Abstract
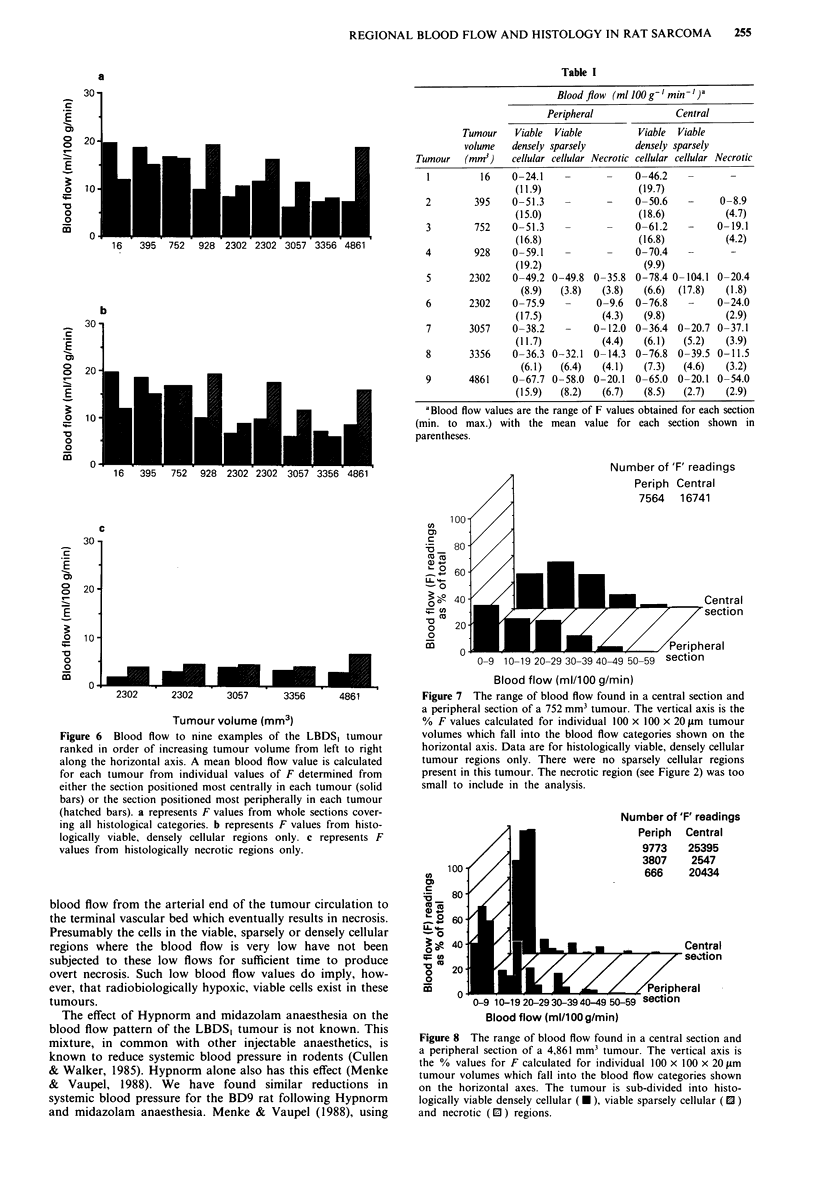
The regional distribution of blood flow to the LBDS1 fibrosarcoma, transplanted into the subcutaneous site in rats, was investigated using the readily diffusible compound 14C-iodo-antipyrine (14C-IAP). Quantitative autoradiography was used to establish absolute values of specific blood flow F for 100 X 100 X 20 microns adjacent tissue volumes of the unperturbed tumour. Mean blood flow to whole tumours was found to decrease with increase in tumour size. This relationship was abolished if blood flow was only measured in sections cut from the periphery of the tumours. Detailed analysis of a sub-group of tumours showed that blood flow to individual tumours was heterogeneous. The range of blood flow was large, indicating that mean blood flow to a whole tumour is a poor reflection of the blood perfusion pattern of that tumour. Necrotic tumour regions were usually very poorly perfused. With the exception of the smallest tumours studied, blood flow was lower in the centre of tumours than in the periphery. Necrosis also tended to develop centrally. However, the peripheral to central gradient of blood flow was apparent even when densely cellular, viable tumour regions and necrotic regions were analysed separately. The decrease in blood flow with tumour size was also apparent in densely cellular, viable tumour regions when analysed separately. Qualitative comparison of tumour histology and regional blood flow showed that there were areas of very low blood flow associated with viable tumour regions. Less common were areas of rather high blood flow associated with necrotic tumour regions. A complicated relationship exists between tumour histology and blood flow. The quantitative autoradiography technique is suitable for investigating the most poorly perfused and the most well perfused viable fractions of animal tumours which may limit the efficacy of different types of therapy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blasberg R. G., Molnar P., Horowitz M., Kornblith P., Pleasants R., Fenstermacher J. Regional blood flow in RT-9 brain tumors. J Neurosurg. 1983 Jun;58(6):863–873. doi: 10.3171/jns.1983.58.6.0863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasberg R., Horowitz M., Strong J., Molnar P., Patlak C., Owens E., Fenstermacher J. Regional measurements of [14C]misonidazole distribution and blood flow in subcutaneous RT-9 experimental tumors. Cancer Res. 1985 Apr;45(4):1692–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATALAND S., COHEN C., SAPIRSTEIN L. A. Relationship between size and perfusion rate of transplanted tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1962 Aug;29:389–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. J., Olive P. L., Durand R. E. Intermittent blood flow in a murine tumor: radiobiological effects. Cancer Res. 1987 Jan 15;47(2):597–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. M., Walker H. C. The effect of several different anaesthetics on the blood pressure and heart rate of the mouse and on the radiation response of the mouse sarcoma RIF-1. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1985 Nov;48(5):761–771. doi: 10.1080/09553008514551861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk P. Differences in vascular pattern between the spontaneous and the transplanted C3H mouse mammary carcinoma. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1982 Feb;18(2):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(82)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk P. Patterns of vasculature in two pairs of related fibrosarcomas in the rat and their relation to tumour responses to single large doses of radiation. Eur J Cancer. 1978 Mar;14(3):237–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(78)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk P. The vascular pattern of the spontaneous C3H mouse mammary carcinoma and its significance in radiation response and in hyperthermia. Eur J Cancer. 1980 Feb;16(2):203–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(80)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groothuis D. R., Pasternak J. F., Fischer J. M., Blasberg R. G., Bigner D. D., Vick N. A. Regional measurements of blood flow in experimental RG-2 rat gliomas. Cancer Res. 1983 Jul;43(7):3362–3367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menke H., Vaupel P. Effect of injectable or inhalational anesthetics and of neuroleptic, neuroleptanalgesic, and sedative agents on tumor blood flow. Radiat Res. 1988 Apr;114(1):64–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurada O., Kennedy C., Jehle J., Brown J. D., Carbin G. L., Sokoloff L. Measurement of local cerebral blood flow with iodo [14C] antipyrine. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):H59–H66. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1978.234.1.H59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C. W., Kang M. S., Rhee J. G., Levitt S. H. Effect of hyperthermia on vascular function in normal and neoplastic tissues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;335:35–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb50735.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiig H. Microvascular pressures in DMBA-induced rat mammary tumours. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1982 Apr;42(2):165–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiig H., Tveit E., Hultborn R., Reed R. K., Weiss L. Interstitial fluid pressure in DMBA-induced rat mammary tumours. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1982 Apr;42(2):159–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]