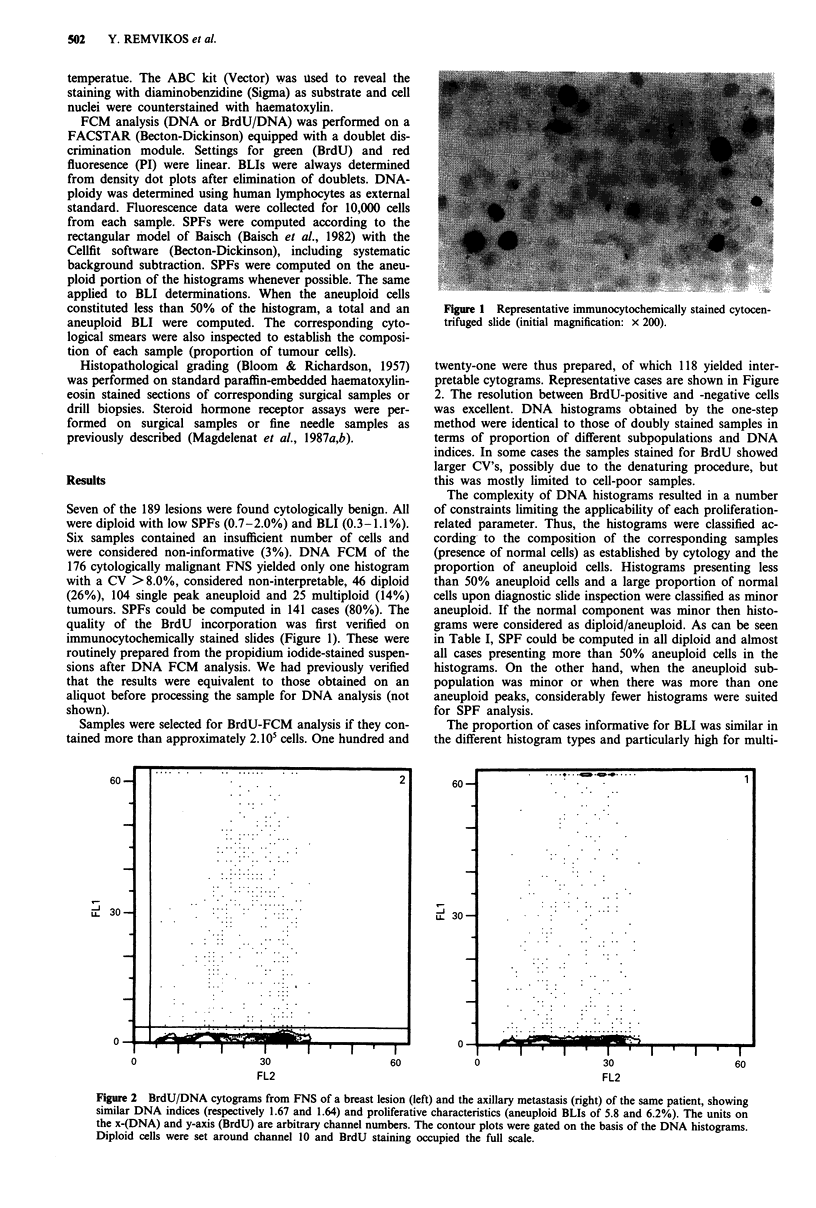
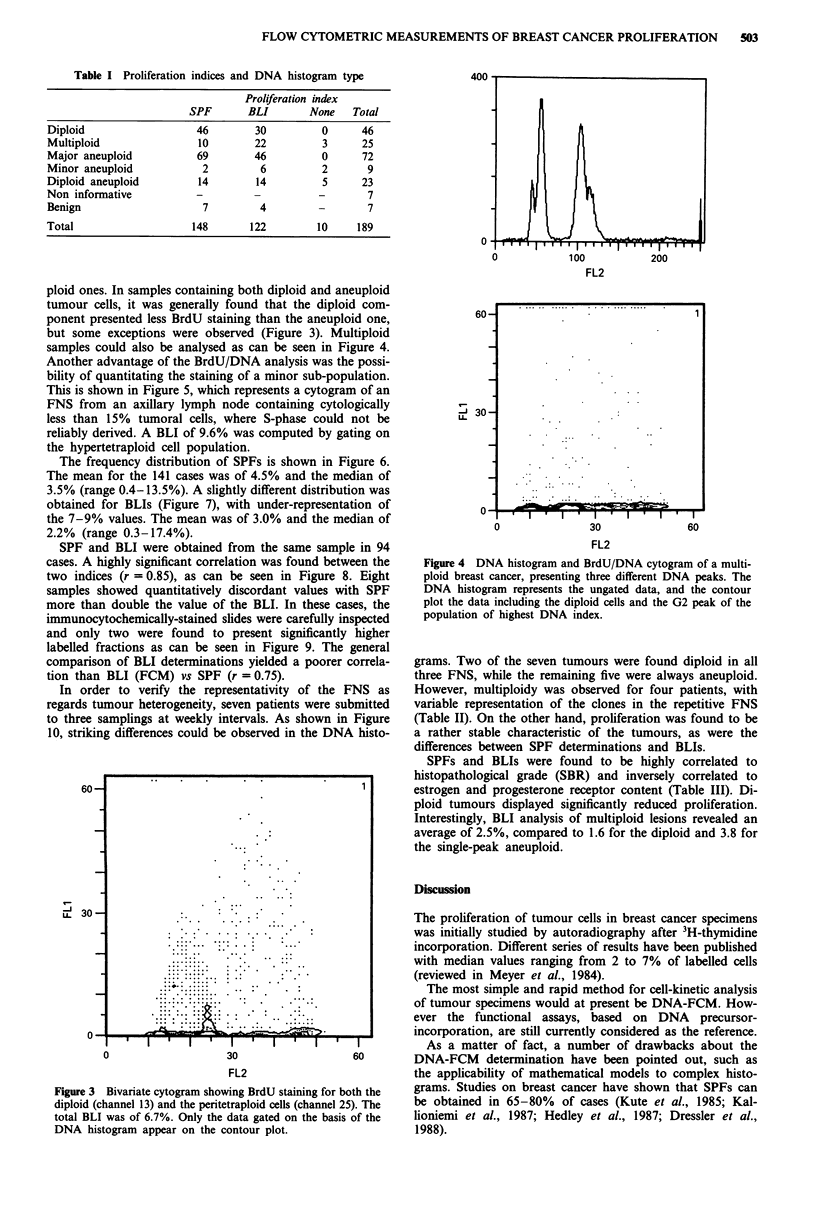
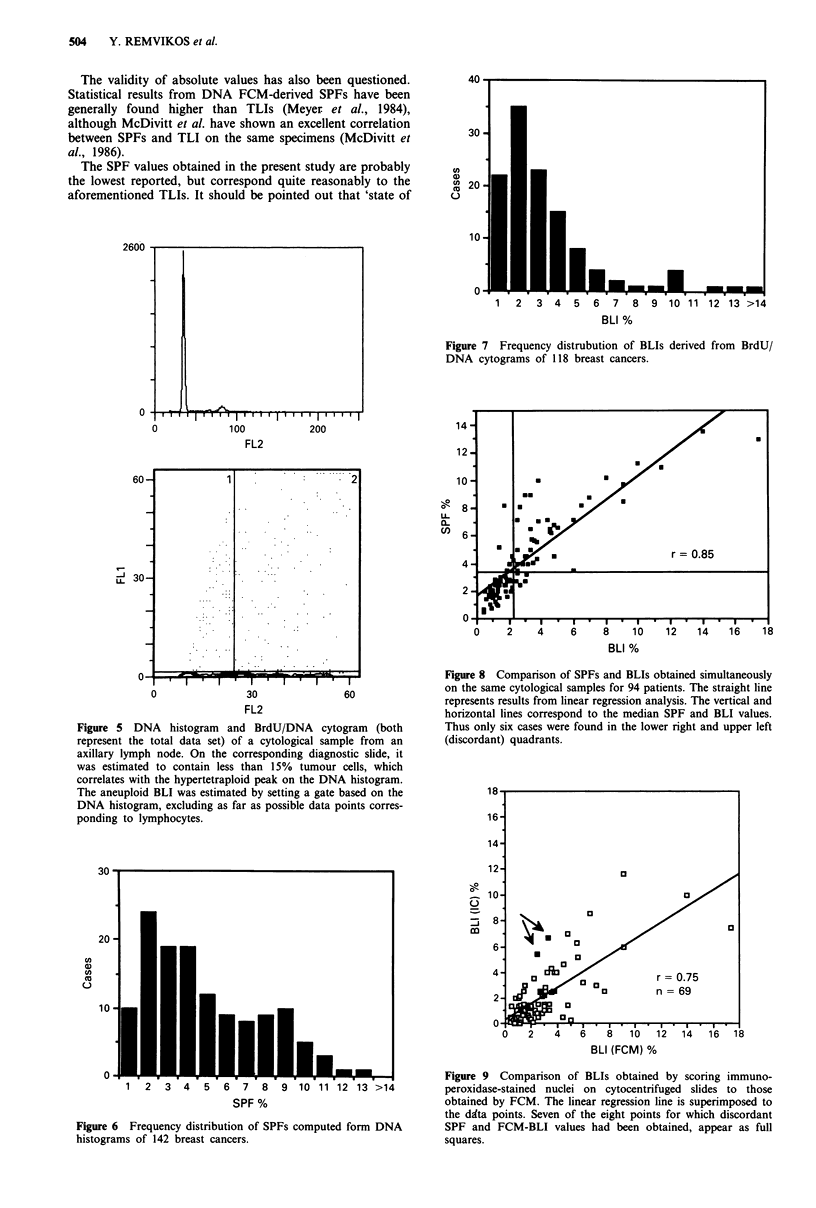
Abstract
Cell kinetics have been shown to be an important predictor of clinical evolution of operated breast cancer. We established a method for the estimation of the proliferative activity of tumour cells obtained by fine needle sampling without aspiration (FNS), using simultaneously S-phase fractions (SPF) measured on DNA histograms and 5-bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) labelling index (BLI) measured by flow cytometry. Biparametric BrdU/DNA flow cytometry could be performed in 122 of 189 (65%) consecutive patients. The mean BLI of the cytologically malignant FNS (118) was of 3.0 and the median of 2.2%. One hundred and forty-eight DNA histograms (78%) were suitable for SPF analysis, of which 141 presented malignant cells, showing a mean of 4.5 and a median of 3.5%, comparable to BLIs. These results were obtained from fluorescence peak area histograms with doublet discrimination and background subtraction allowing the measurements of SPFs as low as 0.4%. An excellent correlation was thus observed between BLIs and SPFs, for the 94 cases for which both results were available (r = 0.85). Infrequent discordances (9%) were noted with SPFs considerably higher than BLIs. Seven patients had three consecutive FNS of their tumour at weekly intervals before treatment. Some variability in the proportions of multiple subpopulations of tumour cells was observed on the DNA histograms. In contrast, proliferation indices (SPF or BLI) were reproducible, suggesting homogeneous growth rates. We conclude that an estimation of the proliferative activity of breast tumours at any stage of the disease is possible routinely by SPF and/or BLI analysis of FNS. At least one quantitative proliferation index could be obtained for 91% of patients.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOOM H. J., RICHARDSON W. W. Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer; a study of 1409 cases of which 359 have been followed for 15 years. Br J Cancer. 1957 Sep;11(3):359–377. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1957.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baisch H., Beck H. P., Christensen I. J., Hartmann N. R., Fried J., Dean P. N., Gray J. W., Jett J. H., Johnston D. A., White R. A. A comparison of mathematical methods for the analysis of DNA histograms obtained by flow cytometry. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1982 May;15(3):235–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1982.tb01043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briffod M., Spyratos F., Tubiana-Hulin M., Pallud C., Mayras C., Filleul A., Rouëssé J. Sequential cytopunctures during preoperative chemotherapy for primary breast carcinoma. Cytomorphologic changes, initial tumor ploidy, and tumor regression. Cancer. 1989 Feb 15;63(4):631–637. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890215)63:4<631::aid-cncr2820630405>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz Z., Traganos F., Melamed M. R. New cell cycle compartments identified by multiparameter flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1980 Sep;1(2):98–108. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990010203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolbeare F., Gratzner H., Pallavicini M. G., Gray J. W. Flow cytometric measurement of total DNA content and incorporated bromodeoxyuridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5573–5577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler L. G., Bartow S. A. DNA flow cytometry in solid tumors: practical aspects and clinical applications. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1989 Feb;6(1):55–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler L. G., Seamer L. C., Owens M. A., Clark G. M., McGuire W. L. DNA flow cytometry and prognostic factors in 1331 frozen breast cancer specimens. Cancer. 1988 Feb 1;61(3):420–427. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880201)61:3<420::aid-cncr2820610303>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haag D., Feichter G., Goerttler K., Kaufmann M. Influence of systematic errors on the evaluation of the S phase portions from DNA distributions of solid tumors as shown for 328 breast carcinomas. Cytometry. 1987 Jul;8(4):377–385. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990080406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D. W., Rugg C. A., Gelber R. D. Association of DNA index and S-phase fraction with prognosis of nodes positive early breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 1;47(17):4729–4735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino T., Nagashima T., Murovic J., Levin E. M., Levin V. A., Rupp S. M. Cell kinetic studies of in situ human brain tumors with bromodeoxyuridine. Cytometry. 1985 Nov;6(6):627–632. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990060619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Héry M., Gioanni J., Lalanne C. M., Namer M., Courdi A. The DNA labelling index: a prognostic factor in node-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1987;9(3):207–211. doi: 10.1007/BF01806381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi O. P., Blanco G., Alavaikko M., Hietanen T., Mattila J., Lauslahti K., Lehtinen M., Koivula T. Improving the prognostic value of DNA flow cytometry in breast cancer by combining DNA index and S-phase fraction. A proposed classification of DNA histograms in breast cancer. Cancer. 