Abstract
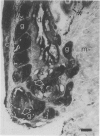
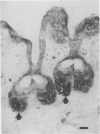
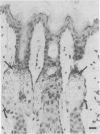
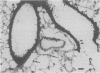
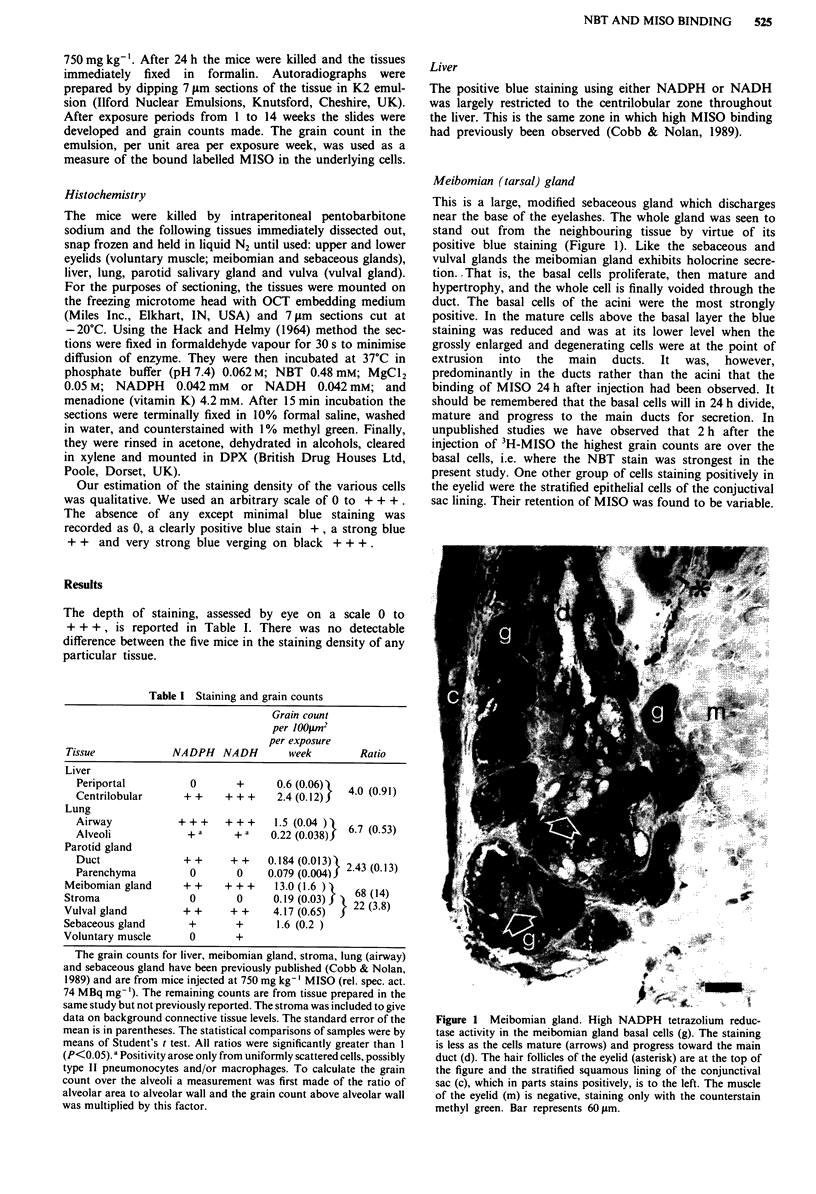
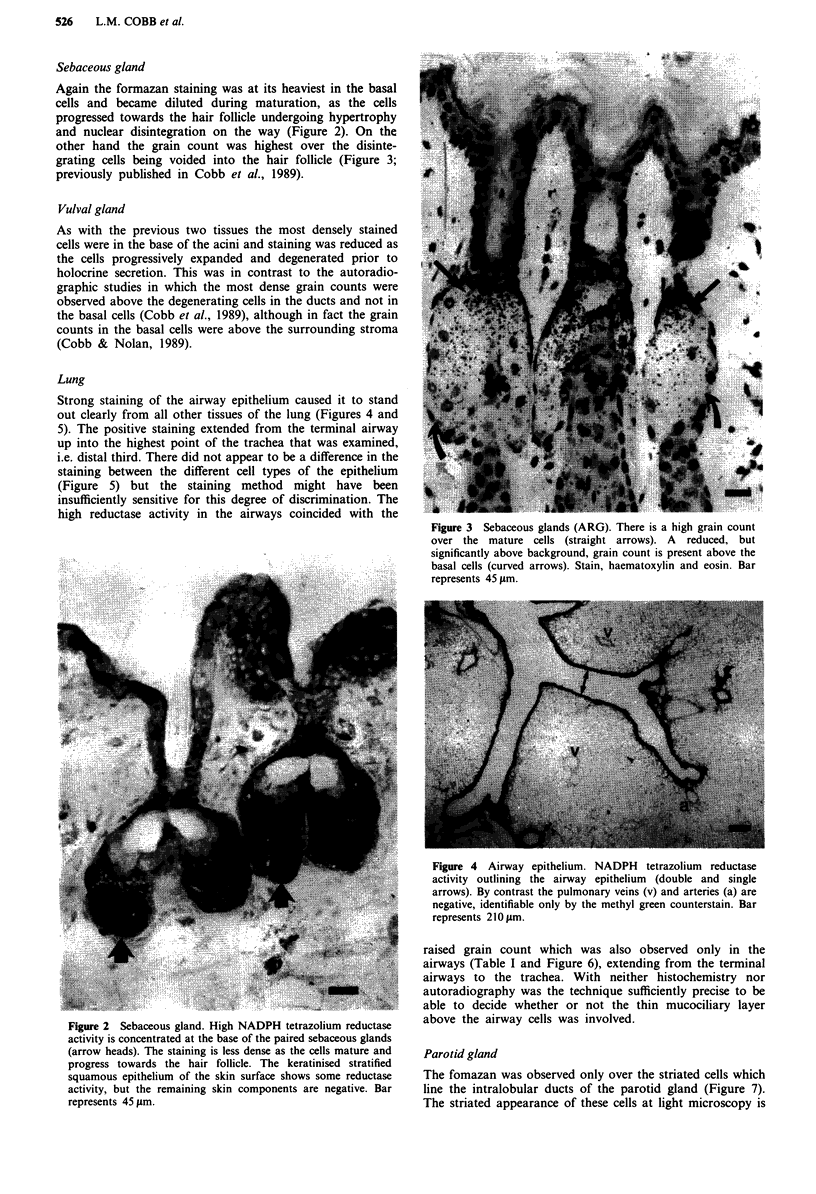
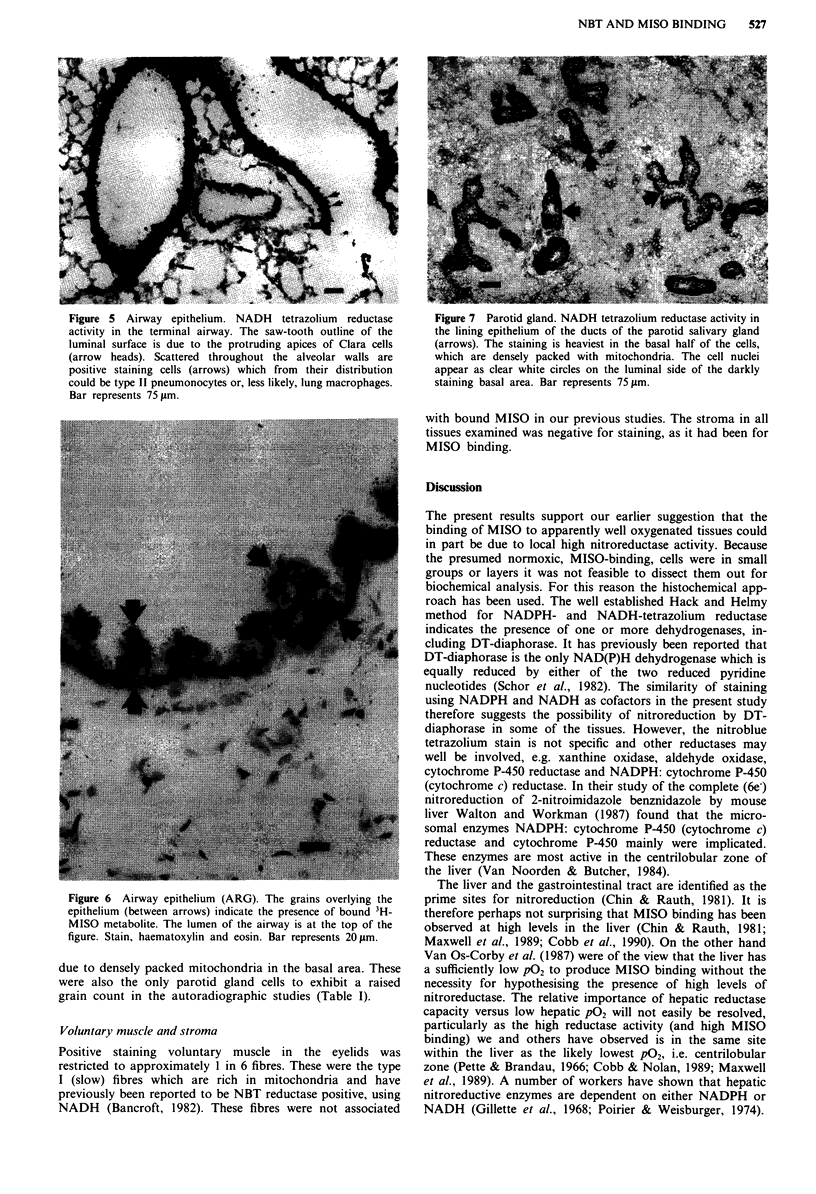
Hack and Helmy's method for the histochemical identification of NAD(P)H nitroblue tetrazolium reductase activity was employed to pinpoint reductase activity in certain cells in the mouse. High activity was observed in the following: lower airway epithelium, liver (centrilobular zone), eyelid (meibomian and sebaceous glands), vulval gland and parotid gland (striated cells of intralobular ducts). All of these cells had previously been identified as sites of binding of the reactive metabolites formed from the enzymic reduction of misonidazole (MISO) (Cobb et al., 1989). It had previously been thought that MISO binding would only take place in significant amounts in hypoxic tissues (tumour and possibly liver) since in normoxic tissues oxygen should reverse the initial one electron enzymic reduction, thus preventing progressive reduction to reactive species. We suggest that the very high levels of reductase in the above listed, probably normoxic, tissues contribute significantly to the accumulation of bound reactive MISO metabolite(s).
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asquith J. C., Watts M. E., Patel K., Smithen C. E., Adams G. E. Electron affinic sensitization. V. Radiosensitization of hypoxic bacteria and mammalian cells in vitro by some nitroimidazoles and nitropyrazoles. Radiat Res. 1974 Oct;60(1):108–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. B., Rauth A. M. The metabolism and pharmacokinetics of the hypoxic cell radiosensitizer and cytotoxic agent, misonidazole, in C3H mice. Radiat Res. 1981 May;86(2):341–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb L. M., Connors T. A., Elson L. A., Khan A. H., Mitchley B. C., Ross W. C., Whisson M. E. 2,4-dinitro-5-ethyleneiminobenzamide (CB 1954): a potent and selective inhibitor of the growth of the Walker carcinoma 256. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Jun;18(6):1519–1527. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb L. M., Nolan J. Autoradiographic study of tritium-labeled misonidazole in the mouse. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989 Apr;16(4):953–956. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(89)90894-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb L. M., Nolan J., O'Neill P. Microscopic distribution of misonidazole in mouse tissues. Br J Cancer. 1989 Jan;59(1):12–16. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb L. M. Toxicity of the selective antitumor agent 5-aziridino-2,4-dinitrobenzamide in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;17(1):231–238. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(70)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockhart I. R., Large P., Troup D., Malcolm S. L., Marten T. R. Pharmacokinetic and metabolic studies of the hypoxic cell radiosensitizer misonidazole. Xenobiotica. 1978 Feb;8(2):97–105. doi: 10.3109/00498257809060388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franko A. J. Misonidazole and other hypoxia markers: metabolism and applications. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986 Jul;12(7):1195–1202. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(86)90257-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franko A. J., Raleigh J. A., Sutherland R. G., Soderlind K. J. Metabolic binding of misonidazole to mouse tissues. Comparison between labels on the ring and side chain, and the production of tritiated water. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Feb 15;38(4):665–670. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90213-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrecht B. M., Chapman J. D. The labelling of EMT-6 tumours in BALB/C mice with 14C-misonidazole. Br J Radiol. 1983 Oct;56(670):745–753. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-56-670-745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillette J. R., Kamm J. J., Sasame H. A. Mechanism of p-nitrobenzoate reduction in liver: the possible role oc cytochrome P-450 in liver microsomes. Mol Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;4(6):541–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall E. J., Roizin-Towle L. Hypoxic sensitizers: radiobiological studies at the cellular level. Radiology. 1975 Nov;117(2):453–457. doi: 10.1148/117.2.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox R. J., Friedlos F., Jarman M., Roberts J. J. A new cytotoxic, DNA interstrand crosslinking agent, 5-(aziridin-1-yl)-4-hydroxylamino-2-nitrobenzamide, is formed from 5-(aziridin-1-yl)-2,4-dinitrobenzamide (CB 1954) by a nitroreductase enzyme in Walker carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Dec 15;37(24):4661–4669. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90335-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koudstaal J., Makkink B., Overdiep S. H. Enzyme histochemical pattern in human tumours. II. Oxidoreductases in carcinoma of the colon and the breast. Eur J Cancer. 1975 Feb;11(2):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(75)90188-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell A. P., MacManus M. P., Gardiner T. A. Misonidazole binding in murine liver tissue: a marker for cellular hypoxia in vivo. Gastroenterology. 1989 Nov;97(5):1300–1303. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91703-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus M. E., Lang M. A., Stuart K., Strong J. Activation of misonidazole by rat liver microsomes and purified NADPH-cytochrome c reductase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):547–552. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. G., Ngan-Lee J., Chapman J. D. Intracellular localization of radioactively labeled misonidazole in EMT-6-tumor cells in vitro. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1982 Mar-Apr;8(3-4):741–744. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(82)90725-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive P. L. Inhibition of DNA synthesis by nitroheterocycles. II. Mechanisms of cytotoxicity. Br J Cancer. 1979 Jul;40(1):94–104. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1979.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pette D., Brandau H. Enzym-Histiogramme und Enzymaktivitätsmuster der Rattenleber. Nachweis Pyridinnukleotid-spezifischer Dehydrogenasen im Gelschicht-Verfahren. Enzymol Biol Clin (Basel) 1966;6(2):79–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier L. A., Weisburger J. H. Enzymic reduction of carcinogenic aromatic nitro compounds by rat and mouse liver fractions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Feb 1;23(3):661–669. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauth A. M. Pharmacology and toxicology of sensitizers: mechanism studies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1984 Aug;10(8):1293–1300. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(84)90335-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed C. J., Lock E. A., De Matteis F. NADPH: cytochrome P-450 reductase in olfactory epithelium. Relevance to cytochrome P-450-dependent reactions. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):585–592. doi: 10.1042/bj2400585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor N. A., Cornelisse C. J. Biochemical and quantitative histochemical study of reduced pyridine nucleotide dehydrogenation by human colonic carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1983 Oct;43(10):4850–4855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor N. A., Morris H. P. The activity of the D-T diaphorase in experimental hepatomas. Cancer Biochem Biophys. 1977;2(1):5–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor N. A., Rice B. F., Huseby R. A., Dunlap C. E. Dehydrogenation of reduced pyridine nucleotides by Leydig cell tumors of the rat testis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Feb;151(2):418–421. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor N. A., Stedman R. B., Epstein N., Schally G. Rat splenic D-T diaphorase and NAD(P)H-nitroblue tetrazolium reductase. Their use to assess the action of polycyclic hydrocarbons in the lymphatic system. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1982;41(1-2):83–93. doi: 10.1007/BF02890273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor N. A. The use of the D-T diaphorase for the detection of foci of early neoplastic transformation in rat liver. Cancer Lett. 1978 Sep;5(3):167–171. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(78)80034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratford I. J., Adams G. E. The toxicity of the radiosensitizer misonidazole towards hypoxic cells in vitro: a model for mouse and man. Br J Radiol. 1978 Sep;51(609):745–746. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-51-609-745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratford I. J., O'Neill P., Sheldon P. W., Silver A. R., Walling J. M., Adams G. E. RSU 1069, a nitroimidazole containing an aziridine group. Bioreduction greatly increases cytotoxicity under hypoxic conditions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Jan 1;35(1):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90566-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urtasun R. C., Chapman J. D., Raleigh J. A., Franko A. J., Koch C. J. Binding of 3H-misonidazole to solid human tumors as a measure of tumor hypoxia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986 Jul;12(7):1263–1267. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(86)90273-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Noorden C. J., Butcher R. G. Histochemical localization of NADP-dependent dehydrogenase activity with four different tetrazolium salts. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Sep;32(9):998–1004. doi: 10.1177/32.9.6747280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Os-Corby D. J., Koch C. J., Chapman J. D. Is misonidazole binding to mouse tissues a measure of cellular pO2? Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Oct 15;36(20):3487–3494. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90330-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese A. J., Gulyas S., Mohindra J. K. Hypoxia-dependent reduction of 1-(2-nitro-1-imidazolyl)-3-methoxy-2-propanol by Chinese hamster ovary cells and KHT tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 1976 Oct;36(10):3761–3765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese A. J., Whitmore G. F. Binding to cellular macromolecules as a possible mechanism for the cytotoxicity of misonidazole. Cancer Res. 1980 Jul;40(7):2165–2169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATTENBERG L. W. A histochemical study of five oxidative enzymes in carcinoma of the large intestine in man. Am J Pathol. 1959 Jan-Feb;35(1):113–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton M. I., Workman P. Nitroimidazole bioreductive metabolism. Quantitation and characterisation of mouse tissue benznidazole nitroreductases in vivo and in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 15;36(6):887–896. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]