Abstract
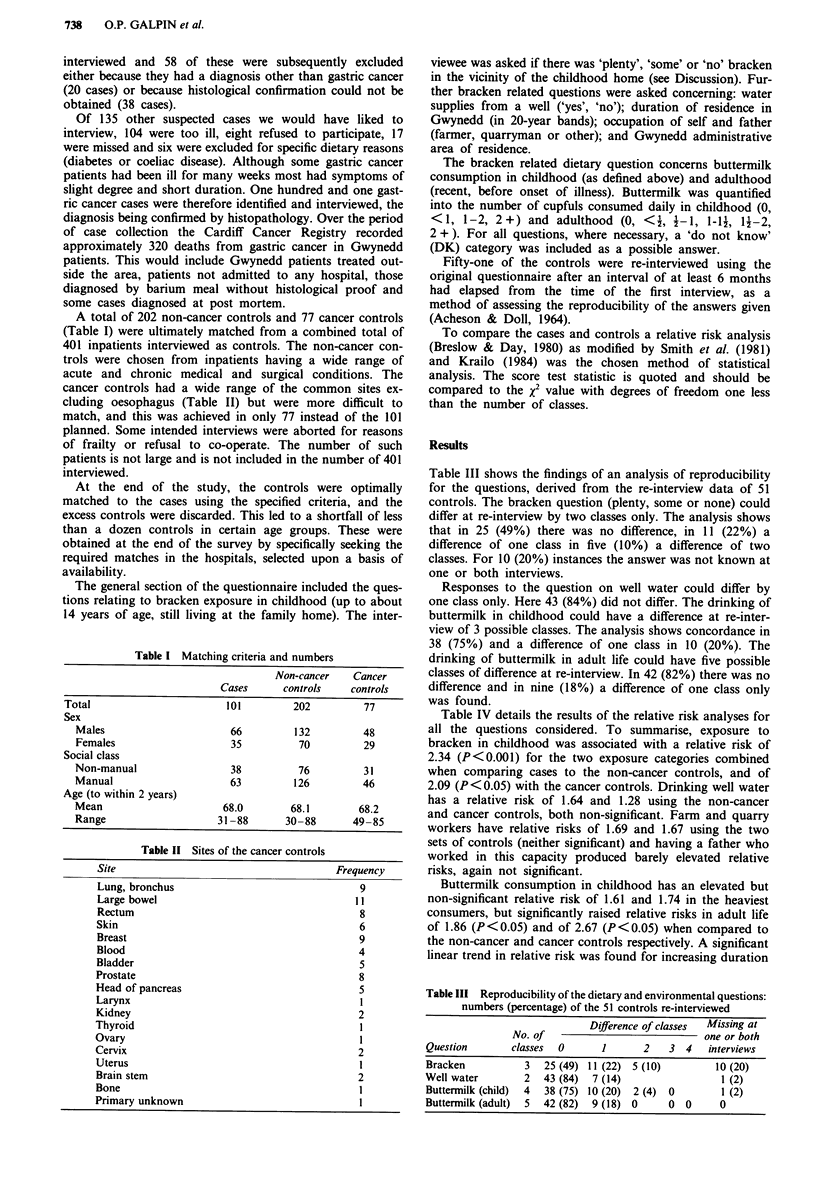
One hundred and one histologically confirmed gastric cancer patients in Gwynedd, North Wales, were matched by sex, age and social class to two hospital inpatients without cancer. Seventy-seven of the gastric cancer cases were also matched, using the same criteria, to a patient with a confirmed cancer of a different site (excluding oesophagus). A questionnaire was used to determine bracken exposure and source of water in childhood. Residential and occupational histories were obtained and the consumption of buttermilk, a potential vector of the bracken carcinogens, was quantified. Comparison of the gastric cancer patients with the non-cancer controls indicated that exposure to bracken in childhood had an increased risk (RR = 2.34, P less than 0.001) compared to no exposure and that length of residence in Gwynedd was associated with increased risk (RR = 2.46 for durations of 61 years and over, P less than 0.01). Consumption of buttermilk in childhood and adulthood was attended by increased risk (RR = 1.61 and 1.86 respectively, the latter being statistically significant, P less than 0.05). Neither the residence effect nor consumption of buttermilk in adulthood remained significant when considered in a multivariate analysis with bracken exposure.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACHESON E. D., DOLL R. DIETARY FACTORS IN CARCINOMA OF THE STOMACH: A STUDY OF 100 CASES AND 200 CONTROLS. Gut. 1964 Apr;5:126–131. doi: 10.1136/gut.5.2.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuello C., Correa P., Haenszel W., Gordillo G., Brown C., Archer M., Tannenbaum S. Gastric cancer in Colombia. I. Cancer risk and suspect environmental agents. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Nov;57(5):1015–1020. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.5.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans I. A., Al-Samarrai A. M., Smith R. M. Bracken toxicology: identification of some water soluble compounds from crozier and rhizome. Res Vet Sci. 1984 Nov;37(3):261–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans I. A. Bracken carcinogenicity. Rev Environ Health. 1987 Jul-Dec;7(3-4):161–199. doi: 10.1515/reveh.1987.7.3-4.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans I. A., Jones R. S., Mainwaring-Burton R. Passage of bracken fern toxicity into milk. Nature. 1972 May 12;237(5350):107–108. doi: 10.1038/237107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans I. A., Mason J. Carcinogenic activity of bracken. Nature. 1965 Nov 27;208(5013):913–914. doi: 10.1038/208913a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAENSZEL W. Cancer mortality among the foreign-born in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1961 Jan;26:37–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenszel W., Kurihara M., Locke F. B., Shimuzu K., Segi M. Stomach cancer in Japan. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Feb;56(2):265–274. doi: 10.1093/jnci/56.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett W. F., McNeil P. E., Grimshaw W. T., Selman I. E., McIntyre W. I. High incidence area of cattle cancer with a possible interaction between an environmental carcinogen and a papilloma virus. Nature. 1978 Jul 20;274(5668):215–217. doi: 10.1038/274215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


