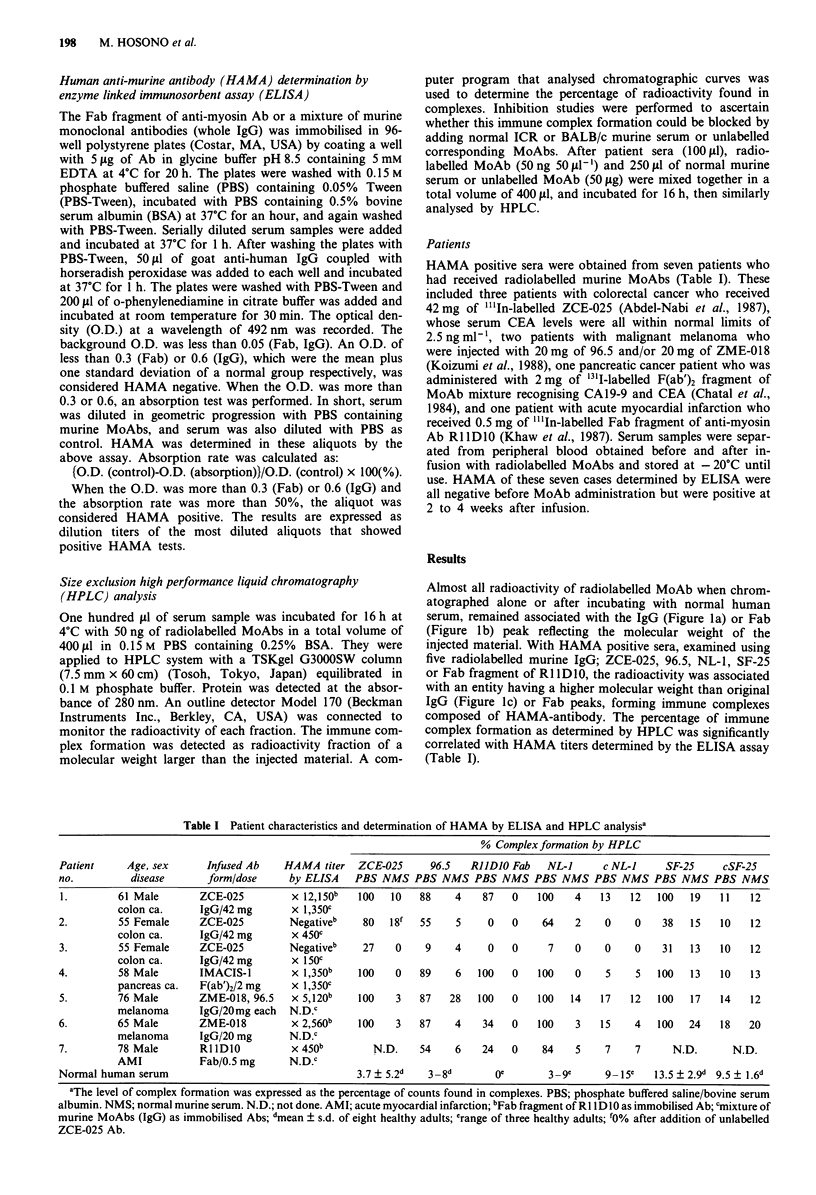
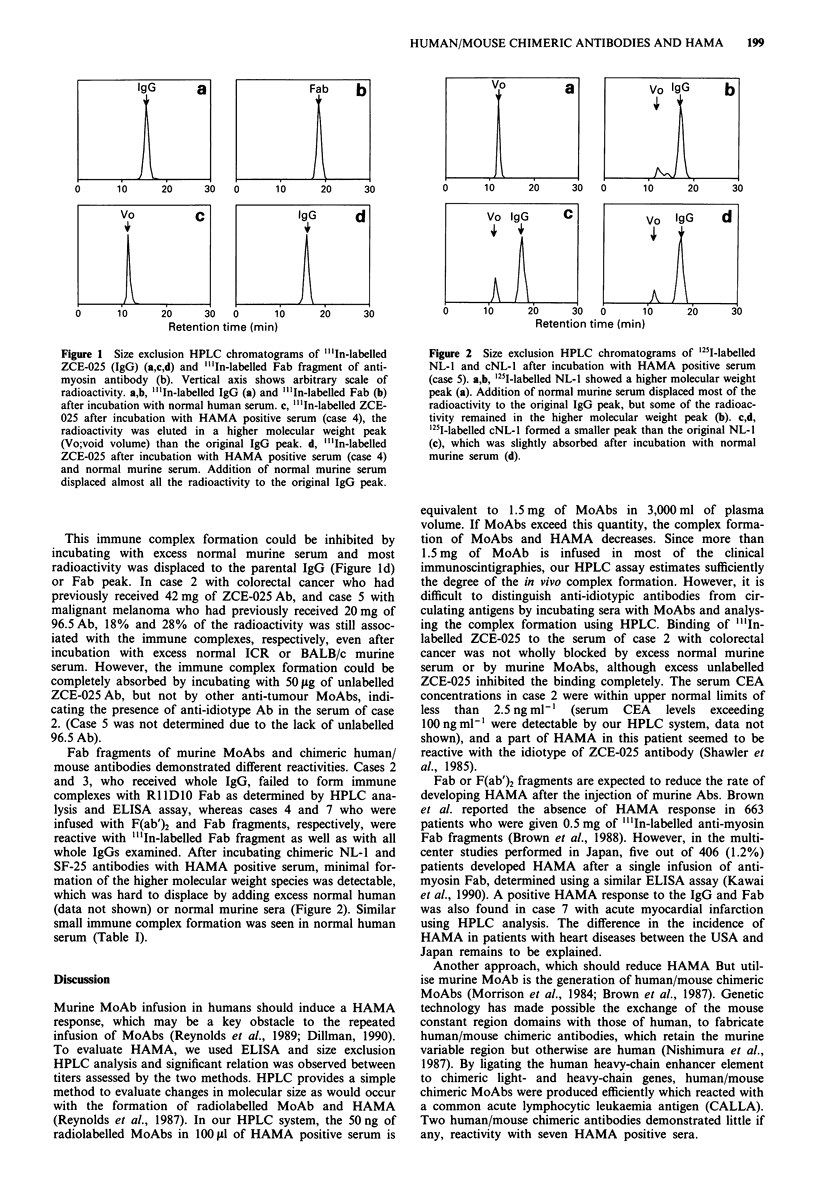
Abstract
Human anti-murine antibody (HAMA) response is a serious problem in the repeated infusion of murine monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs). HAMA positive sera were obtained from seven patients with colorectal cancer, pancreas cancer, malignant melanoma or myocardial infarction who had previously received radiolabelled MoAbs. The nature of HAMA was analysed using size exclusion high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) after incubating with radiolabelled MoAbs including IgG, Fab or human/mouse chimeric Abs. Immune complexes composed of HAMA and MoAbs were formed. The percentage of radioactivity with a high molecular weight was related to HAMA levels determined by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Most radioactivity present in immune complex shifted to the antibody fraction after the addition of normal murine serum. All of seven sera were reactive with all four murine IgGs and this suggests that HAMA in these patients recognised the constant region of MoAbs. In one patient, HAMA was considered to recognise the variable region and to be anti-idiotypic. There was no significant binding with human/mouse chimeric Abs in any HAMA positive serum, although five out of seven patients were reactive with murine MoAb Fab, indicating that HAMA was composed of Abs responsive to the CH1 or CL region of murine IgG. These results suggest that (1) HAMA was composed of Ab responsive to Fc portion and/or CH1 or CL region of murine IgG, and (2) human/mouse chimeric Abs look promising in the repeated infusion of MoAb in HAMA positive patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Nabi H. H., Schwartz A. N., Higano C. S., Wechter D. G., Unger M. W. Colorectal carcinoma: detection with indium-111 anticarcinoembryonic-antigen monoclonal antibody ZCE-025. Radiology. 1987 Sep;164(3):617–621. doi: 10.1148/radiology.164.3.3303117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. A., Davis G. L., Saltzgaber-Muller J., Simon P., Ho M. K., Shaw P. S., Stone B. A., Sands H., Moore G. P. Tumor-specific genetically engineered murine/human chimeric monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res. 1987 Jul 1;47(13):3577–3583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatal J. F., Saccavini J. C., Fumoleau P., Douillard J. Y., Curtet C., Kremer M., Le Mevel B., Koprowski H. Immunoscintigraphy of colon carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 1984 Mar;25(3):307–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colcher D., Milenic D. E., Ferroni P., Carrasquillo J. A., Reynolds J. C., Roselli M., Larson S. M., Schlom