Abstract
By means of their small receptive fields (RFs), neurons in primary visual cortex perform highly localized analyses of the visual scene, far removed from our normal unified experience of vision. Local image elements coded by the RF are put into more global context, however, by means of modulation of the responses of the V1 neurons. Contextual modulation has been shown to follow closely the perceptual interpretation of the scene as a whole. This would suggest that some aspects of contextual modulation can be recorded only in awake and perceiving animals. In this study, multi-unit activity was recorded with implanted electrodes from primary visual cortex of awake, fixating monkeys viewing textured displays in which figure and ground regions were segregated by differences in either orientation or motion. Contextual modulation was isolated from local RF processing, by keeping RF stimulation identical across trials while sampling responses for various positions of the RF relative to figure and ground. Contextual modulation was observed to unfold spatially and temporally in a way that closely resembles the figure-ground percept. When recording was repeated, but with the animals anesthetized, the figure-ground related modulatory activity was selectively suppressed. RF tuning properties, however, remained unaffected. The results show that the modulatory activity is functionally distinct from the RF properties. V1 thus hosts distinct regimes of activity that are mediated by separate mechanisms and that depend differentially on the animal being awake or anesthetized.
The receptive fields (RFs) of neurons in primary visual cortex (V1) are specialized for conveying information of a low-level nature, such as the orientation and spatial frequency of luminance contrast. Moreover, the small dimensions of each neuron’s RF restrict the given cell’s analysis to a very limited portion of the visual field (1–4). The elementary analysis performed by individual V1 neurons’ RFs is indeed so far removed from our sense of vision that some have proposed activity within primary visual cortex to be strictly preperceptual (5–8). There is mounting evidence, however, that V1 neurons signal, through mechanisms apparently distinct from those shaping the RF, information about the perceptual interpretation of larger parts of the scene than covered by the RF. These mechanisms, expressed as a delayed modulation of stimulus-driven responses, appear to rely not on the particular image features that fall within a cell’s RF, but rather on the larger perceptual context of these features (9–18). For example, this kind of modulation may closely reflect perceptual illusions (12) or the percept of figure-ground segregation (16, 18).
For a wide range of display configurations, we previously have demonstrated that contextual modulation in V1 follows the perceived structure of figure-ground displays (16, 18). These results all were obtained in awake, trained animals. In V1, neural activity also can easily be recorded in anesthetized animals. RF tuning properties, like orientation selectivity, mostly have been studied in such preparations. These RF properties remain largely unaffected by anesthesia and compare well to the situation in the awake animal (2, 19, 20). Contextual effects of various kinds also have been reported in anesthetized preparations (9–13), but as there has been no direct comparison, it is unclear whether these effects are similar to those in the awake animal. The administration of anesthetics interferes with perception; if contextual modulation is an integral part of perception, then anesthesia should be expected to strongly suppress this modulation. To study this, we compared figure-ground segregation-related contextual modulation between the awake and fixating animal and the animal that was paralyzed and anesthetized.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
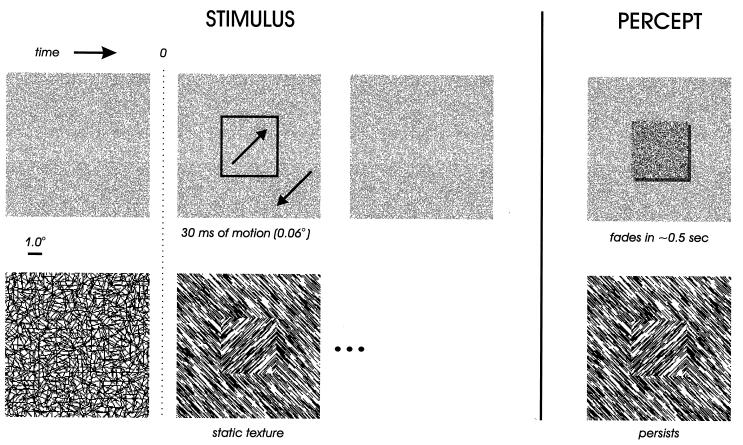
