Abstract
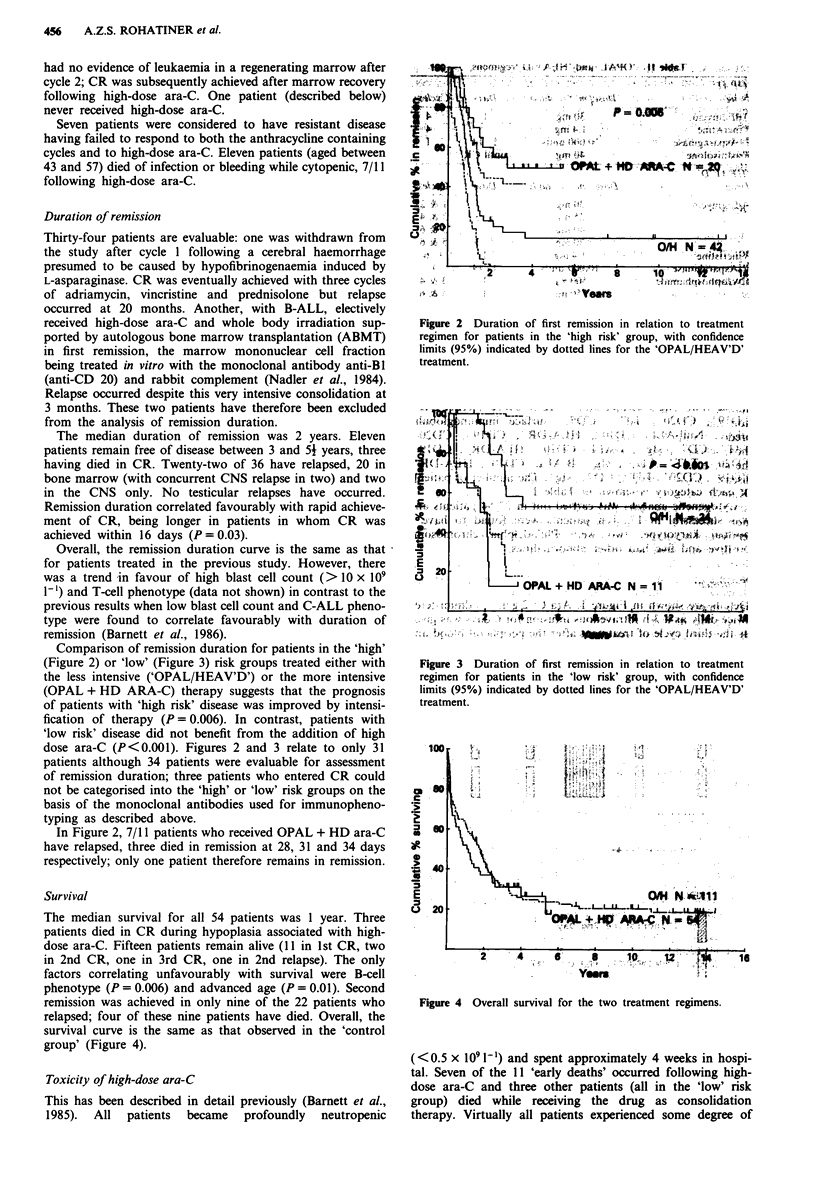
In a study conducted at St Bartholomew's Hospital between 1972 and 1982, using moderately intensive therapy (OPAL/HEAV'D), a low blast count at presentation (less than 10 x 10(9) 1(-1)) and common ALL (C-ALL) phenotype correlated favourably with duration of remission. Fifty-four patients (age range 15-57, median 32) subsequently received a modification of the previous treatment programme which included high-dose ara-C 2 g m-2 b.d. for 6 days as cycle 3 (OPAL + HD ARA-C). CR was achieved in 36/54 (67%) patients, response correlating favourably with younger age (15-30 years vs 31-57 years, P = 0.02). Three patients died in CR. Overall, there was no difference in survival or remission duration between patients who received high dose ara-C and those in the control group. However, in contrast to the early results, there was a reversal in the relevance of the prognostic factors with a trend in favour of high blast count (greater than 10 x 10(9) 1(-1)) and T-cell phenotype in terms of remission duration. Moreover, comparison of duration of remission for the previously defined prognostic groups according to therapy suggests that the prognosis of patients with 'high risk' disease (T, B, null ALL or high blast count) is improved with more intensive therapy. In contrast, those with 'low risk' disease (C-ALL and low blast count) have a better prognosis with less intensive therapy. These observations confirm those of others and allow for individualization of therapy on the basis of pre-treatment variables.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baccarani M., Amadori S., Willemze R., Haanen C., Corbelli G., Gobbi M., Meloni G., Mandelli F., Tura S. E-rosette positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in adolescents and adults. Br J Haematol. 1983 Oct;55(2):295–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb01250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccarani M., Corbelli G., Amadori S., Drenthe-Schonk A., Willemze R., Meloni G., Cardozo P. L., Haanen C., Mandelli F., Tura S. Adolescent and adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: prognostic features and outcome of therapy. A study of 293 patients. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):677–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett M. J., Greaves M. F., Amess J. A., Gregory W. M., Rohatiner A. Z., Dhaliwal H. S., Slevin M. L., Biruls R., Malpas J. S., Lister T. A. Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in adults. Br J Haematol. 1986 Nov;64(3):455–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1986.tb02201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett M. J., Waxman J. H., Richards M. A., Ganesan T. S., Bragman K. S., Rohatiner A. Z., Lister T. A. High-dose cytosine arabinoside in the initial treatment of acute leukemia. Semin Oncol. 1985 Jun;12(2 Suppl 3):133–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. M., Catovsky D., Daniel M. T., Flandrin G., Galton D. A., Gralnick H. R., Sultan C. Proposals for the classification of the acute leukaemias. French-American-British (FAB) co-operative group. Br J Haematol. 1976 Aug;33(4):451–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb03563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitran J. D. Prognostic value of immunologic markers in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1978 Dec 7;299(23):1317–1317. doi: 10.1056/nejm197812072992321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollum F. J. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase as a hematopoietic cell marker. Blood. 1979 Dec;54(6):1203–1215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capizzi R. L., Poole M., Cooper M. R., Richards F., 2nd, Stuart J. J., Jackson D. V., Jr, White D. R., Spurr C. L., Hopkins J. O., Muss H. B. Treatment of poor risk acute leukemia with sequential high-dose ARA-C and asparaginase. Blood. 1984 Mar;63(3):694–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson B., Ellis S., Little C., Gee T., Arlin Z., Mertelsmann R., Andreeff M., Kempin S., Koziner B., Chaganti R. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults. Semin Oncol. 1985 Jun;12(2):160–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingrich R. D., Burns C. P., Armitage J. O., Aunan S. B., Edwards R. W., Dick F. R., Maguire L. C., Leimert J. T. Long-term relapse-free survival in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Treat Rep. 1985 Feb;69(2):153–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzig R. H., Wolff S. N., Lazarus H. M., Phillips G. L., Karanes C., Herzig G. P. High-dose cytosine arabinoside therapy for refractory leukemia. Blood. 