J. In vivo fate of monoclonal antibody B72.3 in patients with colorectal cancer. J Nucl Med. 1990 Jul;31(7):1133–1142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtenay-Luck N. S., Epenetos A. A., Moore R., Larche M., Pectasides D., Dhokia B., Ritter M. A. Development of primary and secondary immune responses to mouse monoclonal antibodies used in the diagnosis and therapy of malignant neoplasms. Cancer Res. 1986 Dec;46(12 Pt 1):6489–6493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai C., Matsumori A., Nishimura T., Endo K. [111In-antimyosin Fab scintigraphy in cardiovascular diseases: (multicenter clinical trial)]. Kaku Igaku. 1990 Dec;27(12):1419–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khaw B. A., Mattis J. A., Melincoff G., Strauss H. W., Gold H. K., Haber E. Monoclonal antibody to cardiac myosin: imaging of experimental myocardial infarction. Hybridoma. 1984;3(1):11–23. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1984.3.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khaw B. A., Yasuda T., Gold H. K., Leinbach R. C., Johns J. A., Kanke M., Barlai-Kovach M., Strauss H. W., Haber E. Acute myocardial infarct imaging with indium-111-labeled monoclonal antimyosin Fab. J Nucl Med. 1987 Nov;28(11):1671–1678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi M., Endo K., Watanabe Y., Saga T., Sakahara H., Konishi J., Arano Y., Miyachi Y., Kashihara-Sawami M., Imamura S. Immunoscintigraphy and pharmacokinetics of indium-111-labeled ZME-018 monoclonal antibody in patients with malignant melanoma. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1988 Aug;79(8):973–981. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1988.tb00063.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letarte M., Vera S., Tran R., Addis J. B., Onizuka R. J., Quackenbush E. J., Jongeneel C. V., McInnes R. R. Common acute lymphocytic leukemia antigen is identical to neutral endopeptidase. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1247–1253. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losa G. A., Heumann D., Carrel S., von Fliedner V., Mach J. P. Characterization of membrane vesicles circulating in the serum of patients with common acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Lab Invest. 1986 Nov;55(5):573–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith R. F., LoBuglio A. F., Plott W. E., Orr R. A., Brezovich I. A., Russell C. D., Harvey E. B., Yester M. V., Wagner A. J., Spencer S. A. Pharmacokinetics, immune response, and biodistribution of iodine-131-labeled chimeric mouse/human IgG1,k 17-1A monoclonal antibody. J Nucl Med. 1991 Jun;32(6):1162–1168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monod L., Diserens A. C., Jongeneel C. V., Carrel S., Ronco P., Verroust P., de Tribolet N. Human glioma cell lines expressing the common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (cALLa) have neutral endopeptidase activity. Int J Cancer. 