Stimuli were presented on a 21-inch computer monitor, driven by a Number Nine GXi True Color graphics board, running tiga software. The display resolution was 1,024 × 768 pixels, the refresh rate was 72.3375 Hz. The monkey was seated in a custom-made primate chair, at a distance of 75 cm from the monitor, in an otherwise dark room. The screen subtended 28° × 21° of visual angle. Our figure-ground displays consist of a 4° square textured figure on a textured ground, the figure by far exceeding the V1 RFs in size. The figures were defined by structure from motion or by oriented texture. The structure-from-motion stimuli consist of a random dot pattern (Fig. 1 Upper) that before movement looks like a flat surface. During a very brief period of motion, dots inside and outside of the square-shaped region move in opposite directions. Although the duration of the motion is very brief (30 ms) and its amplitude very small (each dot moves only 0.06°), the stimulus evokes a rich percept of a square figure against a ground that persists for up to half a second over the now stationary pattern if the observer maintains fixation. For the displays based on oriented texture, stimulus onset consists of the abrupt transition from a texture of randomly oriented line segments to a texture with a 90° orientation difference between figure and ground (Fig. 1 Lower). This remained on the screen for 500 ms. In random dot displays, half the pixels were black and half white; dot size was 0.03°. In oriented-texture displays, line segments were 0.6° long and 0.03° wide; density was 11 line segments per square degree.
Figure 1.
Sequences of visual stimulation and resulting percepts for two varieties of figure-ground displays. (Upper) Structure from motion defines a square figure region of 4° width. Initially, the display is covered with a random dot pattern; 300 ms after fixation, a brief period of motion (30 ms) occurs in which dots inside and outside of a square region move in opposite directions, each dot moving 0.06°. After the motion, the random dot pattern remains stationary and contains no physical trace of the figure. The percept obtained from this sequence of stimulation is of a square figure that persists against the static random dot pattern for approximately half a second after the motion, if fixation is maintained. (Lower) Orientation contrast defines a square figure region. Initially, the display is covered with randomly oriented line segments; 300 ms after fixation onset, these are replaced by oriented texture in which line segments inside and outside of the 4° square region are orthogonal; this remains for 500 ms. The percept obtained from this sequence of stimulation is of a square figure that persists for the duration of the presentation. In the actual displays used in our experiments, background textures subtended 28° × 21° of visual angle, and thus were in fact more extensive than the ground texture shown in these examples.
Two awake, behaving macaque monkeys were trained to fixate a spot on a graphics monitor as one of the above sequences of stimuli appeared on the screen; one sequence occurred per trial, and for maintaining fixation during the trial, monkeys were rewarded with a drop of apple juice. Eye movements were monitored with scleral search coils (21). We used the modified double magnetic induction method (22). Saved eye movements were digitized at 400 Hz, at a spatial resolution of 0.0006°. Although monkeys were not required to respond to the content of the displays, we previously have shown that monkeys easily detect textured figures induced either by motion or orientation differences (16); the same holds for the monkeys in this study, because in different, but related, experiments they had no difficulty in detecting the same figure squares as we use here.
Neural activity was recorded with surgically implanted Trimel-coated platinum-iridium wires of 25 μm diameter, with exposed tips of 50–150 μm. The obtained signals were amplified (40,000×), band-pass filtered (750–5,000 Hz), full wave rectified, and then low pass filtered (<200 Hz). This resulted in a low frequency signal, representing the amount (or envelope) of high frequency (i.e., spiking) activity (23), without any bias for high amplitude spiking neurons, as is often the case when (arbitrary) amplitude thresholds are used. This signal was digitized (400 Hz), stored on disk, and analyzed off-line. Sixteen channels were recorded simultaneously in each of the two monkeys. Aggregate RFs of the neurons contributing to each channel were assessed with dark moving bars on a white background. RF eccentricity ranged from 1.3° to 5.45°, size from 0.18° to 1.4° (mean size 0.52°), which is not very different from what is found in single unit studies (20).
