Abstract
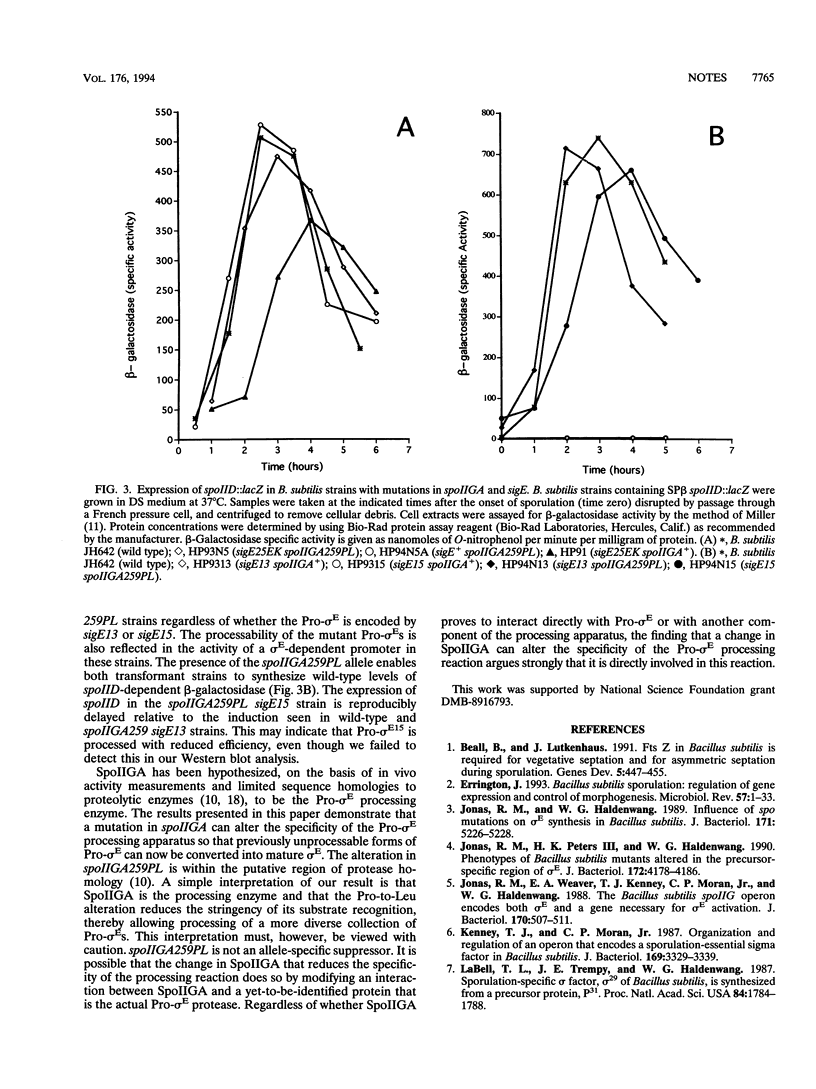
sigma E, a sporulation-essential sigma factor of Bacillus subtilis, is formed by a developmentally regulated proteolysis which removes 27 to 29 amino acids from the amino terminus of an inactive precursor protein (Pro-sigma E). A mutation which facilitates the conversion of inefficiently processed Pro-sigma E variants into mature sigma E was identified and mapped to spoIIGA. The isolation of such a mutation argues that SpoIIGA is directly involved in the Pro-sigma E processing reaction.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beall B., Lutkenhaus J. FtsZ in Bacillus subtilis is required for vegetative septation and for asymmetric septation during sporulation. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):447–455. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J. Bacillus subtilis sporulation: regulation of gene expression and control of morphogenesis. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):1–33. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.1-33.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas R. M., Haldenwang W. G. Influence of spo mutations on sigma E synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5226–5228. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5226-5228.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas R. M., Peters H. K., 3rd, Haldenwang W. G. Phenotypes of Bacillus subtilis mutants altered in the precursor-specific region of sigma E. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4178–4186. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4178-4186.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas R. M., Weaver E. A., Kenney T. J., Moran C. P., Jr, Haldenwang W. G. The Bacillus subtilis spoIIG operon encodes both sigma E and a gene necessary for sigma E activation. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):507–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.507-511.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney T. J., Moran C. P., Jr Organization and regulation of an operon that encodes a sporulation-essential sigma factor in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3329–3339. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3329-3339.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBell T. L., Trempy J. E., Haldenwang W. G. Sporulation-specific sigma factor sigma 29 of Bacillus subtilis is synthesized from a precursor protein, P31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1784–1788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin P. A., Losick R. Characterization of a cell division gene from Bacillus subtilis that is required for vegetative and sporulation septum formation. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(5):1451–1459. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.5.1451-1459.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Stragier P. Crisscross regulation of cell-type-specific gene expression during development in B. subtilis. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):601–604. doi: 10.1038/355601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda E. S., Anaguchi H., Sato T., Takeuchi M., Kobayashi Y. Nucleotide sequence of the sporulation gene spoIIGA from Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):657–657. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyao A., Theeragool G., Takeuchi M., Kobayashi Y. Bacillus subtilis spoVE gene is transcribed by sigma E-associated RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(13):4081–4086. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.13.4081-4086.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters H. K., 3rd, Carlson H. C., Haldenwang W. G. Mutational analysis of the precursor-specific region of Bacillus subtilis sigma E. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4629–4637. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4629-4637.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rong S., Rosenkrantz M. S., Sonenshein A. L. Transcriptional control of the Bacillus subtilis spoIID gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):771–779. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.771-779.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satola S. W., Baldus J. M., Moran C. P., Jr Binding of Spo0A stimulates spoIIG promoter activity in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1448–1453. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1448-1453.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Bonamy C., Karmazyn-Campelli C. Processing of a sporulation sigma factor in Bacillus subtilis: how morphological structure could control gene expression. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):697–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90407-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Bouvier J., Bonamy C., Szulmajster J. A developmental gene product of Bacillus subtilis homologous to the sigma factor of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):376–378. doi: 10.1038/312376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trempy J. E., Bonamy C., Szulmajster J., Haldenwang W. G. Bacillus subtilis sigma factor sigma 29 is the product of the sporulation-essential gene spoIIG. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4189–4192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trempy J. E., Morrison-Plummer J., Haldenwang W. G. Synthesis of sigma 29, an RNA polymerase specificity determinant, is a developmentally regulated event in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):340–346. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.340-346.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasbin R. E., Wilson G. A., Young F. E. Transformation and transfection in lysogenic strains of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):540–548. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.540-548.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]