Abstract
Since the treatment of postmenopausal breast cancer patients with aminoglutethimide caused hypothyroidism with an unexpectedly high frequency previous treatment was suspected to contribute to hypofunction of the thyroid. Serum thyrotropin, triiodothyronine and free thyroxine index were compared between breast cancer patients who had undergone irradiation of regional lymph nodes and non-irradiated breast cancer patients, as well as patients having endometrial or colorectal carcinoma. Subclinical and clinical primary hypothyroidism was significantly more frequent in breast cancer patients who had previously received irradiation on supraclavicular lymph nodes comprising a minor part of the thyroid. Testing for the presence of autoantibodies against thyroid tissue components gave no evidence for radiation-induced autoimmune thyroiditis. Drugs suppressing thyroid hormone synthesis like aminoglutethimide may frequently cause myxedema in such irradiated women, especially at postmenopausal age.
Full text
PDF
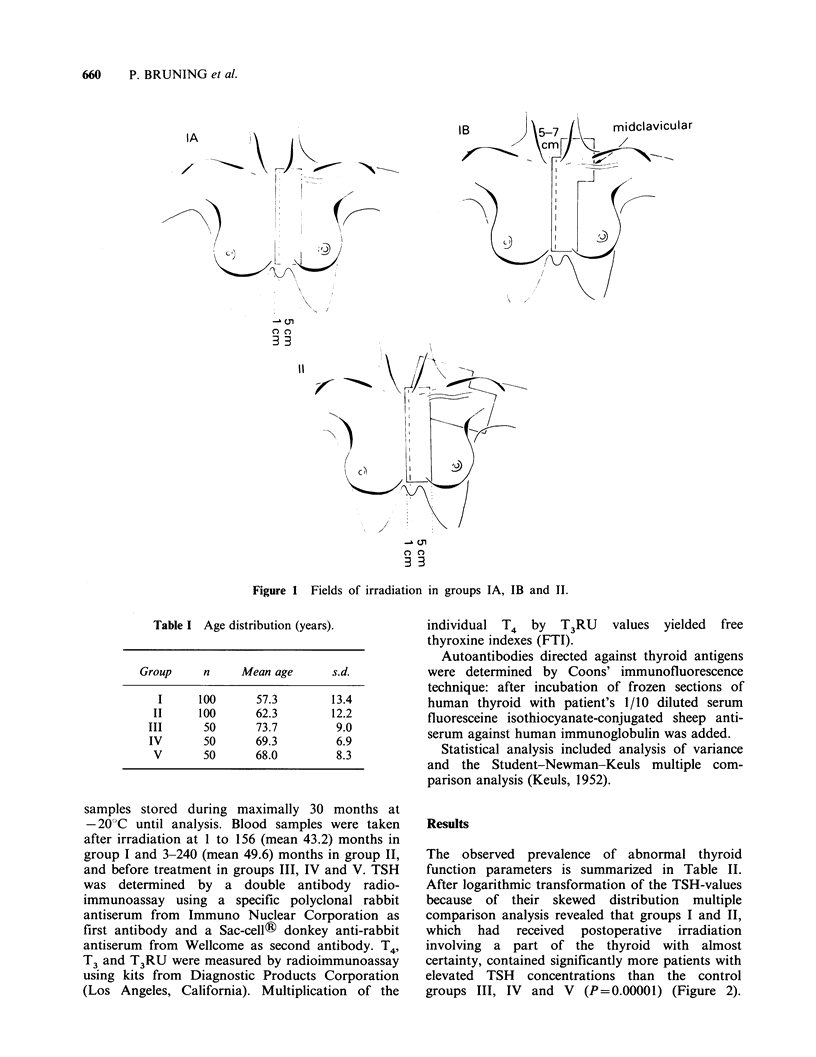
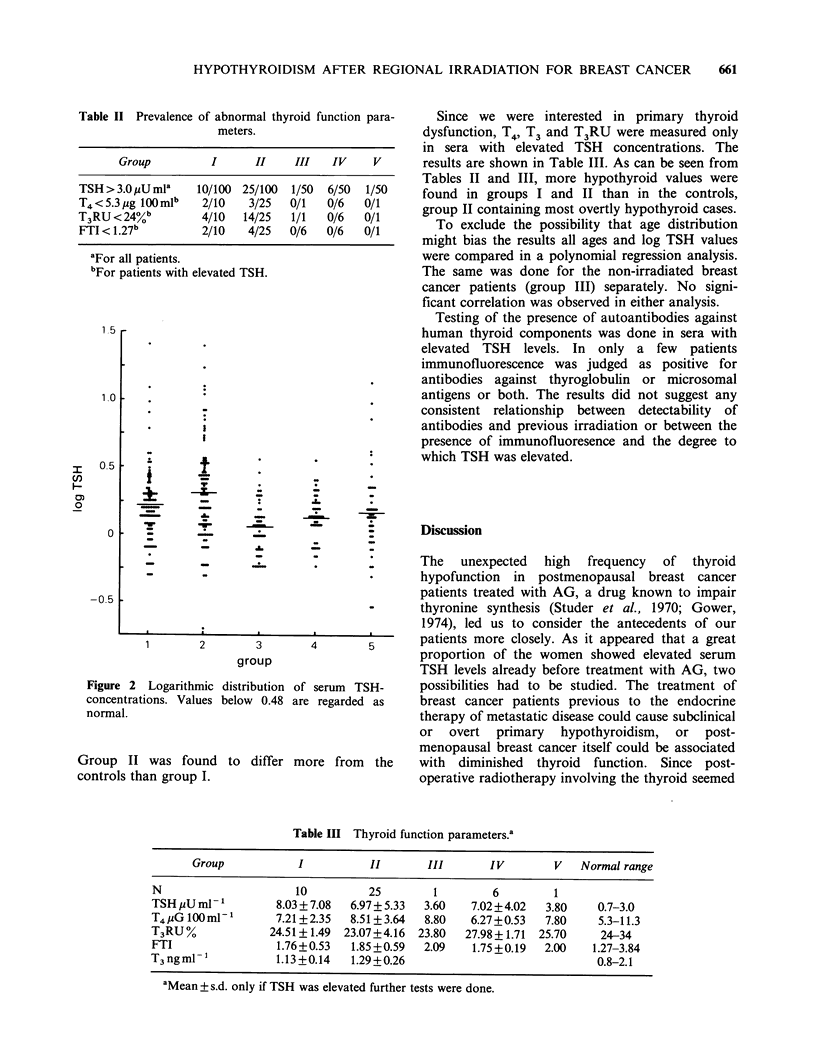


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruning P. F., Bonfrèr J. G., Engelsman E., Hamersma-vd Linden E., de Jong-Bakker M., Nooyen W. Pros and cons of aminoglutethimide for advanced postmenopausal breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1984;4(4):289–295. doi: 10.1007/BF01806041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gower D. B. Modifiers of steroid-hormone metabolism: a review of their chemistry, biochemistry and clinical applications. J Steroid Biochem. 1974 Aug;5(5):501–523. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(74)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley A. J., Jones S. J., Spiegelhalter D. J., Clements P., Bewsher P. D., Simpson J. G., Weir R. D. Breast cancer in thyroid disease: fact or fallacy? Lancet. 1981 Jan 17;1(8212):131–133. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90712-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundell G., Jonsson J. Thyroid antibodies and hypothyroidism in 131-I therapy for hyperthyroidism. Acta Radiol Ther Phys Biol. 1973 Oct;12(5):443–453. doi: 10.3109/02841867309130411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden N. R., Davey P. G., Browning M. C. Radiotherapy and thyroid function. Lancet. 