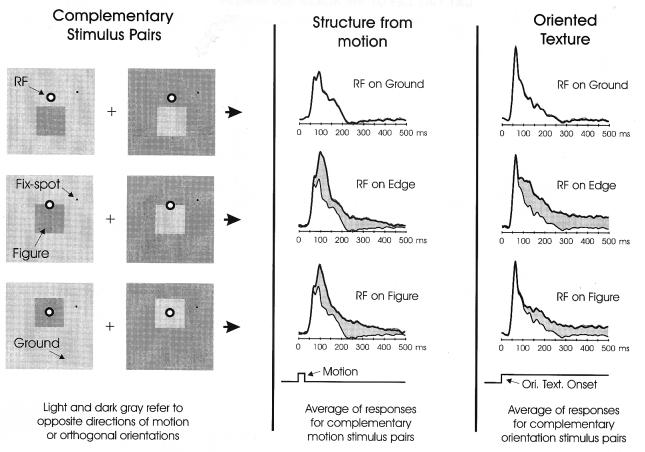
By varying the position of the figure relative to the fixation spot, we could in different trials sample neural responses with a given electrode’s RF positioned on ground, within the figure, or on the figure-ground edge (Fig. 2 Left). Although the percept of figure-ground does not depend on the particular orientation or direction of motion of the texture elements—as long as they clearly differ between figure and ground—the responses of any given V1 cell or multi-unit site may be influenced by just this detail, as V1 RFs typically are tuned for orientation and sometimes for direction of motion as well. To factor out these confounding variables, we always included in our stimulus set complementary pairs of stimuli (Fig. 2 Left) that are structurally identical at the level of figure and ground, but have the property that orientation or motion have orthogonal or opposite values at each point (indicated by the light and dark gray shading in the schematic displays in Fig. 2). Thus, by measuring and averaging V1 responses to the complimentary stimuli, we can insure that, regardless of whether the RF falls in the figure or on the background, the RF will be exposed on average to the same set of local features. Likewise, when the RF is on the figure-ground edge, the local features do not reveal whether the figure is above or below the contour. In this way we are able to investigate specifically how V1 neural responses are modulated by the figure-ground context in which the RF falls (see also ref. 16).
Figure 2.
Sampling of V1 neural responses with the RF located at various positions in the figure-ground displays. To avoid having results depend on local RF features such as texture orientation or direction of motion, we always used complementary pairs of stimuli with the same figure-ground relationships but opposing local features (Left); for a given position of the RF relative to the figure, the responses to these complementary stimuli were averaged. The results for structure from motion (Middle) and oriented texture (Right) are shown. For purpose of comparison, the response for the RF on ground is depicted in composite (thin lines) with edge and figure responses. The difference in response is indicated by gray shading. SEM of each response is given by the dotted lines above each plot. When the RF appeared on the edge or within the motion-defined figure, an elevation in response can be seen, relative to the response to ground, that faded approximately 500 ms after motion onset. When the RF appeared on the edge or within the orientation-defined figure, a persistent elevation in response, relative to the ground response, is observed for as long as the figure remains. The responses shown are the average from all 32 micro-electrodes implanted in area V1 of two awake, behaving macaque monkeys trained to maintain fixation during stimulus presentation.
In our analyses, we use all relevant recorded data, rather than selecting electrodes that show properties of interest. To have equal representation of each electrode in a population average, we must factor out the absolute rate of response at each electrode. We do this by normalizing the responses at each electrode by the maximum response recorded at that electrode, considering all the different positions of figure with respect to RF. Of course this is done separately for the structure-from-motion and for the oriented-texture experiments. We used a set of positions that enabled simultaneous recording from electrodes, such that each electrode was used an equal number of times (≈200 averages per position, per monkey). In the population averages, vertical positions of RF relative to figure were aligned within 0.25°.