1988 Nov 15;62(10):2183–2190. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19881115)62:10<2183::aid-cncr2820621019>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi O. P., Hietanen T., Mattila J., Lehtinen M., Lauslahti K., Koivula T. Aneuploid DNA content and high S-phase fraction of tumour cells are related to poor prognosis in patients with primary breast cancer. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Mar;23(3):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kute T. E., Muss H. B., Hopkins M., Marshall R., Case D., Kammire L. Relationship of flow cytometry results to clinical and steroid receptor status in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1985;6(2):113–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02235742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magdelenat H., Laine-Bidron C., Merle S., Zajdela A. Estrogen and progestin receptor assay in fine needle aspirates of breast cancer: methodological aspects. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Apr;23(4):425–431. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDivitt R. W., Stone K. R., Craig R. B., Palmer J. O., Meyer J. S., Bauer W. C. A proposed classification of breast cancer based on kinetic information: derived from a comparison of risk factors in 168 primary operable breast cancers. Cancer. 1986 Jan 15;57(2):269–276. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19860115)57:2<269::aid-cncr2820570214>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. S. Cell kinetics in selection and stratification of patients for adjuvant therapy of breast carcinoma. NCI Monogr. 1986;(1):25–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. S., McDivitt R. W., Stone K. R., Prey M. U., Bauer W. C. Practical breast carcinoma cell kinetics: review and update. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1984;4(2):79–88. doi: 10.1007/BF01806389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullen P., Miller W. R. Variations associated with the DNA analysis of multiple fine needle aspirates obtained from breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 1989 May;59(5):688–691. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenskjöld B., Löwhagen T., Westerberg H., Zajicek J. 3H-thymidine incorporation into mammary carcinoma cells obtained by needle aspiration before and during endocrine therapy. Acta Cytol. 