (5FU)RNA. Cancer. 1980 Mar 15;45(5 Suppl):1129–1134. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19800315)45:5+<1129::aid-cncr2820451317>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman S., Sawyer R., Nayak R., Ritzi E., Stolfi R., Martin D. Improving the anti-tumor activity of 5-fluorouracil by increasing its incorporation into RNA via metabolic modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4966–4970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenram U. Autoradiographic, biochemiical, and ultrastructural studies into the effect of actinomycin, 5-fluorouracil, and adenosine on nucleolar and cellular structure and function. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Dec;23:379–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenram U. The effects of fluorouracil and actinomycin, single and combined, on the nucleolar ultrastructure of various tissues of the rat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969;94(2):282–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00339362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto C. H., Cadman E. C., Armstrong R. D. Precursor-dependent differences in the incorporation of fluorouracil in RNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;29(6):637–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto C. H., Tan Y. Y., Cadman E. C., Armstrong R. D. Correlation between ribosomal RNA production and RNA-directed fluoropyrimidine cytotoxicity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Oct 1;36(19):3243–3248. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90640-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





