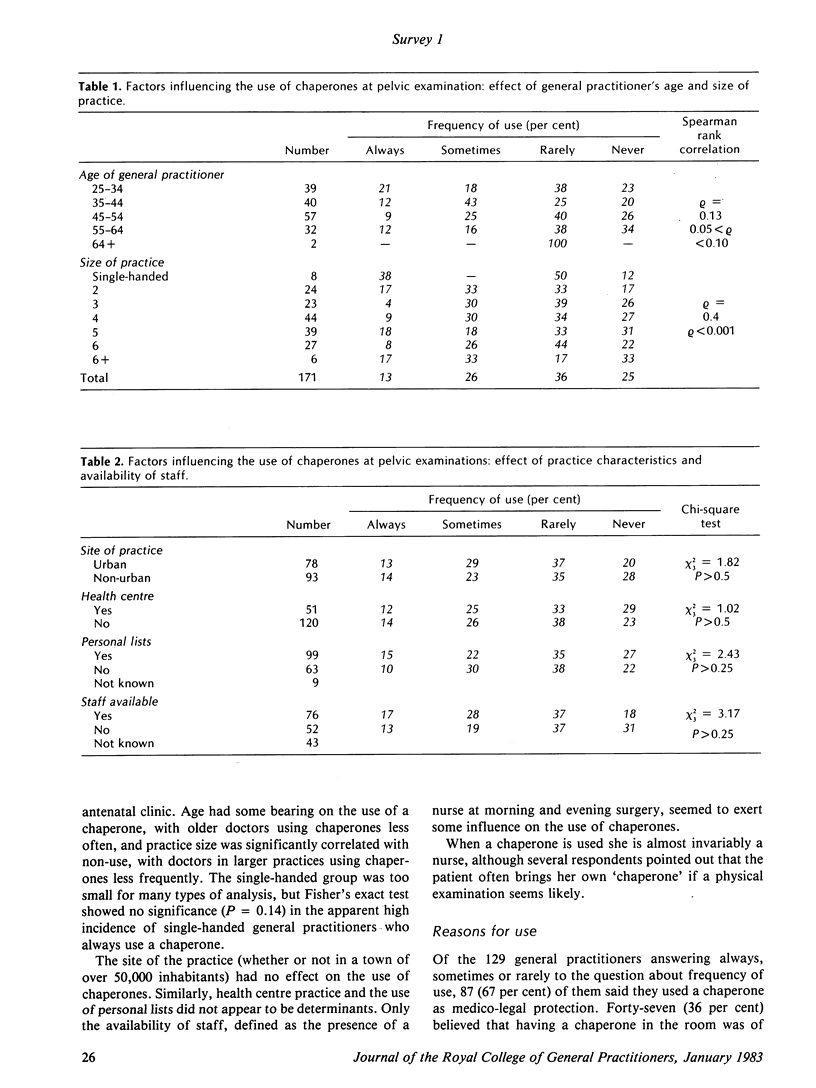
Abstract
A postal questionnaire was sent to 200 male general practitioners to assess attitudes towards chaperones and the extent of their use when female patients are being examined. The response rate was 85.5 per cent. Of the 171 respondents, 23 (13 per cent) claimed they always use a chaperone and 42 (25 per cent) said they never do. Reported use and non-use were related to the doctor's age and to the size of the practice in which he works. The patient's youth and single marital status are apparently important determinants of the decision to use a chaperone, although many of the general practitioners rely on `instinct'. Reasons given for non-use included inconvenience and habit. Many of the doctors said they felt the presence of a third party to be detrimental to the doctor-patient relationship and just as many said they believed the chaperone's presence to be beneficial.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Henderson J. A. Gynaecological examination and equipment in the surgery. Br Med J. 1971 Jan 30;1(5743):273–274. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5743.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kardener S. H., Fuller M., Mensh I. N. A survey of physicians' attitudes and practices regarding erotic and nonerotic contact with patients. Am J Psychiatry. 1973 Oct;130(10):1077–1081. doi: 10.1176/ajp.130.10.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L., Meadow R. Women's attitudes toward gynecologic practices. Obstet Gynecol. 1979 Jul;54(1):110–114. doi: 10.1097/00006250-197907000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