1983 Aug;62(2):361–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoelzer D., Thiel E., Löffler H., Büchner T., Ganser A., Heil G., Koch P., Freund M., Diedrich H., Rühl H. Prognostic factors in a multicenter study for treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):123–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. R., Ettinger L. J. Continuous infusion of high-dose cytosine arabinoside for treatment of childhood acute leukemia and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in relapse. Semin Oncol. 1985 Jun;12(2 Suppl 3):150–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantarjian H. M., Estey E. H., Plunkett W., Keating M. J., Walters R. S., Iacoboni S., McCredie K. B., Freireich E. J. Phase I-II clinical and pharmacologic studies of high-dose cytosine arabinoside in refractory leukemia. Am J Med. 1986 Sep;81(3):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90287-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarino M., Morra E., Alessandrino E. P., Canevari A., Salvaneschi L., Castelli G., Brusamolino E., Pagnucco G., Isernia P., Orlandi E. Adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Response to therapy according to presenting features in 62 patients. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1982 Sep;18(9):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(82)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lister T. A., Whitehouse J. M., Beard M. E., Brearley R. L., Wrigley P. F., Oliver R. T., Freeman J. E., Woodruff R. K., Malpas J. S., Paxton A. M. Combination chemotherapy for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in adults. Br Med J. 1978 Jan 28;1(6107):199–203. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6107.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus R. E., Catovsky D., Johnson S. A., Gregory W. M., Talavera J. G., Goldman J. M., Galton D. A. Adult acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a study of prognostic features and response to treatment over a ten year period. Br J Cancer. 1986 Feb;53(2):175–180. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Takvorian T., Botnick L., Bast R. C., Finberg R., Hellman S., Canellos G. P., Schlossman S. F. Anti-B1 monoclonal antibody and complement treatment in autologous bone-marrow transplantation for relapsed B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Lancet. 1984 Aug 25;2(8400):427–431. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92907-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters W. G., Willemze R., Colly L. P. Intermediate and high-dose cytosine arabinoside-containing regimens for induction and consolidation therapy for patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphoblastic non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: the Leyden experience and review of the literature. Semin Oncol. 1987 Jun;14(2 Suppl 1):86–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plunkett W., Liliemark J. O., Estey E., Keating M. J. Saturation of ara-CTP accumulation during high-dose ara-C therapy: pharmacologic rationale for intermediate-dose ara-C. Semin Oncol. 1987 Jun;14(2 Suppl 1):159–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohatiner A., Slevin M. L., Dhaliwal H. S., Malpas J. S., Lister T. A. High-dose cytosine arabinoside: response to therapy in acute leukaemia and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1984;12(2):90–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00254596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick S. A., Cadman E. C., Capizzi R. L., Skeel R. T., Bertino J. R., McIntosh S. High dose cytosine arabinoside (HDARAC) in refractory acute leukemia. Cancer. 1979 Oct;44(4):1189–1193. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197910)44:4<1189::aid-cncr2820440404>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slevin M. L., Piall E. M., Aherne G. W., Harvey V. J., Johnston A., Lister T. A. Effect of dose and schedule on pharmacokinetics of high-dose cytosine arabinoside in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Oncol. 1983 Sep;1(9):546–551. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1983.1.9.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storring R. A., Jameson B., McElwain T. J., Wiltshaw E. Oral non-absorbed antibiotics prevent infection in acute non-lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet. 1977 Oct 22;2(8043):837–840. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90779-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willemze R., Hillen H., Hartgrink-Groeneveld C. A., Haanen C. Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adolescents and a-dults: A retrospective study of 41 patients (1970-1973). Blood. 1975 Dec;46(6):823–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