1989 Nov 15;44(5):948–951. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura Y., Yokoyama M., Araki K., Ueda R., Kudo A., Watanabe T. Recombinant human-mouse chimeric monoclonal antibody specific for common acute lymphocytic leukemia antigen. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 15;47(4):999–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. C., Del Vecchio S., Sakahara H., Lora M. E., Carrasquillo J. A., Neumann R. D., Larson S. M. Anti-murine antibody response to mouse monoclonal antibodies: clinical findings and implications. Int J Rad Appl Instrum B. 1989;16(2):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0883-2897(89)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saga T., Endo K., Koizumi M., Kawamura Y., Watanabe Y., Konishi J., Ueda R., Nishimura Y., Yokoyama M., Watanabe T. In vitro and in vivo properties of human/mouse chimeric monoclonal antibody specific for common acute lymphocytic leukemia antigen. J Nucl Med. 1990 Jun;31(6):1077–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakahara H., Endo K., Nakashima T., Koizumi M., Ohta H., Torizuka K., Furukawa T., Ohmomo Y., Yokoyama A., Okada K. Effect of DTPA conjugation on the antigen binding activity and biodistribution of monoclonal antibodies against alpha-fetoprotein. J Nucl Med. 1985 Jul;26(7):750–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakahara H., Reynolds J. C., Carrasquillo J. A., Lora M. E., Maloney P. J., Lotze M. T., Larson S. M., Neumann R. D. In vitro complex formation and biodistribution of mouse antitumor monoclonal antibody in cancer patients. J Nucl Med. 1989 Aug;30(8):1311–1317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroff R. W., Foon K. A., Beatty S. M., Oldham R. K., Morgan A. C., Jr Human anti-murine immunoglobulin responses in patients receiving monoclonal antibody therapy. Cancer Res. 1985 Feb;45(2):879–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shawler D. L., Bartholomew R. M., Smith L. M., Dillman R. O. Human immune response to multiple injections of murine monoclonal IgG. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1530–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Wilson B., Ozturk M., Motté P., Strauss W., Isselbacher K. J., Wands J. R. In vivo localization of human colon adenocarcinoma by monoclonal antibody binding to a highly expressed cell surface antigen. Cancer Res. 1988 Nov 15;48(22):6573–6579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


