Abstract
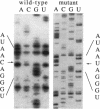
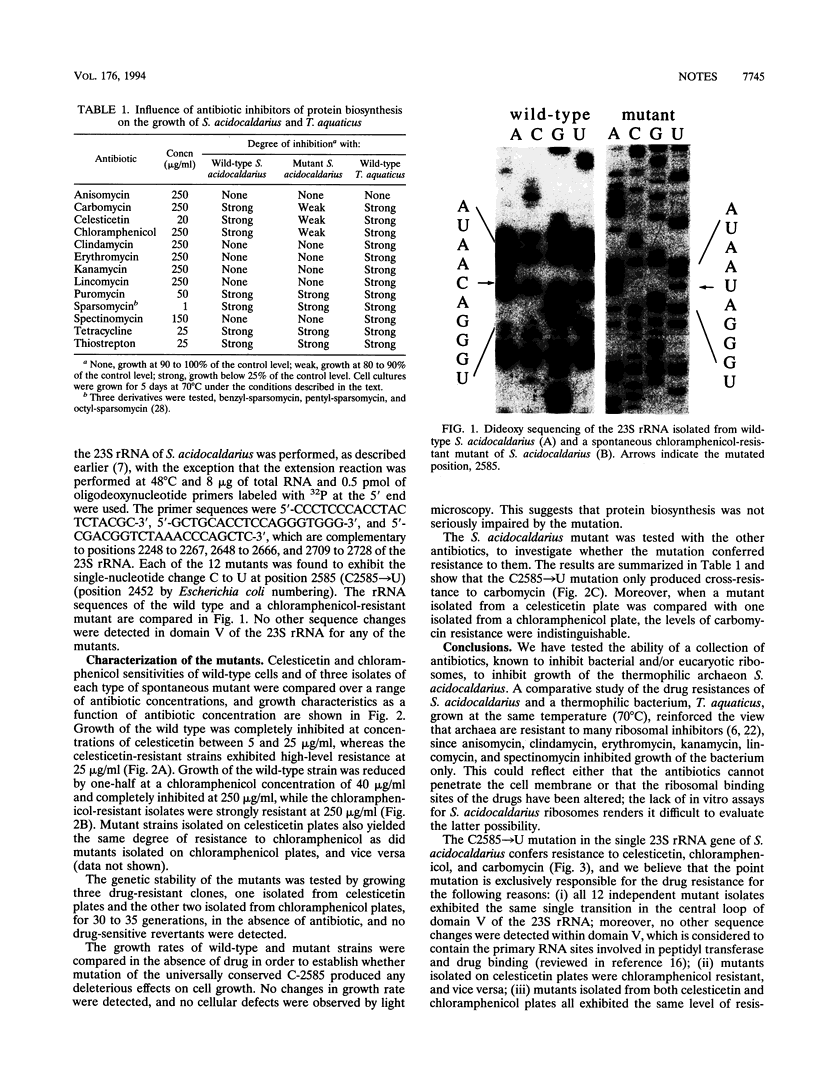
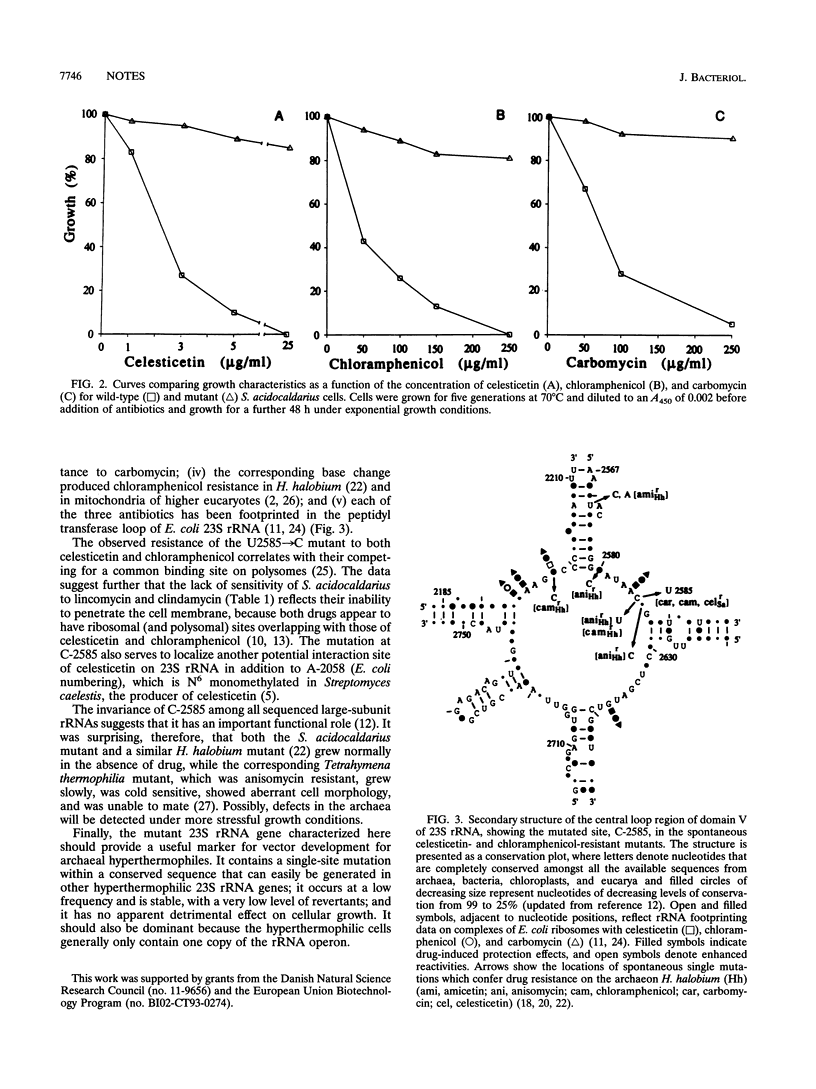
Development of transformable vectors for thermophilic archaea requires the characterization of appropriate selectable marker genes. Many antibiotic inhibitors of protein biosynthesis are known to bind to rRNA; therefore, we screened 14 for their capacity to inhibit growth of the thermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Carbomycin, celesticetin, chloramphenicol, puromycin, sparsomycin, tetracycline, and thiostrepton all inhibited growth by different degrees. Spontaneous drug-resistant mutants were isolated from plates containing celesticetin or chloramphenicol. Six mutants from each plate exhibited a C-2585-to-U transition in the peptidyl transferase loop of 23S rRNA (corresponding to C-2452 in Escherichia coli 23S rRNA). The single-site mutation also conferred resistance to carbomycin. The mutated 23S rRNA gene provides a potentially useful and dominant marker for a thermophilic archael vector.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanc H., Wright C. T., Bibb M. J., Wallace D. C., Clayton D. A. Mitochondrial DNA of chloramphenicol-resistant mouse cells contains a single nucleotide change in the region encoding the 3' end of the large ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3789–3793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Brock K. M., Belly R. T., Weiss R. L. Sulfolobus: a new genus of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria living at low pH and high temperature. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(1):54–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00408082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Freeze H. Thermus aquaticus gen. n. and sp. n., a nonsporulating extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):289–297. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.289-297.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calcutt M. J., Cundliffe E. Cloning of a lincosamide resistance determinant from Streptomyces caelestis, the producer of celesticetin, and characterization of the resistance mechanism. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4710–4714. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4710-4714.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammarano P., Teichner A., Londei P., Acca M., Nicolaus B., Sanz J. L., Amils R. Insensitivity of archaebacterial ribosomes to protein synthesis inhibitors. Evolutionary implications. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):811–816. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03702.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgaard J. Z., Garrett R. A., Belfort M. A site-specific endonuclease encoded by a typical archaeal intron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5414–5417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douthwaite S. Interaction of the antibiotics clindamycin and lincomycin with Escherichia coli 23S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 25;20(18):4717–4720. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.18.4717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Garrett R. A. Binding sites of the antibiotics pactamycin and celesticetin on ribosomal RNAs. Biochimie. 1991 Jul-Aug;73(7-8):1145–1149. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90158-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Munoz R., Monro R. E., Torres-Pinedo R., Vazquez D. Substrate- and antibiotic-binding sites at the peptidyl-transferase centre of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Studies on the chloramphenicol. lincomycin and erythromycin sites. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(1):185–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett R. A., Dalgaard J., Larsen N., Kjems J., Mankin A. S. Archaeal rRNA operons. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jan;16(1):22–26. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90011-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel H., Böck A. 23S ribosomal RNA mutations in halobacteria conferring resistance to the anti-80S ribosome targeted antibiotic anisomycin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2431–2443. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel H., Böck A. Thiostrepton resistance mutations in the gene for 23S ribosomal RNA of halobacteria. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):857–861. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90212-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leviev I. G., Rodriguez-Fonseca C., Phan H., Garrett R. A., Heilek G., Noller H. F., Mankin A. S. A conserved secondary structural motif in 23S rRNA defines the site of interaction of amicetin, a universal inhibitor of peptide bond formation. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1682–1686. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindström E. B., Sehlin H. M. High Efficiency of Plating of the Thermophilic Sulfur-Dependent Archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):3020–3021. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.3020-3021.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin A. S., Garrett R. A. Chloramphenicol resistance mutations in the single 23S rRNA gene of the archaeon Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3559–3563. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3559-3563.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin A. S., Zyrianova I. M., Kagramanova V. K., Garrett R. A. Introducing mutations into the single-copy chromosomal 23S rRNA gene of the archaeon Halobacterium halobium by using an rRNA operon-based transformation system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6535–6539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Chloramphenicol, erythromycin, carbomycin and vernamycin B protect overlapping sites in the peptidyl transferase region of 23S ribosomal RNA. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):879–884. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. XIX. Effect of antibiotics on peptidyl puromycin synthesis on polyribosoms from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4669–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slott E. F., Jr, Shade R. O., Lansman R. A. Sequence analysis of mitochondrial DNA in a mouse cell line resistant to chloramphenicol and oligomycin. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1694–1702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney R., Yao C. H., Yao M. C. A mutation in the large subunit ribosomal RNA gene of Tetrahymena confers anisomycin resistance and cold sensitivity. Genetics. 1991 Feb;127(2):327–334. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Broek L. A., Liskamp R. M., Colstee J. H., Lelieveld P., Remacha M., Vázquez D., Ballesta J. P., Ottenheijm H. C. Structure-activity relationships of sparsomycin and its analogues. Inhibition of peptide bond formation in cell-free systems and of L1210 and bacterial cell growth. J Med Chem. 1987 Feb;30(2):325–333. doi: 10.1021/jm00385a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]