In the anesthetized monkey experiments, anesthesia was induced with Ketamine and maintained by artificially ventilating the lungs with a mixture of oxygen (50%), nitrous oxide (50%), and Isoflurane (0.6–1.0%). Paralysis was obtained by continuous intravenous administration of Norcuron, the concentration of which was adjusted so that leg or arm muscle responses evoked by electrical stimulation were just abolished. It generally is considered very difficult to judge depth of anesthesia from paralyzed animals (24). However, we used a level of anesthesia that, without the use of the neuromuscular blocking agent, was sufficiently deep to perform light surgical procedures (e.g., stitching). The recordings did not involve any invasive or otherwise painful procedures. Stimuli were presented at the same distance and on the same equipment as in the awake experiments. After the administration of drops of local anesthetic and mydriatic, eyes were fitted with a contact lens with a 3-mm artificial pupil. Refraction was estimated with an ophthalmoscope and corrected with additional lenses. We furthermore fine-tuned eye focus by testing the neural responses to high spatial frequency, low-contrast checkerboard stimuli until the neural sensitivity was as good as in the awake animals. Neural responses were recorded in sequential periods of about 10 to 15 min. Between these we checked for drift of eye position, by plotting the RFs of several electrodes. When the RFs appeared to have drifted for more than 0.25° we discarded the data recorded in the period before this and readjusted stimulus alignment for subsequent recording.
RESULTS
In Fig. 2 (on the right half) we show the average neural responses recorded from all 32 electrodes in the two monkeys for structure-from-motion displays (Middle) and oriented-texture displays (Right). As explained above, the responses are the means of the complementary stimulus pairs, such that RF specificity for local features has been averaged away. When the RF was positioned on ground, the recorded neurons gave a transient response to the movement of the dots or the appearance of the oriented texture. When the RF was positioned on the figure-ground edge, the cells initially showed the same response as to ground, but approximately 60 ms after the motion onset or 80 ms after oriented-texture onset their responses began to grow substantially larger (in Fig. 2, the difference in response is indicated by shading). A similar result was obtained when the RF was entirely within the figure, although the elevation in response began somewhat later for the oriented-texture display (100 ms). The differences between the responses shown are highly significant, as can be judged from the SEM values that are shown above each plot (dotted lines; however the SEM values are so small that they are not always discernible in the figure). Thus, V1 neural activity shows a striking sensitivity to the larger figure-ground context in which the RF falls. The large amount of data that we have collected here with the awake monkeys allows us to observe three important points that go beyond our previous observations (16, 18). First, there is a clear difference in the delay between the onset of modulation for structure from motion compared with oriented-texture displays. This may suggest that separate subsystems underlie contextual modulation for these two cues. Second, we here observe that the motion-induced modulation fades with a long time course of ≈500 ms, a good match to the perceptual fade-out of the motion-induced figure. Thus the circuits that underlie contextual modulation for motion must be capable of sustaining activity long after the inducing stimulus has disappeared. Third, modulatory activity is greater at the figure edges, and, at least for oriented texture, appears earlier than the modulation in the center of the figure.
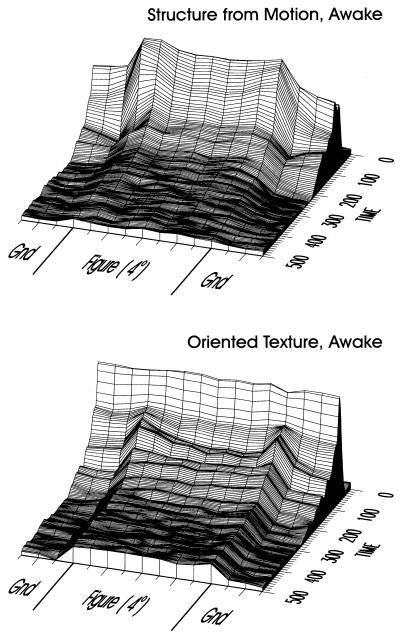
We can gain a better sense for these observations by representing the data in a format that shows how this neural activity unfolds through space and time. To do this, we sample the figure-ground displays at many positions along a line passing through the figure and graph the results as surface plots. The data in Fig. 3 are the result of sampling the 4° wide squares, and part of the adjacent texture background, at 0.5° increments; again, the data shown are the average from all 32 electrodes in the two monkeys. It is important to note that a given position of the figure relative to the fixation spot resulted in either a “RF on figure” or “RF on ground” response, depending on the position of the RF. Thus we averaged responses depending on the relative position of figure and RF. Results for structure from motion are at the top, and those for oriented-texture on the bottom. The two data sets have an essential characteristic in common: after the initial response, activity within the figure region of the display maintains a uniformly higher level of activation than on the textured background. This occurs despite the fact that the average stimulation of the RF is the same for positions where the RF lies inside the figure or on the ground, by virtue of the complementary stimulus pairs. In the structure-from-motion display, this effect occurs earlier than in the oriented-texture display. The uniform elevation induced by motion fades over the course of hundreds of milliseconds, just like the motion-induced percept (this also can be seen nicely in Fig. 2). For the oriented-texture display we observe an intriguing progression, beginning with elevation for the edges only (starting at about 80 ms), and following with elevation for the figure as a whole (≈100 ms), suggesting separate dynamics for contours and surface. The elevated response for figure versus ground persists for the duration of the stimulus presentation. Thus, for both types of figure-ground display, we find neural activity in area V1 of the awake animal to closely reflect the perceived figure-ground relationships. Also in our previous studies, we invariably found a close link between perceived global structure of the displays and the presence or absence of the delayed modulatory activity in V1 (16, 18).
