Abstract
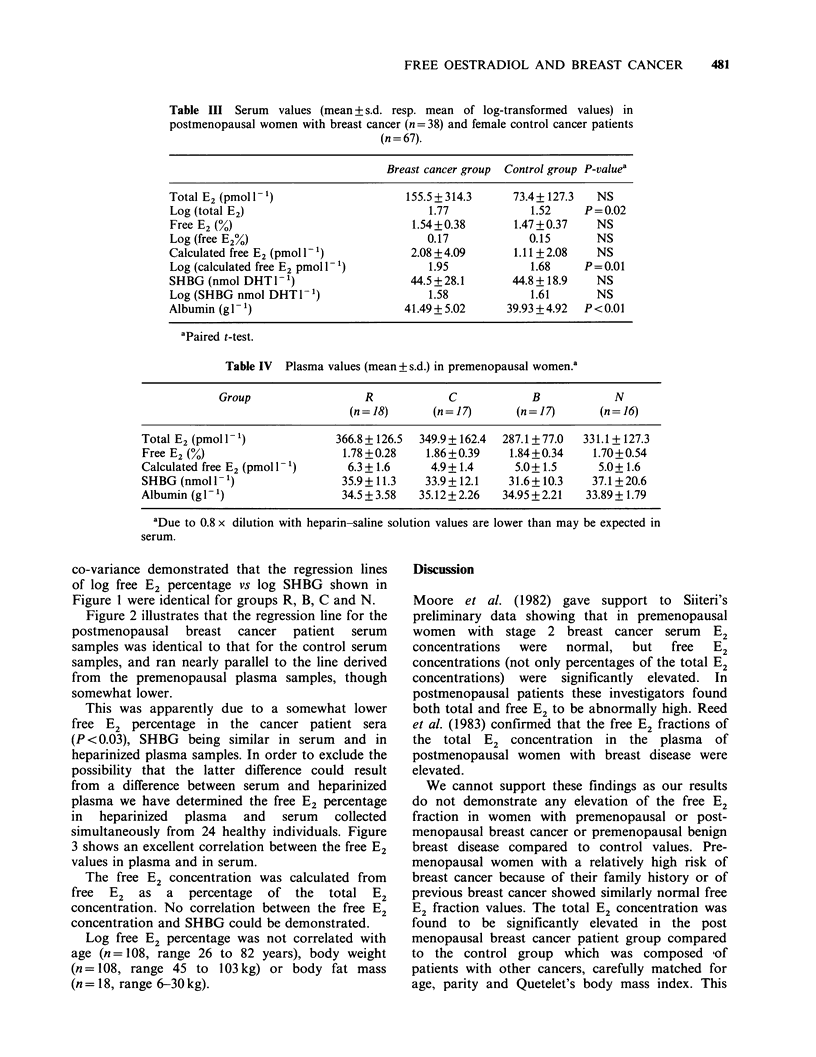
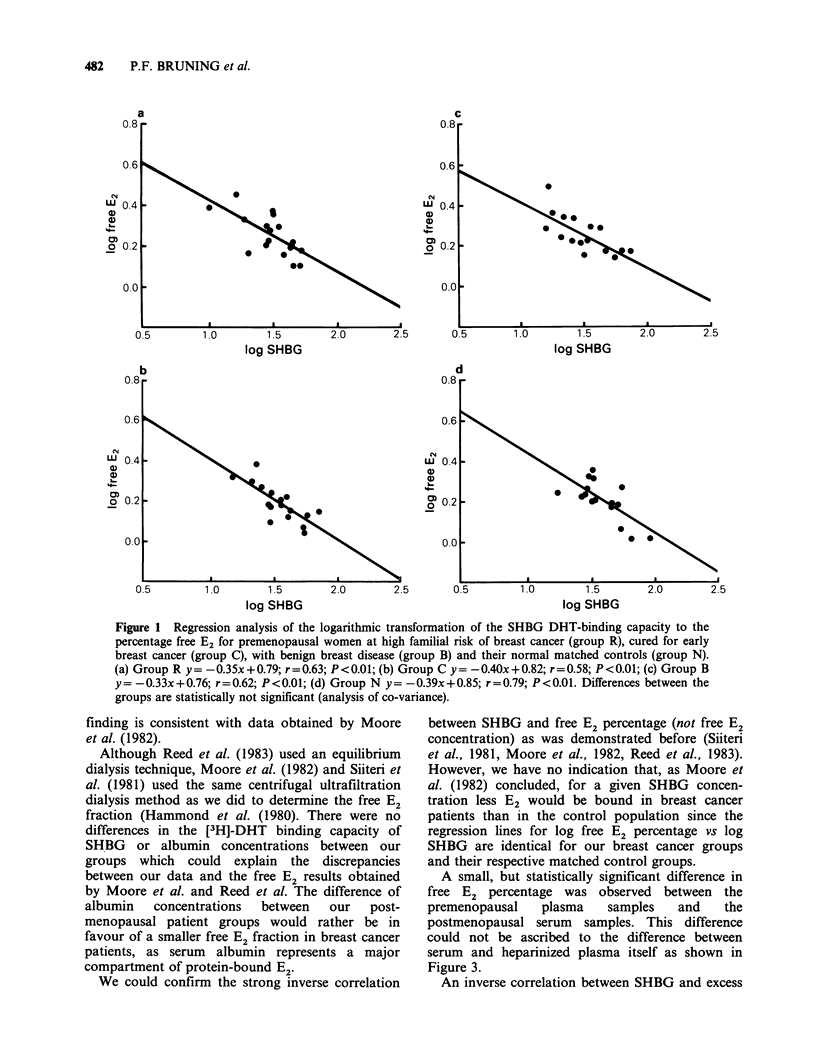
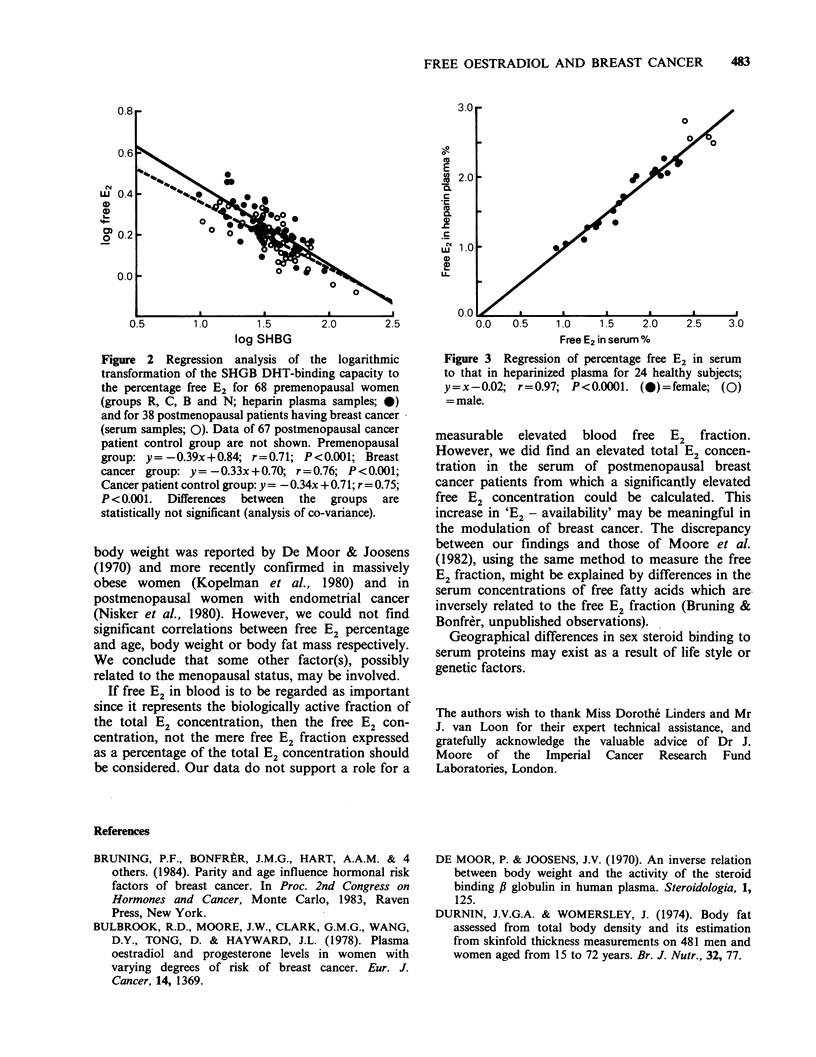
It has recently been found by various authors that despite a normal serum concentration of oestradiol (E2), the percentage of non-protein-bound or free E2 is abnormally high in breast cancer patients. Since it is the free E2 which is considered to be biologically active, confirmation of this finding would be most relevant to the pathogenesis of breast cancer. Using Hammond's centrifugal ultrafiltration dialysis method we have measured free E2 in heparinized plasma from 68 premenopausal women (a) at high familial risk of breast cancer (n = 18), (b) with benign breast disease (n = 17), (c) cured of T1N0M0 breast cancer at least 6 months previously (n = 17) and (d) normal controls matched for age, parity and Quetelet index (n = 16). Sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) was measured as [3H]-dihydrotestosterone binding capacity. Free E2 and SHBG were also measured in the serum of (e) postmenopausal patients having breast cancer (n = 38) and (f) matched control cancer patients (n = 67). We confirmed a very good inverse correlation between log free E2 per cent and log SHBG (P less than 0.0001). The regression lines for groups (a)-(d) were not statistically different. The regression lines for groups (e) and (f) were identical and ran nearly parallel to those for groups (a)-(d) though somewhat lower. This small difference may be ascribed