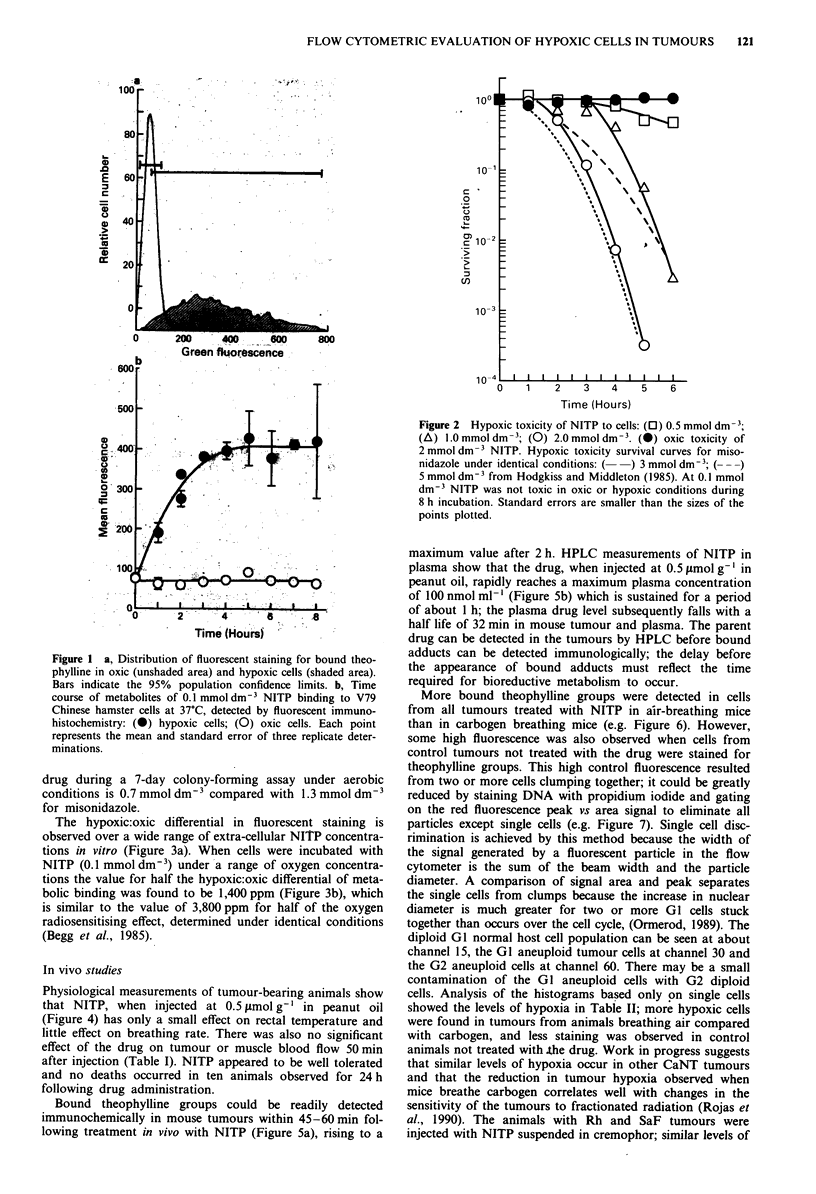
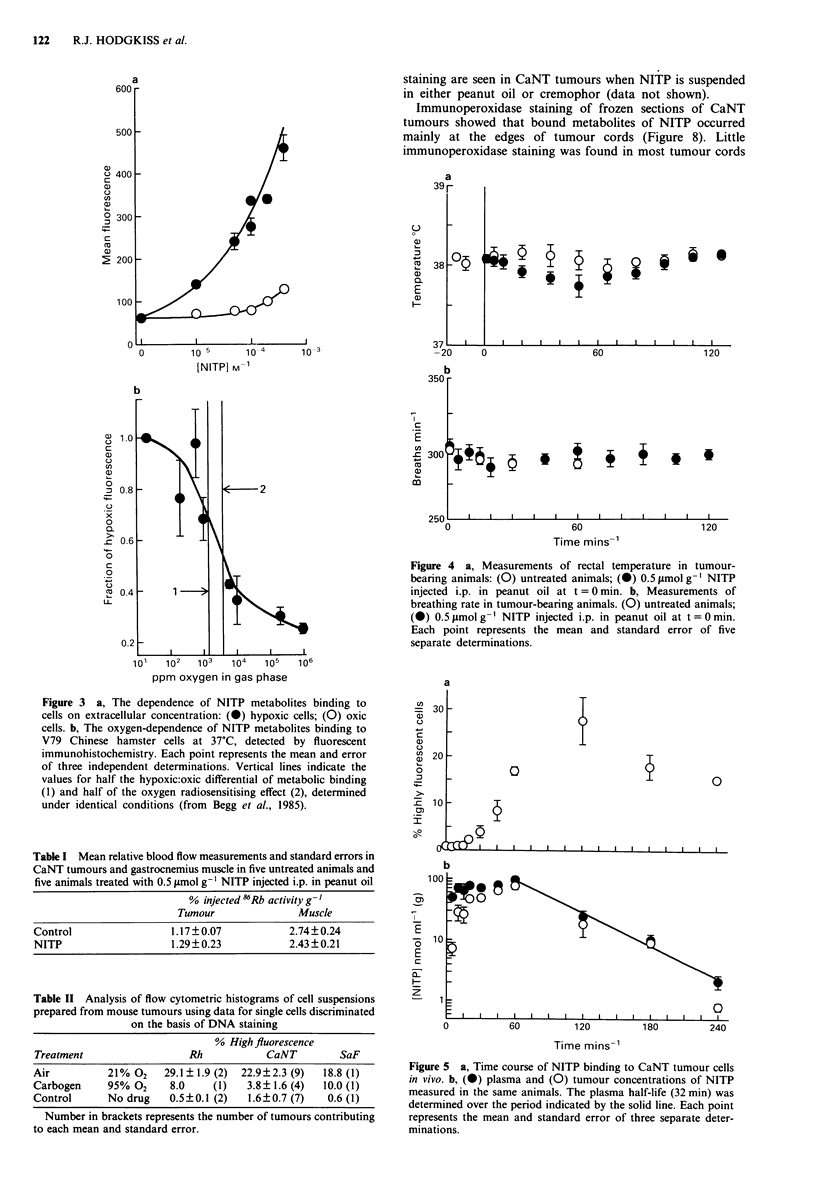
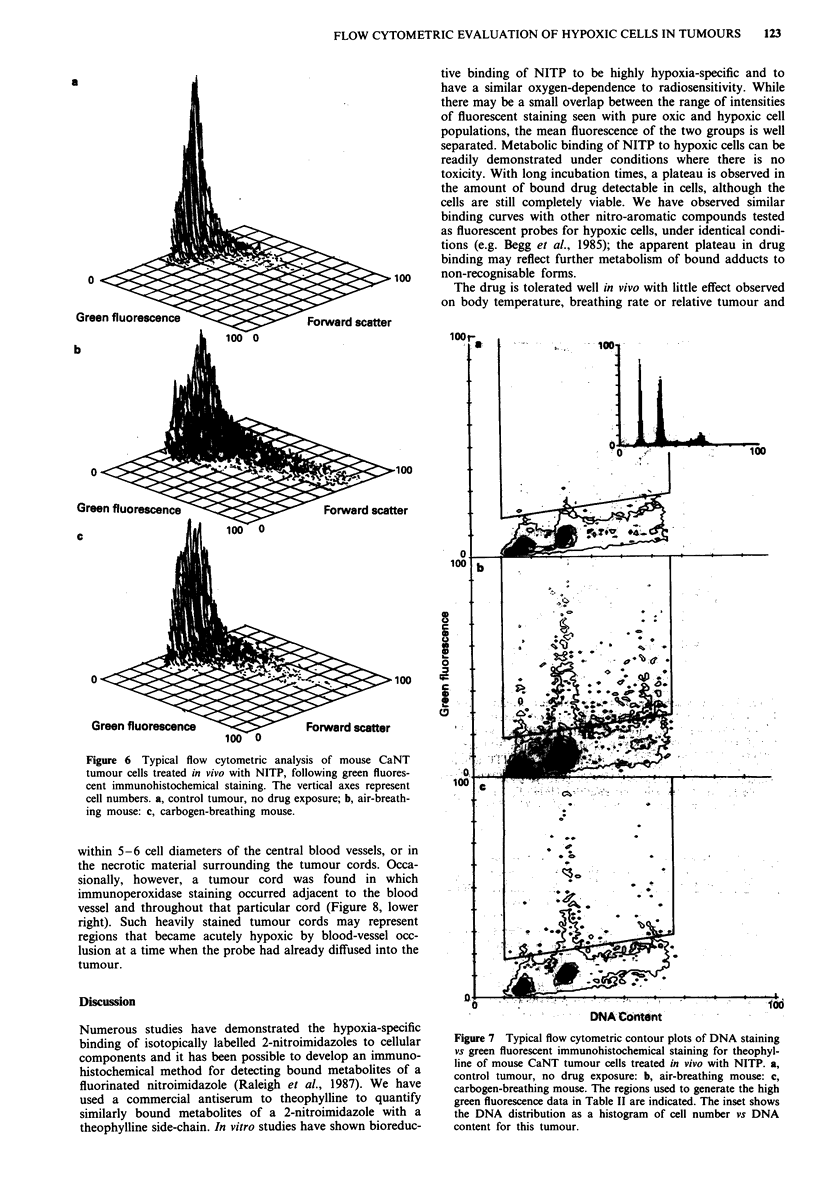
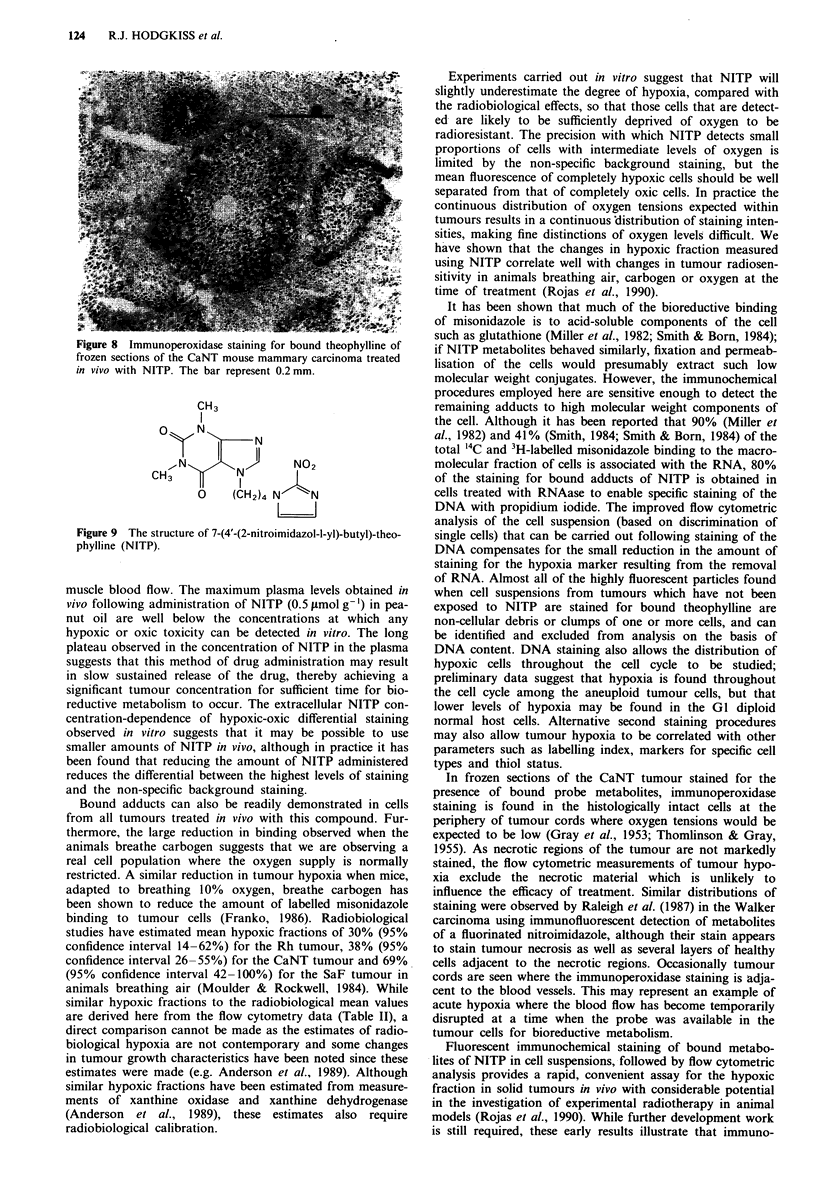
Abstract
Numerous methods have been proposed for the detection of hypoxic cells using nitroimidazoles labelled with both radioactive and stable isotopes where the isotopic label becomes bound as a result of reductive metabolism of the nitro group. A new probe for hypoxia, 7-(4'-(2-nitroimidazol-l-yl)-butyl)-theophylline, is described where an immunologically recognisable hapten (theophylline) is covalently linked to a 2-nitroimidazole. Bioreduction of the nitroimidazole leads to binding of bioreductive metabolites, and hence the theophylline side-chain, to intracellular molecules. Immunochemical procedures are then used to stain cells containing the bound theophylline using an FITC-conjugated anti-serum. Flow cytometric analysis of stained cells is facilitated by co-staining cellular DNA, which allows discrimination of single cells in the sample and rejection of cell clumps and debris. The alternative use of an immunoperoxidase-conjugated anti-serum has been used to demonstrate the localisation of hypoxic cells in frozen tumour sections.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. F., Patel K. B., Reghebi K., Hill S. A. Conversion of xanthine dehydrogenase to xanthine oxidase as a possible marker for hypoxia in tumours and normal tissues. Br J Cancer. 1989 Aug;60(2):193–197. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begg A. C., Hodgkiss R. J., McNally N. J., Middleton R. W., Stratford M. R., Terry N. H. Fluorescent markers of hypoxic cells: a comparison of two compounds on three cell lines. Br J Radiol. 1985 Jul;58(691):645–654. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-58-691-645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush R. S., Jenkin R. D., Allt W. E., Beale F. A., Bean H., Dembo A. J., Pringle J. F. Definitive evidence for hypoxic cells influencing cure in cancer therapy. Br J Cancer Suppl. 1978 Jun;3:302–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. D., Franko A. J., Sharplin J. A marker for hypoxic cells in tumours with potential clinical applicability. Br J Cancer. 1981 Apr;43(4):546–550. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1981.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill-Davidson I., Foster C. A., Wiernik G., Collins C. D., Pizey N. C., Skeggs D. B., Purser P. R. The place of oxygen in radiotherapy. Br J Radiol. 1966 May;39(461):321–331. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-39-461-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dische S. Chemical sensitizers for hypoxic cells: a decade of experience in clinical radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 1985 Feb;3(2):97–115. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(85)80015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dische S., Saunders M. I., Warburton M. F. Hemoglobin, radiation, morbidity and survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986 Aug;12(8):1335–1337. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(86)90166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franko A. J., Chapman J. D. Binding of 14C-misonidazole to hypoxic cells in V79 spheroids. Br J Cancer. 1982 May;45(5):694–699. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franko A. J. Misonidazole and other hypoxia markers: metabolism and applications. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986 Jul;12(7):1195–1202. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(86)90257-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY L. H., CONGER A. D., EBERT M., HORNSEY S., SCOTT O. C. The concentration of oxygen dissolved in tissues at the time of irradiation as a factor in radiotherapy. Br J Radiol. 1953 Dec;26(312):638–648. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-26-312-638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrecht B. M., Chapman J. D. The labelling of EMT-6 tumours in BALB/C mice with 14C-misonidazole. Br J Radiol. 1983 Oct;56(670):745–753. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-56-670-745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. A., Smith K. A., Denekamp J. Reduced thermal sensitivity of the vasculature in a slowly growing tumour. Int J Hyperthermia. 1989 May-Jun;5(3):359–370. doi: 10.3109/02656738909140462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkiss R. J., Middleton R. W. Effects of glutathione depletion using buthionine sulphoximine on the cytotoxicity of nitroaromatic compounds in mammalian cells in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Jun 15;34(12):2175–2178. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkiss R. J., Middleton R. W., Stratford M. R., Del Buono R. Toxicity of 3-nitronaphthalimides to V79 379A Chinese hamster cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 May 1;36(9):1483–1487. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. G., Ngan-Lee J., Chapman J. D. Intracellular localization of radioactively labeled misonidazole in EMT-6-tumor cells in vitro. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1982 Mar-Apr;8(3-4):741–744. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(82)90725-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. E., Rockwell S. Hypoxic fractions of solid tumors: experimental techniques, methods of analysis, and a survey of existing data. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1984 May;10(5):695–712. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(84)90301-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Klieser W., Vaupel P., Manz R., Schmidseder R. Intracapillary oxyhemoglobin saturation of malignant tumors in humans. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1981 Oct;7(10):1397–1404. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(81)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overgaard J., Hansen H. S., Jørgensen K., Hjelm Hansen M. Primary radiotherapy of larynx and pharynx carcinoma--an analysis of some factors influencing local control and survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986 Apr;12(4):515–521. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(86)90058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh J. A., Franko A. J., Koch C. J., Born J. L. Binding of misonidazole to hypoxic cells in monolayer and spheroid culture: evidence that a side-chain label is bound as efficiently as a ring label. Br J Cancer. 1985 Feb;51(2):229–235. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh J. A., Franko A. J., Treiber E. O., Lunt J. A., Allen P. S. Covalent binding of a fluorinated 2-nitroimidazole to EMT-6 tumors in Balb/C mice: detection by F-19 nuclear magnetic resonance at 2.35 T. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986 Jul;12(7):1243–1245. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(86)90268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh J. A., Miller G. G., Franko A. J., Koch C. J., Fuciarelli A. F., Kelly D. A. Fluorescence immunohistochemical detection of hypoxic cells in spheroids and tumours. Br J Cancer. 1987 Oct;56(4):395–400. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasey J. S., Krohn K. A., Grunbaum Z., Conroy P. J., Bauer K., Sutherland R. M. Further characterization of 4-bromomisonidazole as a potential detector of hypoxic cells. Radiat Res. 1985 Apr;102(1):76–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAPIRSTEIN L. A. Regional blood flow by fractional distribution of indicators. Am J Physiol. 1958 Apr;193(1):161–168. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.193.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. R., Born J. L. Metabolism and excretion of [3H]misonidazole by hypoxic rat liver. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1984 Aug;10(8):1365–1370. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(84)90350-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. R. Hypoxia-enhanced reduction and covalent binding of [2-3H]misonidazole in the perfused rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Apr 15;33(8):1379–1381. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90199-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMLINSON R. H., GRAY L. H. The histological structure of some human lung cancers and the possible implications for radiotherapy. Br J Cancer. 1955 Dec;9(4):539–549. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1955.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis E. L., Vojnovic B., Davies E. E., Hirst D. G. A plethysmographic method for measuring function in locally irradiated mouse lung. Br J Radiol. 1979 Jan;52(613):67–74. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-52-613-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urtasun R. C., Chapman J. D., Raleigh J. A., Franko A. J., Koch C. J. Binding of 3H-misonidazole to solid human tumors as a measure of tumor hypoxia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986 Jul;12(7):1263–1267. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(86)90273-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



