Abstract
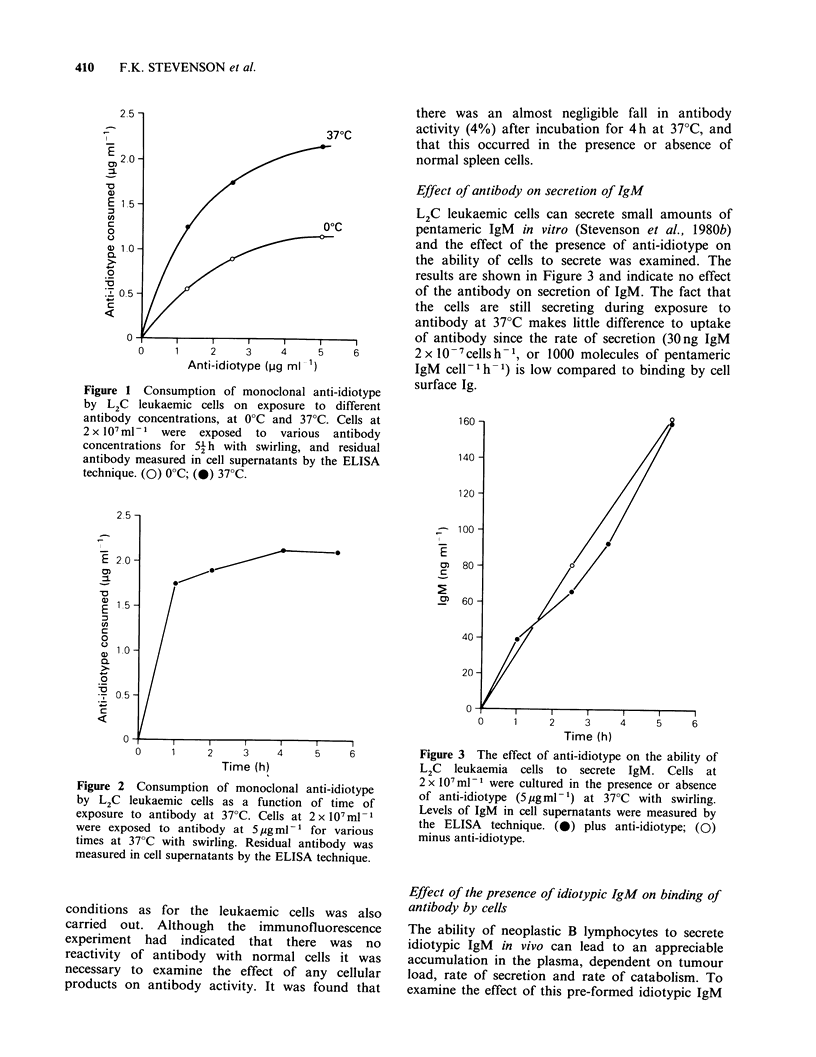
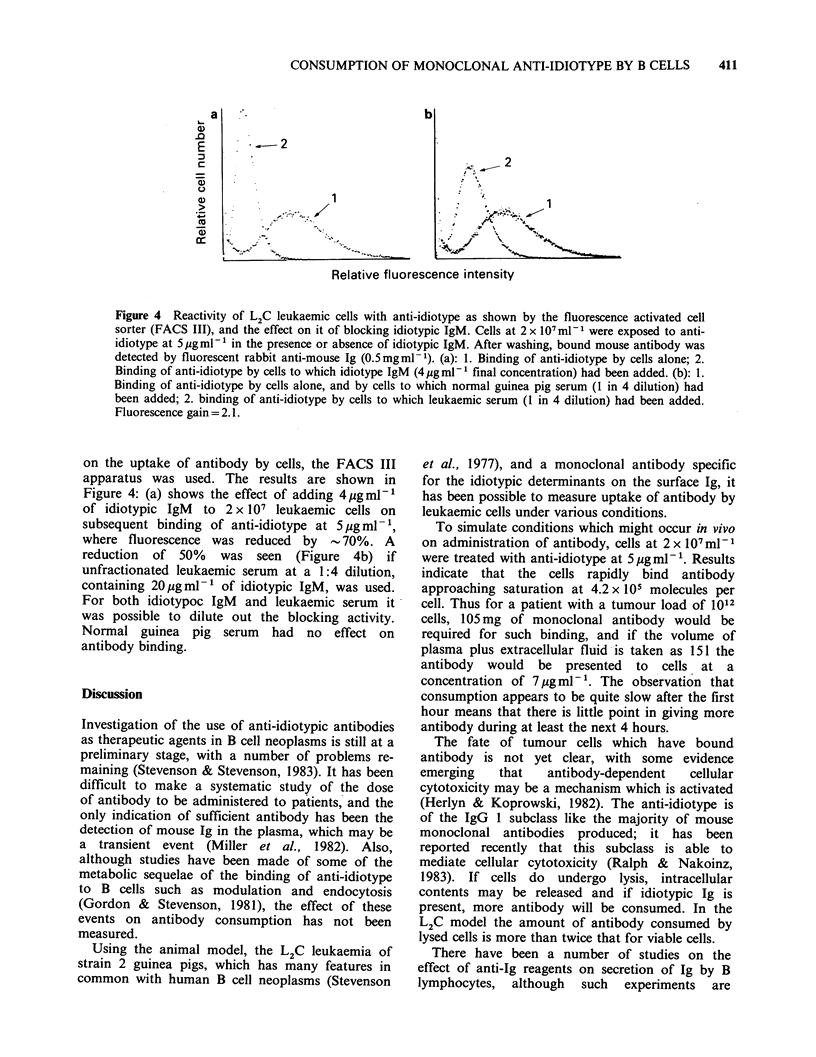
A quantitative analysis in vitro of events which might occur on administration of mouse monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibody to a recipient with a B cell neoplasm has been made. The L2C leukaemic cells of guinea pigs, which closely resemble those of human lymphoma in expression and metabolism of immunoglobulin have been used as a model. Exposure of neoplastic B cells to antibody results in rapid binding of approximately 420,000 molecules of antibody per cell at saturation, and the amount consumed does not increase markedly over the next 4 h of exposure at 37 degrees C. This is in spite of the fact that secretion of idiotypic IgM continues unaffected by the presence of antibody, and reflects the fact that the amount of IgM secreted during this period is low compared to the amount displayed on the cell surface. If cells undergo lysis, however, the antibody consumed is approximately doubled: thus a recipient with an estimated tumour load of 10(12) cells would require 200 mg of monoclonal anti-idiotype for binding to surface and intracellular antigen. The effect of the soluble idiotypic IgM found in serum on the ability of antibody to bind target cells has been examined by means of the fluorescence activated cell sorter. Access of antibody to the cells is efficiently blocked by competing idiotypic IgM in the fluid phase, with no indication of preferential binding to cell surface idiotype. Immunotherapeutic doses should be designed therefore to overcome this additional antigenic load in secreting tumours, which form the majority of B cell neoplasms.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S. Indirect immunoenzyme techniques for the intracellular detection of antigens. Immunochemistry. 1969 Nov;6(6):825–831. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90288-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bona C. A., Fauci A. S. In vitro idiotypic suppression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia lymphocytes secreting monoclonal immunoglobulin M anti-sheep erythrocyte antibody. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):761–767. doi: 10.1172/JCI109724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D. Towards a chemical definition of idiotypy. Fed Proc. 1977 Feb;36(2):204–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykes P. W., Hine K. R., Bradwell A. R., Blackburn J. C., Reeder T. A., Drolc Z., Booth S. N. Localisation of tumour deposits by external scanning after injection of radiolabelled anti-carcinoembryonic antigen. Br Med J. 1980 Jan 26;280(6209):220–222. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6209.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glennie M., Stevenson F. K., Stevenson G. T., Virji M. Cross-linking of lymphocytic surface immunoglobulin inhibits its production via a cyclic nucleotide mechanism. Nature. 1979 Sep 27;281(5729):305–307. doi: 10.1038/281305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Stevenson G. T. Antigenic modulation of lymphocytic surface immunoglobulin yielding resistance to complement-mediated lysis. II. Relationship to redistribution of the antigen. Immunology. 1981 Jan;42(1):13–17. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin T. J., Abdul-Ahad A. K., Gordon J., Stevenson F. K., Stevenson G. T. Preliminary experience in treating lymphocytic leukaemia with antibody to immunoglobulin idiotypes on the cell surfaces. Br J Cancer. 1980 Oct;42(4):495–502. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haughton G., Lanier L. L., Babcock G. F., Lynes M. A. Antigen-induced murine B cell lymphomas. II. Exploitation of the surface idiotype as tumor specific antigen. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2358–2362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn D., Koprowski H. IgG2a monoclonal antibodies inhibit human tumor growth through interaction with effector cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4761–4765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough D. W., Chapple J. C., Stevenson F. K., Stevenson G. T. Further studies of immunoglobulin synthesis by guinea pig leukaemic lymphocytes. Immunology. 1978 May;34(5):889–899. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krolick K. A., Isakson P. C., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S. BCL1, a murine model for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: use of the surface immunoglobulin idiotype for the detection and treatment of tumor. Immunol Rev. 1979;48:81–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch R. G., Graff R. J., Sirisinha S., Simms E. S., Eisen H. N. Myeloma proteins as tumor-specific transplantation antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1540–1544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCubrey J., Risser R. Genetic interactions in the spontaneous production of endogenous murine leukemia virus in low leukemic mouse strains. J Exp Med. 1982 Aug 1;156(2):337–349. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn G. L., Lynch R. G. Immunoregulation of murine myeloma in vitro. II. Suppression of MOPC-315 immunoglobulin secretion and synthesis by idiotype-specific suppressor T cells. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):852–862. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Maloney D. G., Warnke R., Levy R. Treatment of B-cell lymphoma with monoclonal anti-idiotype antibody. N Engl J Med. 1982 Mar 4;306(9):517–522. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198203043060906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primus F. J., Bennett S. J., Kim E. E., DeLand F. H., Zahn M. C., Goldenberg D. M. Circulating immune complexes in cancer patients receiving goat radiolocalizing antibodies to carcinoembryonic antigen. Cancer Res. 1980 Mar;40(3):497–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Nakoinz I. Cell-mediated lysis of tumor targets directed by murine monoclonal antibodies of IgM and all IgG isotypes. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):1028–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M., Ellman L., Davie J. M., Green I. L2C Guinea pig lymphatic leukemia: a "B" cell leukemia. Blood. 1972 Jan;39(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson F. K., Hamblin T. J., Stevenson G. T., Tutt A. L. Extracellular idiotypic immunoglobulin arising from human leukemic B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1484–1496. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson F. K., Morris D., Stevenson G. T. Immunoglobulin produced by guinea-pig leukaemic B lymphocytes: its source and use as a monitor of tumour load. Immunology. 1980 Oct;41(2):313–321. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson G. T., Eady R. P., Hough D. W., Jurd R. D., Stevenson F. K. Surface immunoglobulin of guinea-pig leukaemic lymphocytes. Immunology. 1975 May;28(5):807–820. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson G. T., Elliott E. V., Stevenson F. K. Idiotypic determinants on the surface immunoglobulin of neoplastic lymphocytes: a therapeutic target. Fed Proc. 1977 Aug;36(9):2268–2271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson G. T., Stevenson F. K. Antibody to a molecularly-defined antigen confined to a tumour cell surface. Nature. 1975 Apr 24;254(5502):714–716. doi: 10.1038/254714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson G. T., Stevenson F. K. Treatment of lymphoid tumors with anti-idiotype antibodies. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1983;6(1):99–115. doi: 10.1007/BF01857369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tutt A. L., Stevenson F. K., Smith J. L., Stevenson G. T. Antibodies against urinary light chain idiotypes as agents for detection and destruction of human neoplastic B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3058–3063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