Figure 3.
Spatio-temporal representation of neural activity in response to figure-ground displays in awake monkeys. The figure-ground display was sampled at 15 positions (including the three shown in Fig. 2); samples were taken at 0.5° increments across the figure-ground display. For both the structure-from-motion display (Upper) and for the oriented-texture display (Lower), a uniform level of elevated activation within the figure region of the display evolves after the initial response. Before being combined in the population average, the responses from each electrode were normalized by the maximum of the responses evoked at the various positions of RF relative to figure. In this way, each electrode contributed equally to the average, independent of the absolute response level at the particular electrode.
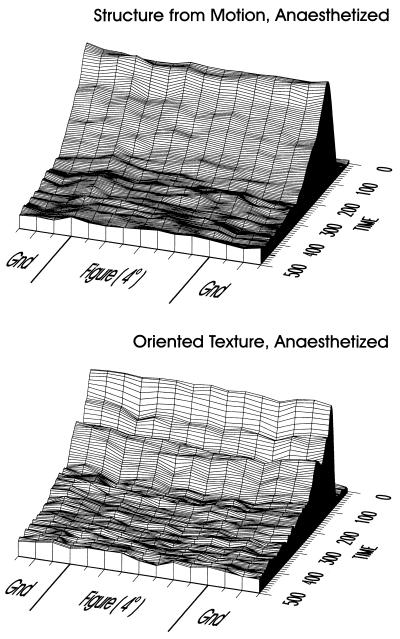
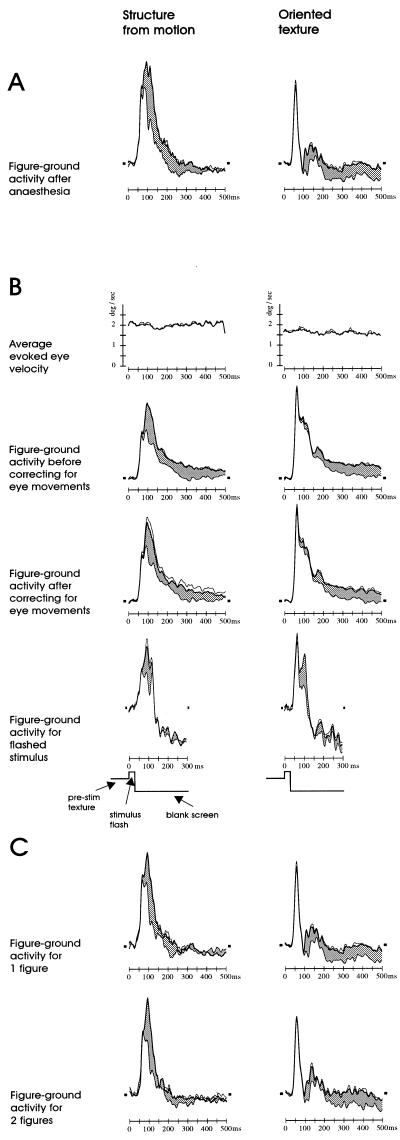
The main point of this paper is to test the hypothesis that the modulatory activity is more vulnerable to a manipulation impeding with perception than are the RF tuning properties. Therefore, we repeated the experiment with the animals paralyzed and anesthetized. Fig. 4 illustrates the average results of the figure-ground experiments conducted on anesthetized animals on four separate days; data is presented in the same format as in Fig. 3. The difference between awake and anesthetized responses is clear: the initial transient response is roughly of the same form as in the awake condition, but the elevated figure-ground signals, both those pertaining to edge and figure, are eliminated in both structure-from-motion and oriented-texture displays. It is as though the neurons were responding only to the RF stimulation, and not to the larger scene context. As RF stimulation is balanced across positions, by virtue of the complementary stimulus pairs, the responses are the same across the figure-ground display. After the anesthesia experiments we ensured that this suppression of figure-ground signals was reversible by confirming that the elevated signals still could be evoked in the awake animal (Fig. 5A).
