Abstract
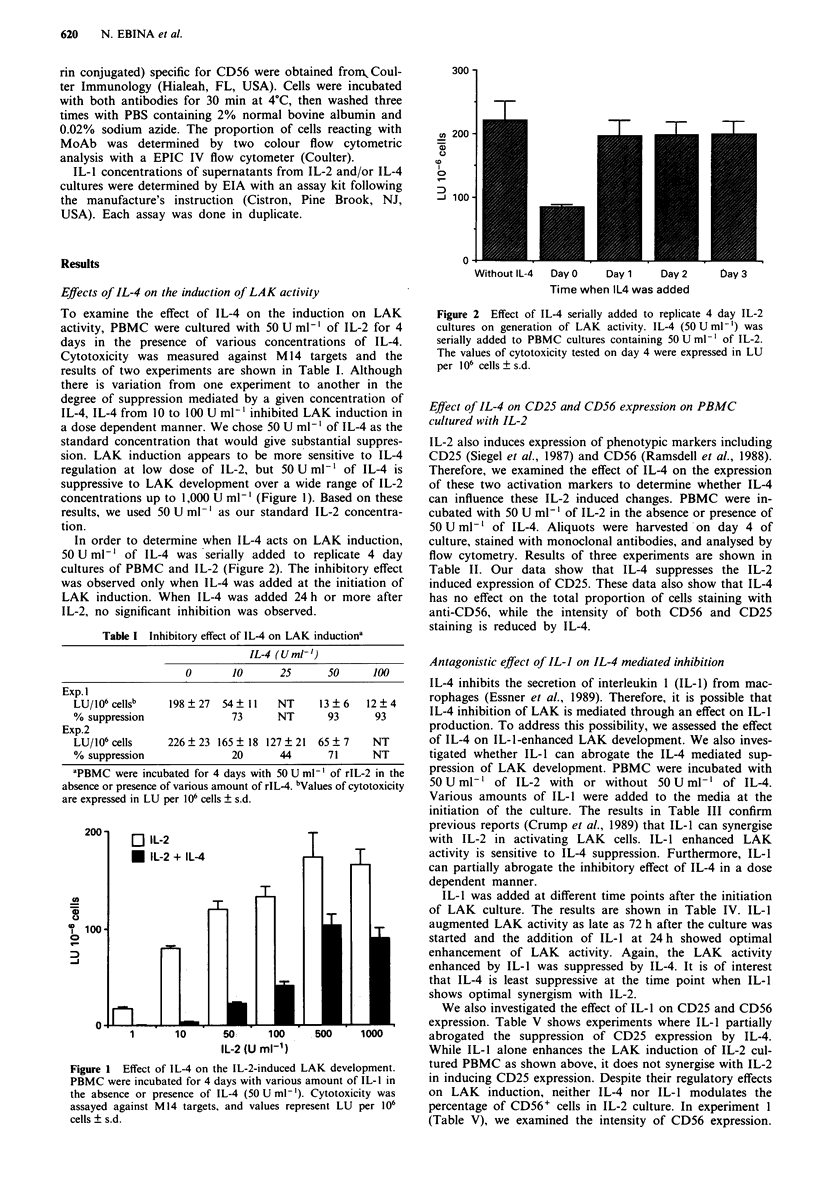
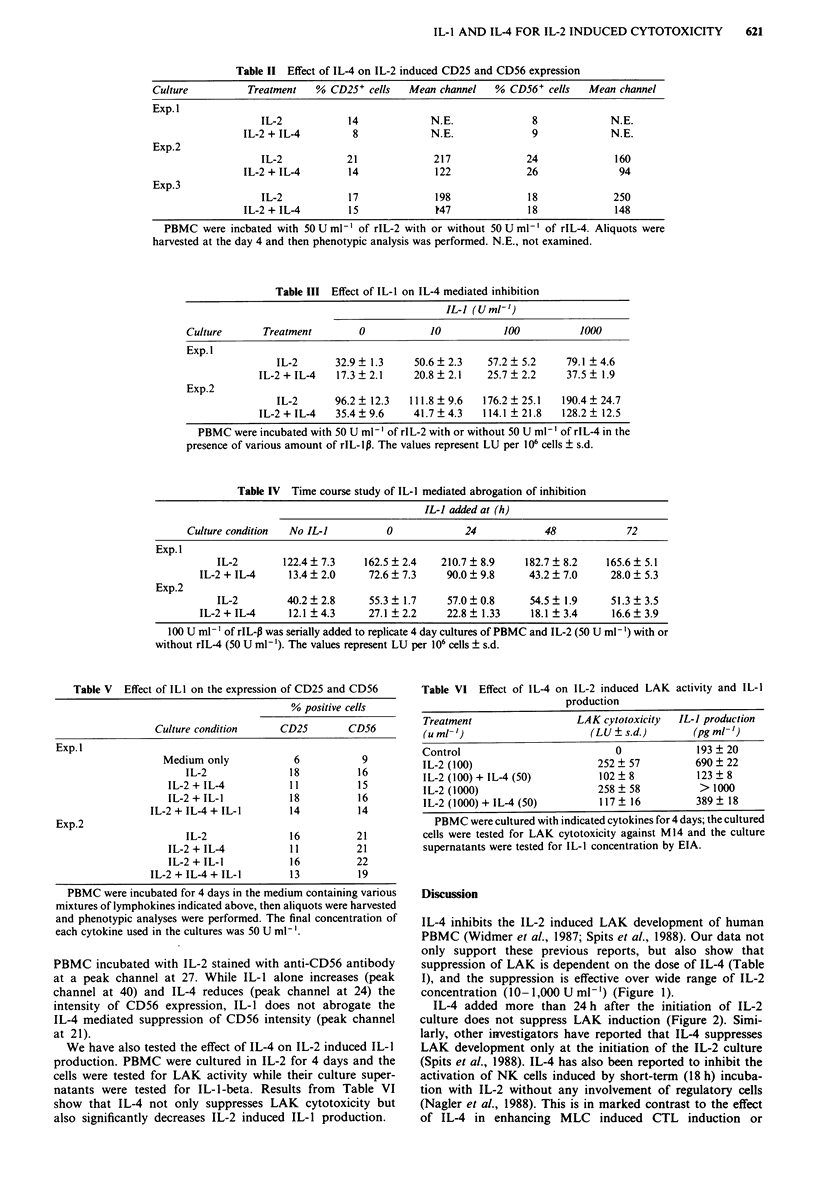
Interleukin 4 (IL-4) suppresses the interleukin 2 (IL-2) induced lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cell development from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). Suppression is observed at high (1,000 U ml-1) as well as low (10 U ml-1) concentrations of IL-2. IL-4 needs to be present at the beginning of the IL-2 culture to exert the suppressive effect. IL-4 also inhibits the development of CD25 (Tac) antigen on the PBMC cultured in IL-2. Interleukin 1 (IL-1) can reverse the suppressive effect of IL-4 on LAK induction when added at the early phase of the IL-2 culture. IL-1 enhances IL-2 induced LAK development, which may partially explain the reversion of IL-4 inhibition by IL-1. IL-1 also reverses the inhibitory effect of IL-4 on the development of CD25 antigen expression, although IL-1 alone does not enhance the induction of CD25 expression in PBMC cultured by IL-2. Furthermore, IL-4 suppresses IL-2 induced IL-1 production in PBMC. Thus, suppression of CD25 may be a pathway for the suppression of LAK induction. The expression of CD56 is not directly associated with the expression of LAK activity. IL-4, IL-1 or combination of the two cytokines has no effect on IL-2 induced expression of CD56. These results indicate that IL-4 has an antagonistic effect and IL-1 has a synergistic effect on IL-2-induced LAK development.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks B., Rees R. C. Human recombinant IL-4 suppresses the induction of human IL-2 induced lymphokine activated killer (LAK) activity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):162–165. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crump W. L., 3rd, Owen-Schaub L. B., Grimm E. A. Synergy of human recombinant interleukin 1 with interleukin 2 in the generation of lymphokine-activated killer cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Jan 1;49(1):149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essner R., Rhoades K., McBride W. H., Morton D. L., Economou J. S. IL-4 down-regulates IL-1 and TNF gene expression in human monocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3857–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gause W. C., Takashi T., Mountz J. D., Finkelman F. D., Steinberg A. D. Activation of CD 4-, CD 8- thymocytes with IL 4 vs IL 1 + IL 2. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2240–2245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Robb R. J., Roth J. A., Neckers L. M., Lachman L. B., Wilson D. J., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. III. Evidence that IL-2 is sufficient for direct activation of peripheral blood lymphocytes into lymphokine-activated killer cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1356–1361. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horohov D. W., Crim J. A., Smith P. L., Siegel J. P. IL-4 (B cell-stimulatory factor 1) regulates multiple aspects of influenza virus-specific cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4217–4223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami Y., Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T. Interleukin 4 promotes the growth of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes cytotoxic for human autologous melanoma. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2183–2191. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern D. E., Peace D. J., Klarnet J. P., Cheever M. A., Greenberg P. D. Il-4 is an endogenous T cell growth factor during the immune response to a syngeneic retrovirus-induced tumor. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2824–2830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulé J. J., Krosnick J. A., Rosenberg S. A. IL-4 regulation of murine lymphokine-activated killer activity in vitro. Effects on the IL-2-induced expansion, cytotoxicity, and phenotype of lymphokine-activated killer effectors. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):726–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulé J. J., Smith C. A., Rosenberg S. A. Interleukin 4 (B cell stimulatory factor 1) can mediate the induction of lymphokine-activated killer cell activity directed against fresh tumor cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):792–797. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagler A., Lanier L. L., Phillips J. H. The effects of IL-4 on human natural killer cells. A potent regulator of IL-2 activation and proliferation. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2349–2351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peace D. J., Kern D. E., Schultz K. R., Greenberg P. D., Cheever M. A. IL-4-induced lymphokine-activated killer cells. Lytic activity is mediated by phenotypically distinct natural killer-like and T cell-like large granular lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3679–3685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Takeshita T., Sugamura K., Lanier L. L. Activation of natural killer cells via the p75 interleukin 2 receptor. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):291–296. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pross H. F., Baines M. G., Rubin P., Shragge P., Patterson M. S. Spontaneous human lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor target cells. IX. The quantitation of natural killer cell activity. J Clin Immunol. 1981 Jan;1(1):51–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00915477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsdell F. J., Shau H., Golub S. H. Role of proliferation in LAK cell development. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1988;26(2):139–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00205607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shau H. Y., Golub S. H. Signals for activation of natural killer and natural killer-like activity. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul. 1985;4(3):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shau H., Gray J. D., Golub S. H. Studies on cytotoxicity generated in human mixed lymphocyte culture. IV. Interleukin 2 alone or from mixed lymphocyte culture yields natural killer-like cytotoxic cells distinct from allospecific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1988;27(3):255–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00205448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. P., Sharon M., Smith P. L., Leonard W. J. The IL-2 receptor beta chain (p70): role in mediating signals for LAK, NK, and proliferative activities. Science. 1987 Oct 2;238(4823):75–78. doi: 10.1126/science.3116668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Yssel H., Paliard X., Kastelein R., Figdor C., de Vries J. E. IL-4 inhibits IL-2-mediated induction of human lymphokine-activated killer cells, but not the generation of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in mixed leukocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):29–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Goldman C. K., Bongiovanni K. F., Chan W. C., Winton E. F., Yagita M., Grimm E. A., Waldmann T. A. The p75 peptide is the receptor for interleukin 2 expressed on large granular lymphocytes and is responsible for the interleukin 2 activation of these cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5394–5398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer M. B., Acres R. B., Sassenfeld H. M., Grabstein K. H. Regulation of cytolytic cell populations from human peripheral blood by B cell stimulatory factor 1 (interleukin 4). J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1447–1455. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



