Abstract
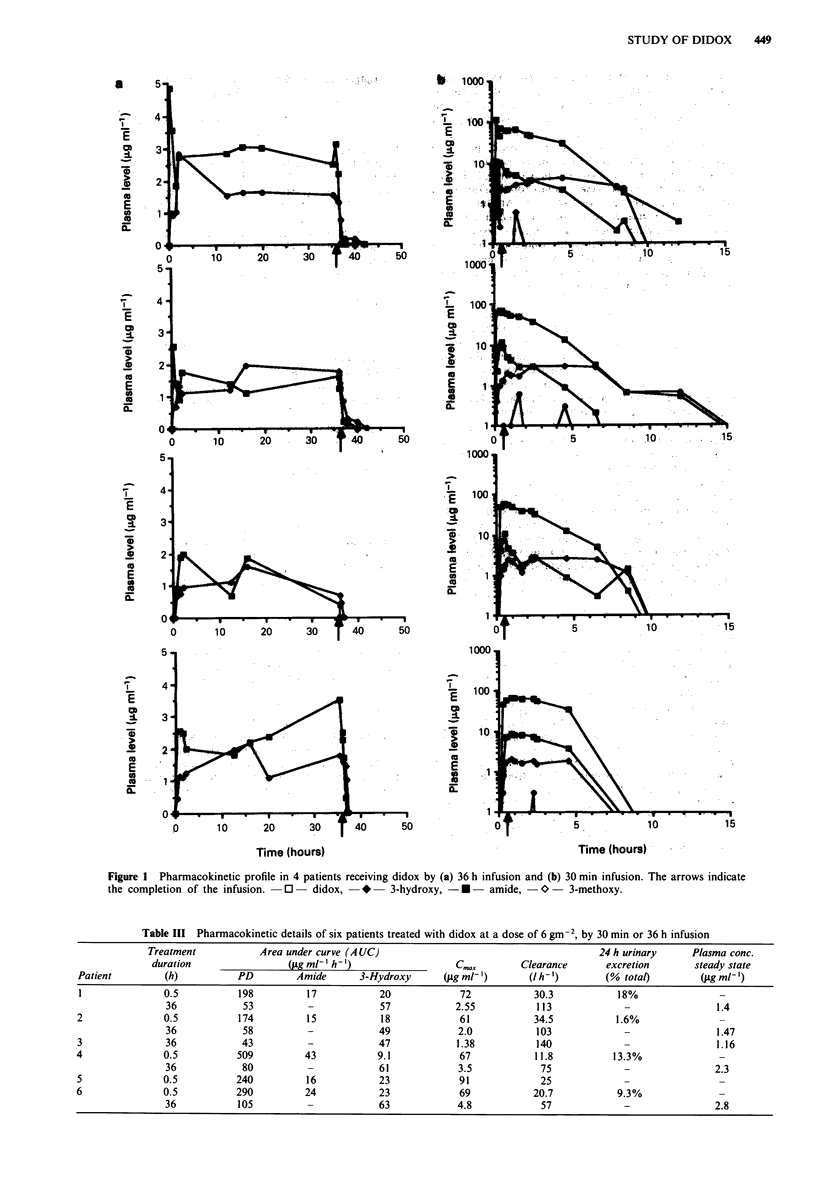
Twelve patients were treated with didox, a new ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor, by 36 h infusion. The maximum tolerated dose was 6 g m-2, above which dose-limiting hepatic toxicity was observed. Patient tolerance was significantly better using the 36 h infusion compared to patients receiving the drug by a 30 min infusion; in particular, there were no reports of nausea or vomiting. No responses were seen in these patients. Detailed pharmacokinetics were performed at 6 g m-2 comparing the 36 h and 30 min infusions in four patients. Parent drug AUC values were lower for the 36 h infusion, 67.8 micrograms ml-1 h-1 compared to 232 micrograms ml-1 h-1 for the 30 min infusion. AUC values for the 3-hydroxy metabolite were much higher following the 36 h infusion: 55.4 compared to 18.6 micrograms ml-1 h-1. In contrast, the amide metabolite was not detected following the 36 h infusion, but AUC values of 23 micrograms ml-1 h-1 were seen after the 30 min infusion. The mean peak plasma level was 72 micrograms ml-1 following 6 g m-2 given by a 30 min infusion compared to 2.8 micrograms ml-1 following the prolonged infusion. Clearance was higher following the 36 h infusion: 97.6 versus 24.4 l h-1.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Elford H. L. Effect of hydroxyurea on ribonucleotide reductase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Oct 10;33(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elford H. L., Freese M., Passamani E., Morris H. P. Ribonucleotide reductase and cell proliferation. I. Variations of ribonucleotide reductase activity with tumor growth rate in a series of rat hepatomas. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 25;245(20):5228–5233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elford H. L., Van't Riet B., Wampler G. L., Lin A. L., Elford R. M. Regulation of ribonucleotide reductase in mammalian cells by chemotherapeutic agents. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1980;19:151–168. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(81)90014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elford H. L., van't Riet B. Inhibition of nucleoside diphosphate reductase by hydroxybenzohydroxamic acid derivatives. Pharmacol Ther. 1985;29(2):239–254. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(85)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. K., Abrams R., Lieberman I. Levels of ribonucleotide reductase activity during the division cycle of the L cell. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3725–3728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veale D., Cantwell B. M., Kerr N., Upfold A., Harris A. L. Phase 1 study of high-dose hydroxyurea in lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1988;21(1):53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00262739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van't Riet B., Wampler G. L., Elford H. L. Synthesis of hydroxy- and amino-substituted benzohydroxamic acids: inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase and antitumor activity. J Med Chem. 1979 May;22(5):589–592. doi: 10.1021/jm00191a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