Figure 4.
Spatio-temporal representation of neural activity in response to figure-ground displays in anesthetized monkeys. The data are represented in the same format as in Fig. 3. The elevation in activity for figure versus ground, as observed in the awake animals, is no longer present for either structure-from-motion or oriented-texture displays.
Figure 5.
Control experiments. (A) After the recordings in anesthetized animals, figure-ground modulation still could be recorded in the awake condition. Shown are average responses for the two types of stimuli with RFs either within the boundaries of the square figure (thick lines) or overlying background (thin lines). The gray shading indicates the difference between figure and ground responses, i.e., the figure-ground specific contextual modulation. (B) Figure-ground modulation in the awake animals is not caused by eye movements. Shown are the average eye velocities during fixation (Top) (eye movements were recorded during about 40% of the data collection resulting in Figs. 2 and 3), showing that the stimulus does not evoke any eye movements beyond the already present low level of micro-saccades within the fixation window. The second and third rows show the figure-ground responses either before or after correcting for eye movements. Correction consisted of removing those 50% of the trials where eye movements within the fixation window were largest. Figure-ground modulation does not appear to depend quantitatively on eye movements. The fourth row shows figure-ground responses for flashed stimuli (see Results), indicating that figure-ground modulation could not have been caused by eye movements over the textures generating responses. (C) Figure-ground modulation in the awake is not an effect of focal attention. Quantitatively similar figure-ground modulation is observed when two figures are presented (Lower) as when one figure is presented (Upper), whereas an effect of focal attention would be expected to split in about equal halves when two figures are presented, thereby diminishing figure-ground modulation for each figure. Format of all figures is: figure responses, thick lines; ground responses, thin lines; SEM of figure responses, dotted lines; prestimulus level of activity, short horizontal dashes; difference between figure and ground responses, gray shading. Not all of these control experiments were performed in both animals.
Despite the major difference in figure-ground contextual activity in awake and anesthetized animals, we found the RFs of the anesthetized animals to function normally. Orientation and direction selectivity of the multi-unit activity at each electrode was determined with moving dark bars on a white background. The average orientation selectivity ratio (peak response at optimal orientation divided by peak response at orientation 90° away) was 1.48 for the awake, 1.50 for the anesthetized condition (with no significant difference, ranges 1.07 to 3.31 and 1.04 to 2.75, respectively). Direction selectivity ratios (peak response at optimal orientation divided by peak response 180° away) were 1.08 and 1.08, respectively (with no significant difference, ranges 1.006 to 2.353 and 1.001 to 1.775). Although positively correlated, the tuning properties at individual electrodes could differ between awake and anesthetized conditions, as they could between extended intervals of awake recording (months). Most likely, this is caused by some electrode drifting. But on average, the sharpness of orientation and direction-of-motion tuning were the same under both the awake and anesthetized conditions. This was to be expected, as previous comparisons of RF properties of V1 neurons in awake and anesthetized animals have revealed at most subtle differences (2, 19, 20). What is important here is that these limited effects of anesthesia on RF tuning properties contrast sharply with the dramatic differences in figure-ground related modulatory activity that we found here.
