Abstract
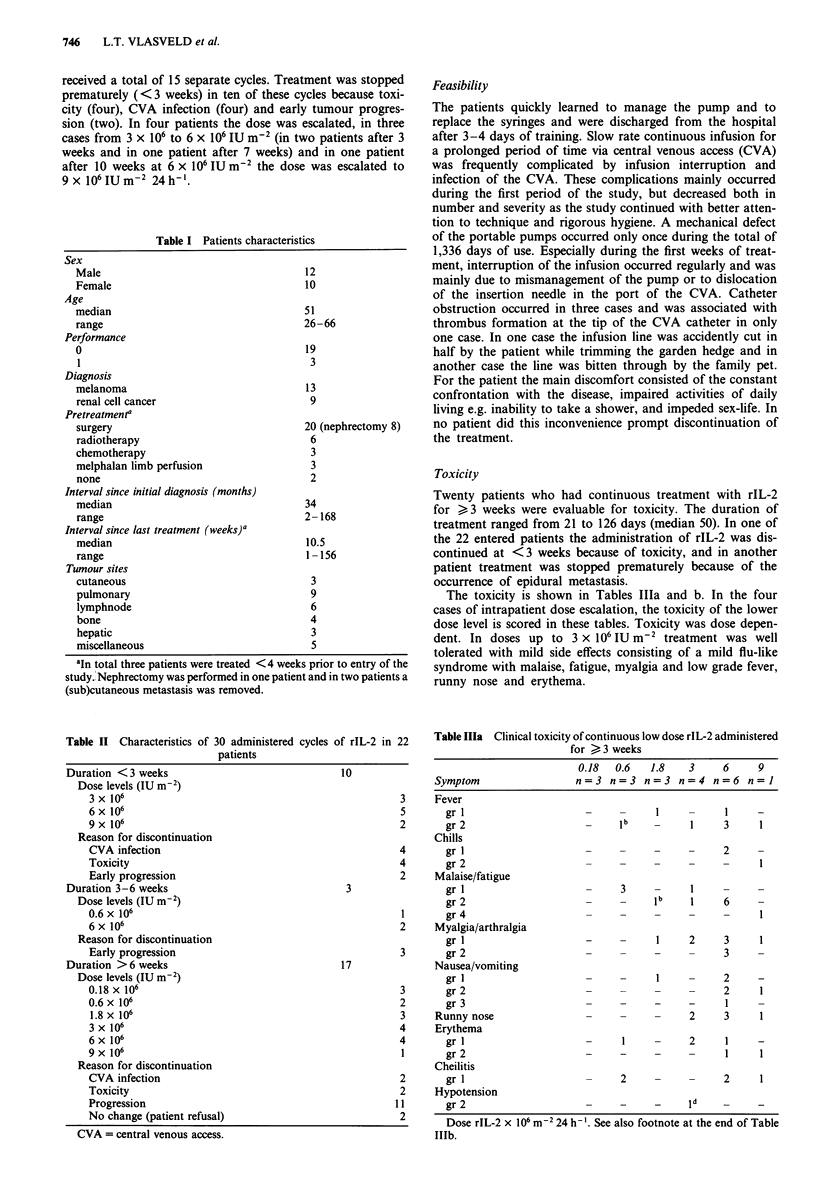
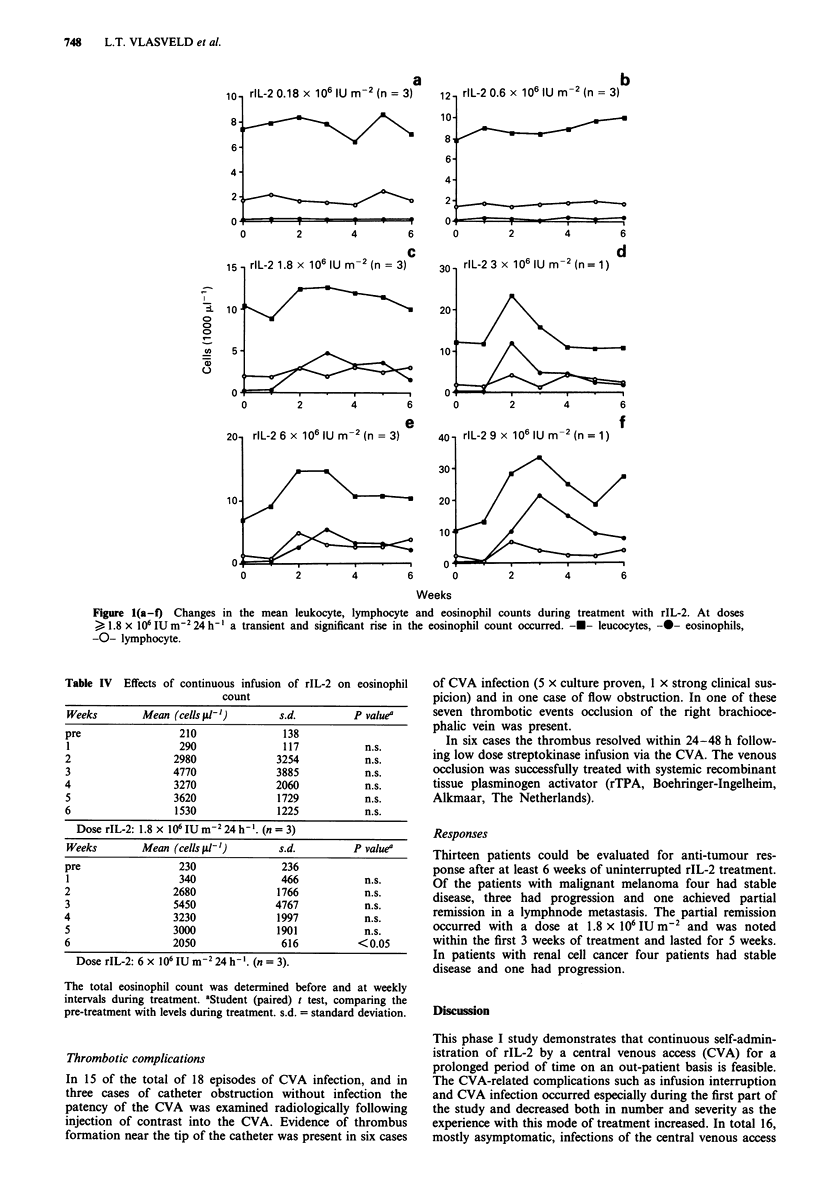
The optimal schedule for recombinant interleukin-2 (rIL-2) administration is unclear. Because the clinical and immunological effects of prolonged continuous exposure to rIL-2 are unknown, we have conducted a phase I study to assess the toxicity and feasibility of continuous low dose infusion of rIL-2 (EuroCetus) using central venous access with a portable infusion device on an out-patient basis. Twenty-two patients entered the study, 13 with melanoma and nine with renal cell cancer, age range 26-66 years (median 51), performance status less than or equal to 1. They were treated with one of the following doses per m2 per 24 h: 0.18 x 10(6) IU, 0.6 x 10(6) IU, 1.8 x 10(6) IU, 3 x 10(6) IU, 6 x 10(6) IU and 9 x 10(6) IU. Toxicity was evaluable in 20 patients receiving greater than or equal to 3 weeks treatment duration or in whom treatment was discontinued prematurely because of toxicity. Constitutional symptoms consisting of fatigue, malaise and fever up to 40 degrees C without significant organ dysfunction occurred with doses greater than or equal to 1.8 x 10(6) IU m-2. The maximum tolerated dose was 6 x 10(6) IU m-2 24 h-1. In all patients toxicity reached a peak at 3 weeks and resolved thereafter despite continued rIL-2 treatment. Peripheral blood eosinophilia (up to 66% of white blood cell count) followed the same pattern. An infection of the central venous access occurred in 55% of the patients but this was mostly asymptomatic. Thirteen patients were treated greater than or equal to 6 weeks and were evaluable for tumour response. A partial remission occurred in a patient with melanoma with a dose of 1.8 x 10(6) IU rIL-2 m-2 24 h-1.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheever M. A., Thompson J. A., Kern D. E., Greenberg P. D. Interleukin 2 (IL 2) administered in vivo: influence of IL 2 route and timing on T cell growth. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3895–3900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. W., Smith J. W., 2nd, Steis R. G., Urba W. J., Crum E., Miller R., McKnight J., Beman J., Stevenson H. C., Creekmore S. Interleukin 2 and lymphokine-activated killer cell therapy: analysis of a bolus interleukin 2 and a continuous infusion interleukin 2 regimen. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 15;50(22):7343–7350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creekmore S. P., Harris J. E., Ellis T. M., Braun D. P., Cohen I. I., Bhoopalam N., Jassak P. F., Cahill M. A., Canzoneri C. L., Fisher R. I. A phase I clinical trial of recombinant interleukin-2 by periodic 24-hour intravenous infusions. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Feb;7(2):276–284. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.2.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing A. J., Thorpe R. The international standard for human interleukin-2. Calibration by international collaborative study. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Nov 10;114(1-2):3–9. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemlo B. T., Palladino M. A., Jr, Jaffe H. S., Espevik T. P., Rayner A. A. Circulating cytokines in patients with metastatic cancer treated with recombinant interleukin 2 and lymphokine-activated killer cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Oct 15;48(20):5864–5867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A. K., Dazzi H., Thatcher N., Moore M. Lack of correlation between peripheral blood lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cell function and clinical response in patients with advanced malignant melanoma receiving recombinant interleukin 2. Int J Cancer. 1989 Mar 15;43(3):410–414. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hank J. A., Robinson R. R., Surfus J., Mueller B. M., Reisfeld R. A., Cheung N. K., Sondel P. M. Augmentation of antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity following in vivo therapy with recombinant interleukin 2. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 1;50(17):5234–5239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Noring R., Mier J. W., Atkins M. B. An acquired chemotactic defect in neutrophils from patients receiving interleukin-2 immunotherapy. N Engl J Med. 1990 Apr 5;322(14):959–965. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199004053221404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. C., Hank J. A., Moore K. H., Storer B., Bechhofer R., Hong R., Sondel P. M. Phase 1 clinical trial of recombinant interleukin-2: a comparison of bolus and continuous intravenous infusion. Cancer Invest. 1989;7(3):213–223. doi: 10.3109/07357908909039840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. C., Sondel P. M. The role of interleukin-2 in cancer therapy. Cancer Surv. 1989;8(4):861–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotze M. T., Custer M. C., Sharrow S. O., Rubin L. A., Nelson D. L., Rosenberg S. A. In vivo administration of purified human interleukin-2 to patients with cancer: development of interleukin-2 receptor positive cells and circulating soluble interleukin-2 receptors following interleukin-2 administration. Cancer Res. 1987 Apr 15;47(8):2188–2195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotze M. T., Matory Y. L., Ettinghausen S. E., Rayner A. A., Sharrow S. O., Seipp C. A., Custer M. C., Rosenberg S. A. In vivo administration of purified human interleukin 2. II. Half life, immunologic effects, and expansion of peripheral lymphoid cells in vivo with recombinant IL 2. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2865–2875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald D., Gordon A. A., Kajitani H., Enokihara H., Barrett A. J. Interleukin-2 treatment-associated eosinophilia is mediated by interleukin-5 production. Br J Haematol. 1990 Oct;76(2):168–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb07867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marumo K., Muraki J., Ueno M., Tachibana M., Deguchi N., Baba S., Jitsukawa S., Hata M., Tazaki H. Immunologic study of human recombinant interleukin-2 (low-dose) in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 1989 Mar;33(3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0090-4295(89)90396-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munn D. H., Cheung N. K. Interleukin-2 enhancement of monoclonal antibody-mediated cellular cytotoxicity against human melanoma. Cancer Res. 1987 Dec 15;47(24 Pt 1):6600–6605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito K., Pellis N. R., Kahan B. D. Effect of continuous administration of interleukin 2 on active specific chemoimmunotherapy with extracted tumor-specific transplantation antigen and cyclophosphamide. Cancer Res. 1988 Jan 1;48(1):101–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez E. A., Scudder S. A., Meyers F. A., Tanaka M. S., Paradise C., Gandara D. R. Weekly 24-hour continuous infusion interleukin-2 for metastatic melanoma and renal cell carcinoma: a phase I study. J Immunother (1991) 1991 Feb;10(1):57–62. doi: 10.1097/00002371-199102000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Chang A. E., Avis F. P., Leitman S., Linehan W. M., Robertson C. N., Lee R. E., Rubin J. T. A progress report on the treatment of 157 patients with advanced cancer using lymphokine-activated killer cells and interleukin-2 or high-dose interleukin-2 alone. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 9;316(15):889–897. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704093161501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Yang J. C., Aebersold P. M., Linehan W. M., Seipp C. A., White D. E. Experience with the use of high-dose interleukin-2 in the treatment of 652 cancer patients. Ann Surg. 1989 Oct;210(4):474–485. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198910000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer H. J., Scheurich P., Rathgeber G., Dose K. Fluorescent photoaffinity labeling of F1 ATPase from Micrococcus luteus with 8-azido-1,N6-etheno-adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):106–111. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90282-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. P., Puri R. K. Interleukin-2 toxicity. J Clin Oncol. 1991 Apr;9(4):694–704. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1991.9.4.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snydman D. R., Sullivan B., Gill M., Gould J. A., Parkinson D. R., Atkins M. B. Nosocomial sepsis associated with interleukin-2. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Jan 15;112(2):102–107. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-2-102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. C., Malkovska V., Morgan S., Galazka A., Aniszewski C., Roy S. E., Shearer R. J., Marsden R. A., Bevan D., Gordon-Smith E. C. The clinical effects of prolonged treatment of patients with advanced cancer with low-dose subcutaneous interleukin-2 [corrected]. Br J Cancer. 1991 Feb;63(2):275–278. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge J. E., Phillips H., Schindler J., Tribble H., Pennington R. Systematic preclinical study on the therapeutic properties of recombinant human interleukin 2 for the treatment of metastatic disease. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 1;47(21):5725–5732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. A., Lee D. J., Cox W. W., Lindgren C. G., Collins C., Neraas K. A., Dennin R. A., Fefer A. Recombinant interleukin 2 toxicity, pharmacokinetics, and immunomodulatory effects in a phase I trial. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 1;47(15):4202–4207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. A., Lee D. J., Lindgren C. G., Benz L. A., Collins C., Levitt D., Fefer A. Influence of dose and duration of infusion of interleukin-2 on toxicity and immunomodulation. J Clin Oncol. 1988 Apr;6(4):669–678. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1988.6.4.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truitt G. A., Brunda M. J., Levitt D., Anderson T. D., Sherman M. I. The therapeutic activity in cancer of IL-2 in combination with other cytokines. Cancer Surv. 1989;8(4):875–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West W. H., Tauer K. W., Yannelli J. R., Marshall G. D., Orr D. W., Thurman G. B., Oldham R. K. Constant-infusion recombinant interleukin-2 in adoptive immunotherapy of advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 9;316(15):898–905. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704093161502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelhake J. L., Gauny S. S. Human recombinant interleukin-2 as an experimental therapeutic. Pharmacol Rev. 1990 Mar;42(1):1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