1976 Mar-Apr;20(2):137–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remvikos Y., Beuzeboc P., Zajdela A., Voillemot N., Magdelénat H., Pouillart P. Correlation of pretreatment proliferative activity of breast cancer with the response to cytotoxic chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Sep 20;81(18):1383–1387. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.18.1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remvikos Y., Magdelénat H., Zajdela A. DNA flow cytometry applied to fine needle sampling of human breast cancer. Cancer. 1988 Apr 15;61(8):1629–1634. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880415)61:8<1629::aid-cncr2820610821>3.0.co;2-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutte B., Reynders M. M., van Assche C. L., Hupperets P. S., Bosman F. T., Blijham G. H. An improved method for the immunocytochemical detection of bromodeoxyuridine labeled nuclei using flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1987 Jul;8(4):372–376. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990080405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestrini R., Costa A., Veneroni S., Del Bino G., Persici P. Comparative analysis of different approaches to investigate cell kinetics. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1988 Mar;21(2):123–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1988.tb00778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestrini R., Daidone M. G., Gasparini G. Cell kinetics as a prognostic marker in node-negative breast cancer. Cancer. 1985 Oct 15;56(8):1982–1987. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19851015)56:8<1982::aid-cncr2820560816>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubiana M., Pejovic M. H., Chavaudra N., Contesso G., Malaise E. P. The long-term prognostic significance of the thymidine labelling index in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1984 Apr 15;33(4):441–445. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910330404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. D., McNally N. J., Dische S., Saunders M. I., Des Rochers C., Lewis A. A., Bennett M. H. Measurement of cell kinetics in human tumours in vivo using bromodeoxyuridine incorporation and flow cytometry. Br J Cancer. 1988 Oct;58(4):423–431. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajdela A., Zillhardt P., Voillemot N. Cytological diagnosis by fine needle sampling without aspiration. Cancer. 1987 Mar 15;59(6):1201–1205. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870315)59:6<1201::aid-cncr2820590628>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]