The responses of each electrode were normalized before compiling the average plots of Figs. 3 and 4, to lend equal weight to the response of each electrode, irrespective of its absolute response level. Compared with the awake condition, the absolute level of evoked activity in the anesthetized condition was a factor of 2.01 (median over electrodes) lower for the motion stimulus, a factor of 1.71 lower for the texture stimulus, and a factor of 1.54 lower for moving bar stimuli. Thus the levels of response to all stimuli were lower in the anesthetized condition, which is a common finding (2, 20). Therefore the lower level of activity itself cannot explain the striking and qualitative difference in sensitivity to anesthesia between RF tuning and figure-ground modulation. Indeed, in the awake animal, reducing the contrast of the figure-ground displays may be used to lower overall response rates; however we found that this does not diminish relative contextual modulation.
In interpreting our results, it is important to ensure that the figure-ground related activity in awake animals is not an indirect result of the percept somehow modifying the monkeys’ behavior in a way that in turn alters the activity in V1; for if the activity was a mere behavioral artifact, its absence in the paralyzed, anesthetized animal would be unsurprising. A potential concern is that the stimuli might evoke small eye movements, which in turn might cause additional stimulation of the V1 receptive fields as the eyes move over the random texture. For example, the moving background of the structure-from-motion stimulus might induce a short tracking movement, thereby increasing the amount of movement over the receptive field when it is inside the figure square, where dots move in the opposite direction. We previously have analyzed eye movements (16, 18) and have shown that figure-ground modulation cannot be attributed to this factor. We also analyzed eye movements for the data presented here. Fig. 5B shows the average absolute tangential eye velocity during the presentation of the stimuli in the awake condition. During the fixation interval, micro-saccades within the fixation window do, of course, occur, resulting in an average eye velocity of about 2°/sec. However, there is no specific increase following stimulus onset, showing that the stimuli do not evoke eye movements. Also when the data are reanalyzed, discarding the 50% of trials were micro-saccades are largest, the figure-ground modulation is not affected (Fig. 5B), showing that the modulation does not quantitatively depend on eye movements. As a third control we recorded with a modification of the stimuli; the screen was set to a blank immediately after 30 ms of stimulus presentation; the brevity of the stimulus in this control ensures that even if there were eye movements, these could not have altered RF stimulation because by the time they could occur, the screen would be blank. This short stimulus presentation is sufficient, however, to evoke the normal contextual modulation, at least for a brief period.
Another potential concern is that the appearance of the figure could draw focal attention to that salient location of the visual field, thereby conceivably increasing the V1 responses (25, 26). However, we found that two figures of equal salience, but on opposites sides of the fixation point, evoke in the awake animal the same amount of modulation as a single figure (Fig. 5C), contrary to what would be expected if focal attention drawn to the lone figure had caused the effect (26). From these results, combined with our previously described control experiments (16, 18), we believe it safe to conclude that the figure-ground modulation as observed in the awake animals is not a behavioral artifact, but a normal part of visual processing.
DISCUSSION
In conclusion, we have shown that the context-sensitive neural activity in V1, which so strikingly corresponds to the way we experience the figure-ground relationships of the surfaces in the scene (Figs. 2 and 3), is absent in the anesthetized animal (Fig. 4), whereas classical RF tuning properties remain unaffected. Others did find contextual modulation with anesthetized animals, using different stimuli (9–13, 27). In a pilot recording in another laboratory, with the animal lightly anesthetized with Fentanyl and nitrous oxide, we also found modulatory effects for figure-ground stimuli in some cells, but these were much smaller than in the awake animal and could be evoked only when using small figure sizes (28). Thus contextual modulation might depend gradually on depth of anesthesia. Also, differences in experimental paradigm or visual stimulation might be important. For example, we do not put much emphasis on matching the stimulus on the RF with its tuning properties and typically use fine grain textures that stimulate the receptive fields only suboptimally (16, 18).
