Abstract
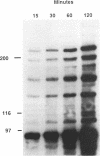
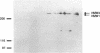
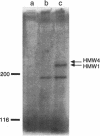
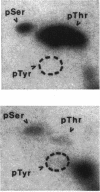
Attachment to host cells of the respiratory epithelium by Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a complex, multicomponent process, requiring a number of accessory proteins in addition to adhesins directly involved in receptor binding. In this study, protein phosphorylation of the cytadherence-accessory proteins HMW1, HMW2, and HMW4 of M. pneumoniae was examined using biochemical and immunological techniques. The initial indication of protein modification came from Western immunoblot analysis of the two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) profile of M. pneumoniae proteins, revealing multiple spots for both HMW1 and HMW4 that varied in pI but not in size. M. pneumoniae cultured in the presence of H3(32)PO4 exhibited numerous phosphorylated proteins as detected by sodium dodecyl sulfate-PAGE and autoradiography. These included proteins corresponding to HMW1, HMW2, and HMW4 in electrophoretic mobility. The Triton X-100 partitioning characteristics of these phosphorylated proteins was identical to that described previously for HMW1, -2, and -4. Furthermore, these protein bands were absent when a noncytadhering variant deficient in HMW1-5 was examined in the same manner. Finally, the availability of antiserum to HMW1 and -4 enabled us to confirm by radioimmunoprecipitation that HMW1 and HMW4 are phosphoproteins. Phosphoamino acid analysis of acid-hydrolyzed HMW1 and HMW2 identified primarily phosphothreonine and, to a lesser extent, phosphoserine in HMW1 and predominantly phosphoserine, with a trace of phosphothreonine, in HMW2. Neither protein contained phosphotyrosine. HMW1-HMW5 are components of a cytoskeleton-like structure in M. pneumoniae that is thought to function in cell division, changes in cell morphology, gliding motility, and the localization of adhesins in the mycoplasma membrane. Phosphorylation may regulate cytoskeleton dynamics involving these cytadherence-accessory proteins.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baseman J. B., Cole R. M., Krause D. C., Leith D. K. Molecular basis for cytadsorption of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1514–1522. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1514-1522.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Morrison-Plummer J., Drouillard D., Puleo-Scheppke B., Tryon V. V., Holt S. C. Identification of a 32-kilodalton protein of Mycoplasma pneumoniae associated with hemadsorption. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 May;23(5):474–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld G., Biberfeld P. Ultrastructural features of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):855–861. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.855-861.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clyde W. A., Jr Mycoplasma pneumoniae respiratory disease symposium: summation and significance. Yale J Biol Med. 1983 Sep-Dec;56(5-6):523–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier A. M., Clyde W. A. Relationships Between Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Human Respiratory Epithelium. Infect Immun. 1971 May;3(5):694–701. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.5.694-701.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A. Estimation of phosphorylation stoichiometry by separation of phosphorylated isoforms. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:251–261. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01023-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzone A. J. Protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:97–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny F. W., Clyde W. A., Jr, Glezen W. P. Mycoplasma pneumoniae disease: clinical spectrum, pathophysiology, epidemiology, and control. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jan;123(1):74–92. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.1.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Kenny G. E., Cooney M. K., Allan I. D. Long-term epidemiology of infections with Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jun;139(6):681–687. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.6.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göbel U., Speth V., Bredt W. Filamentous structures in adherent Mycoplasma pneumoniae cells treated with nonionic detergents. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):537–543. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock K., Tsang V. C. India ink staining of proteins on nitrocellulose paper. Anal Biochem. 1983 Aug;133(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Wilson R. M., Baseman J. B. Two-dimensional gel electrophoretic comparison of proteins from virulent and avirulent strains of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):468–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.468-475.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Surface parasitism by Mycoplasma pneumoniae of respiratory epithelium. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1328–1343. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Granek J., Reisch-Saada A. The adhesins of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and M. pneumoniae. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1984 Jan-Feb;135A(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(84)80055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Tucker S., Leith D. K., Morrison-Plummer J., Baseman J. B. Detection of the major adhesin P1 in triton shells of virulent Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):944–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.944-946.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Cell membrane antigen isolation with the staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1482–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Leith D. K., Baseman J. B. Reacquisition of specific proteins confers virulence in Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):830–836. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.830-836.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Leith D. K., Wilson R. M., Baseman J. B. Identification of Mycoplasma pneumoniae proteins associated with hemadsorption and virulence. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):809–817. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.809-817.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leith D. K., Trevino L. B., Tully J. G., Senterfit L. B., Baseman J. B. Host discrimination of Mycoplasma pneumoniae proteinaceous immunogens. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):502–514. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman R. P., Clyde W. A., Jr, Denny F. W. Characteristics of virulent, attenuated, and avirulent Mycoplasma pneumoniae strains. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1037–1043. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1037-1043.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurides P. A., Akkaraju G. R., Jagus R. Evaluation of protein phosphorylation state by a combination of vertical slab gel isoelectric focusing and immunoblotting. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 15;183(1):144–151. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng K. E., Pfister R. M. Intracellular structures of Mycoplasma pneumoniae revealed after membrane removal. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):390–399. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.390-399.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Hemmings H. C., Jr, Greengard P. Protein kinases in the brain. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:931–976. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt M. W., Reizer J., Rottem S. A 57-kilodalton protein associated with Spiroplasma melliferum fibrils undergoes reversible phosphorylation. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2808–2811. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2808-2811.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt M. W., Rottem S., Milner Y., Barile M. F., Peterkofsky A., Reizer J. Protein phosphorylation in Mycoplasma gallisepticum. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 1;176(1):61–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt M. W., Rottem S. Phosvitin kinase activity in Acholeplasma axanthum. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 19;242(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80993-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Novotny M. J., Hengstenberg W., Saier M. H., Jr Properties of ATP-dependent protein kinase from Streptococcus pyogenes that phosphorylates a seryl residue in HPr, a phosphocarrier protein of the phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):333–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.333-340.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr Introduction: protein phosphorylation and signal transduction in bacteria. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Jan;51(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240510102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Wu L. F., Reizer J. Regulation of bacterial physiological processes by three types of protein phosphorylating systems. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):391–395. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90238-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobeslavsky O., Prescott B., Chanock R. M. Adsorption of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to neuraminic acid receptors of various cells and possible role in virulence. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):695–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.695-705.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens M. K., Krause D. C. Disulfide-linked protein associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae cytadherence phase variation. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3430–3433. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3430-3433.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens M. K., Krause D. C. Localization of the Mycoplasma pneumoniae cytadherence-accessory proteins HMW1 and HMW4 in the cytoskeletonlike Triton shell. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1041–1050. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1041-1050.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens M. K., Krause D. C. Mycoplasma pneumoniae cytadherence phase-variable protein HMW3 is a component of the attachment organelle. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4265–4274. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4265-4274.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]