to menopausal status. Therefore, we found no difference in free E2 percentage, calculated free E2 concentration or SHBG between premenopausal women at risk, women with benign breast disease, patients cured for early breast cancer or having breast cancer and matched controls. However, postmenopausal breast cancer patients had a significantly higher total serum E2 concentration and, by consequence a higher calculated free E2 concentration compared to the carefully matched control group.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bulbrook R. D., Moore J. W., Clark G. M., Wang D. Y., Tong D., Hayward J. L. Plasma oestradiol and progesterone levels in women with varying degrees of risk of breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1978 Dec;14(12):1369–1375. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(78)90120-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnin J. V., Womersley J. Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: measurements on 481 men and women aged from 16 to 72 years. Br J Nutr. 1974 Jul;32(1):77–97. doi: 10.1079/bjn19740060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. L., Nisker J. A., Jones L. A., Siiteri P. K. Estimation of the percentage of free steroid in undiluted serum by centrifugal ultrafiltration-dialysis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5023–5026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopelman P. G., Pilkington T. R., White N., Jeffcoate S. L. Abnormal sex steroid secretion and binding in massively obese women. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1980 Apr;12(4):363–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1980.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisker J. A., Hammond G. L., Davidson B. J., Frumar A. M., Takaki N. K., Judd H. L., Siiteri P. K. Serum sex hormone-binding globulin capacity and the percentage of free estradiol in postmenopausal women with and without endometrial carcinoma. A new biochemical basis for the association between obesity and endometrial carcinoma. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Nov 15;138(6):637–642. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisula B. C., Dunn J. F. Measurement of the testosterone binding parameters for both testosterone-estradiol binding globulin and albumin in individual serum samples. Steroids. 1979 Dec;34(7):771–791. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(79)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnell A. E., Northam B. E. New automated dye-binding method for serum albumin determination with bromcresol purple. Clin Chem. 1978 Jan;24(1):80–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed M. J., Cheng R. W., Noel C. T., Dudley H. A., James V. H. Plasma levels of estrone, estrone sulfate, and estradiol and the percentage of unbound estradiol in postmenopausal women with and without breast disease. Cancer Res. 1983 Aug;43(8):3940–3943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