What we have clearly shown, however, is that at some level of anesthesia the figure-ground related modulatory activity is totally abolished whereas the RF tuning properties remain unaffected. That implies that local and global processing in V1 are based on different mechanisms. Furthermore it appears that figure-ground contextual modulation depends much more critically on information integration mechanisms that only function properly in the awake and perceiving animal. One of these mechanisms might be feedback from extra-striate areas, putting V1 activity into more global context (29), as we have shown that the figure-ground modulation also depends on the integrity of the extra-striate areas (30).
Acknowledgments
We thank Kor Brandsma and Jacques de Feiter for biotechnical assistance during surgery and anesthetized recordings. We thank Peter Brassinga and Hans Meester for technical assistance. We thank I-han Chou and Tai-Sing Lee for assistance with a pilot experiment. K.Z. was supported by the Sloan Center for Theoretical Neurobiology at the Salk Institute and by a gift to D. Zipser from the Systems Development Foundation.
ABBREVIATION
- RF
receptive field
References
- 1.Hubel D H, Wiesel T N. J Physiol (London) 1968;195:215–243. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schiller P H, Finlay B L, Volman S F. J Neurophysiol. 1976;39:1288–1374. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Spillmann L, Ehrenstein W. In: Comprehensive Human Physiology. Greger G, Windhorst U, editors. Vol. 1. New York: Springer; 1996. pp. 861–893. [Google Scholar]
- 4.DeAngelis G C, Ohzawa I, Freeman R D. Trends Neurosci. 1995;18:451–458. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(95)94496-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Crick F, Koch C. Nature (London) 1995;375:121–123. doi: 10.1038/375121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kolb F C, Braun J. Nature (London) 1995;377:336–338. doi: 10.1038/377336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.He S, Cavanagh P, Intriligator J. Nature (London) 1996;383:334–336. doi: 10.1038/383334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Movshon J A, Newsome W T. J Neurosci. 1996;16:7733–7741. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-23-07733.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Allman J, Miezin F, McGuiness E. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1985;8:407–430. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.08.030185.002203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gulyas C G, Orban G A, Maes H. J Neurophysiol. 1987;57:1767–1791. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.6.1767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Allman J, Miezin F, McGuiness E. In: Local and Global Order in Perceptual Maps. Edelman G M, editor. New York: Wiley–Liss; 1990. pp. 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gilbert C D, Wiesel T N. Vision Res. 1990;30:1389–1701. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(90)90153-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gilbert C D. Neuron. 1992;9:1–13. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90215-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Knierim J J, VanEssen D C. J Neurophysiol. 1992;67:961–980. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.67.4.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kapadia M K, Ito M, Gilbert C D, Westheimer G. Neuron. 1995;15:843–856. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lamme V A F. J Neurosci. 1995;15:1605–1615. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-02-01605.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gilbert C D. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1996;6:269–274. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(96)80083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zipser K, Lamme V A F, Schiller P H. J Neurosci. 1996;16:7376–7389. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-22-07376.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dow B M, Snyder A Z, Vautin R G, Bauer R. Exp Brain Res. 1981;44:213–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00237343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Snodderly D M, Gur M. J Neurophysiol. 1996;74:2100–2125. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.74.5.2100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Robinson D A. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1963;10:137–145. doi: 10.1109/tbmel.1963.4322822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bour L J, Van Gisbergen J A M, Bruijns J, Ottes F P. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1984;31:419–427. doi: 10.1109/TBME.1984.325281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Legatt A D, Arezzo J, Vaughan H G. J Neurosci Methods. 1980;2:203–217. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(80)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Drummond J C, Todd M M, Saidman L J. Anesthesiology. 1996;85:697–699. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199610000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Motter B. J Neurophysiol. 1993;70:909–919. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.3.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Desimone R, Duncan J. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1995;18:193–222. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.18.030195.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sillito A M, Grieve K L, Jones H E, Cudeiro J, Davis J. Nature (London) 1995;378:492–496. doi: 10.1038/378492a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zipser K, Lamme V A F, Spekreijse H. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997;38:4491. (abstr.). [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mumford D. Biol Cybernetics. 1992;66:241–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00198477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lamme V A F, Zipser K, Spekreijse H. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997;38:4490. (abstr.). [Google Scholar]