1982 Jun 19;1(8286):1410–1411. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92523-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner M. R., Ervin T. J., Miller D., Fabian R. L., Norris C. M., Jr, Weichselbaum R. R., Rose C. Incidence of hypothyroidism following multimodality treatment for advanced squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. Laryngoscope. 1984 Apr;94(4):451–454. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198404000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D. P., Davis T. E. Plasma thyroid-stimulating hormone and thyroxine concentrations in breast cancer. Cancer. 1978 Feb;41(2):666–669. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197802)41:2<666::aid-cncr2820410234>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpff S. C., Diggs C. H., Wiswell J. G., Salvatore P. C., Wiernik P. H. Radiation-related thyroid dysfunction: implications for the treatment of Hodgkin's disease. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jan;92(1):91–98. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schottenfeld D. The relationship of breast cancer to thyroid disease. J Chronic Dis. 1968 Aug;21(5):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(68)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer R. B., Nuttall F. Q., Pollak K., Kuisk H. Thyroid function after radiation and surgery for head and neck cancer. Arch Intern Med. 1975 Jun;135(6):843–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Jr, Adler R. A., Clark P., Brinck-Johnsen T., Tulloh M. E., Colton T. Thyroid function after mantle irradiation in Hodgkin's disease. JAMA. 1981 Jan 2;245(1):46–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studer H., Kohler H., Bürgi H., Dorner E., Forster R., Rohner R. Goiters with high radioiodine uptake and other characteristics of iodine deficiency in rats chronically treated with aminoglutethimide. Endocrinology. 1970 Nov;87(5):905–914. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-5-905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B. S., Bulbrook R. D., Russell M. J., Hayward J. L., Millis R. Thyroid function in early breast cancer. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1983 Sep;19(9):1213–1219. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(83)90198-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


