Abstract
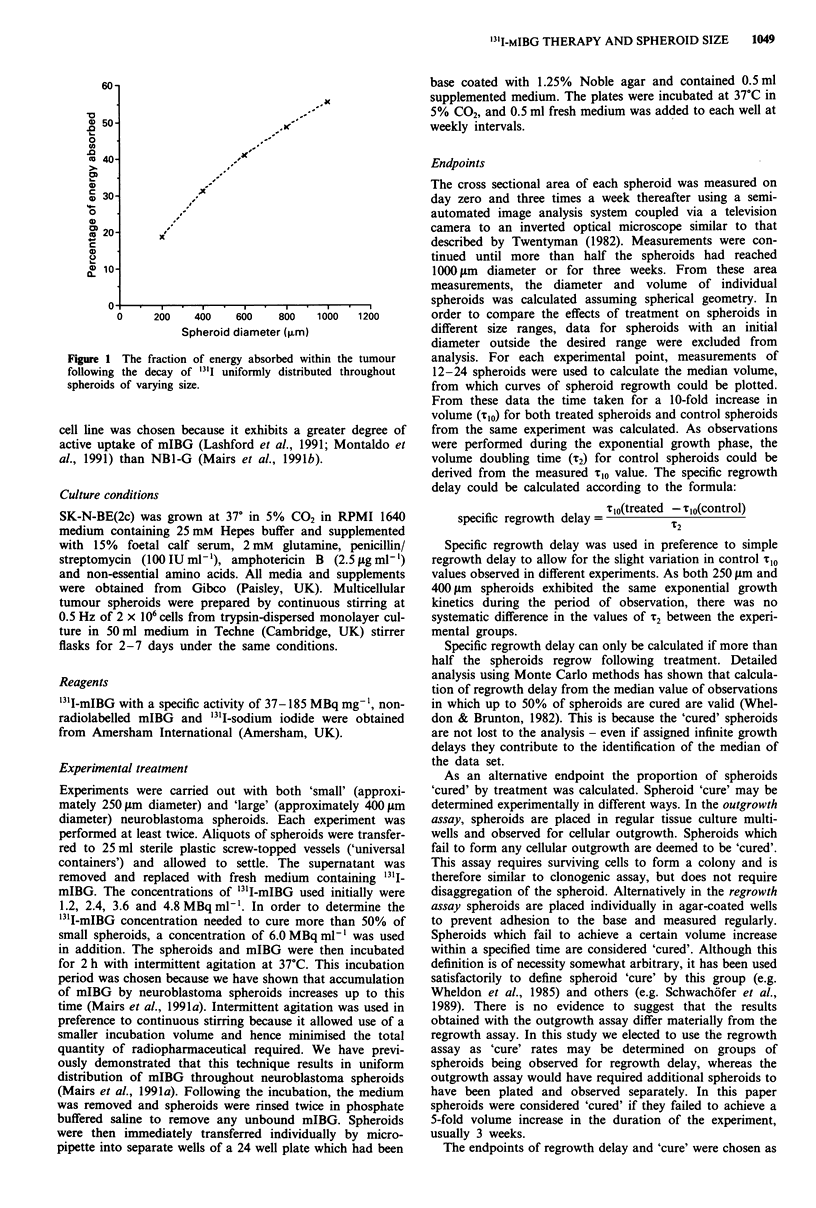
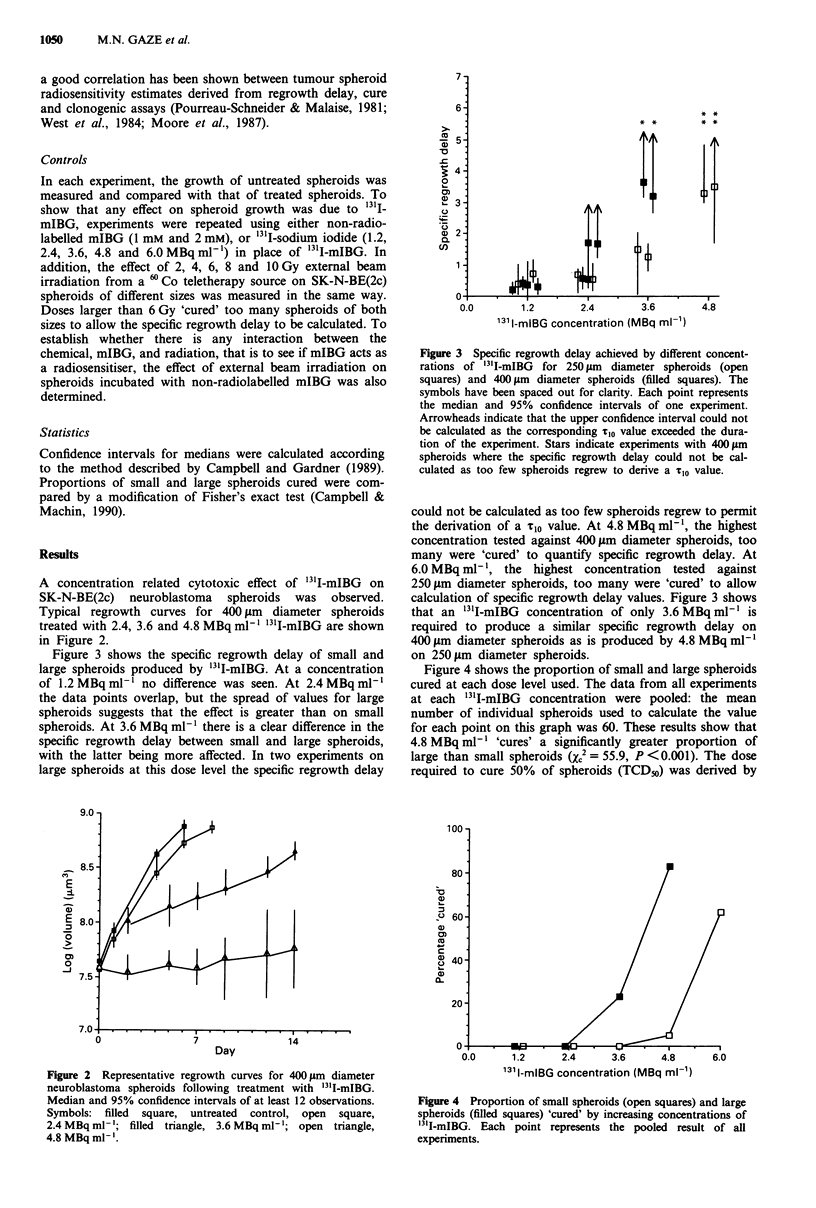
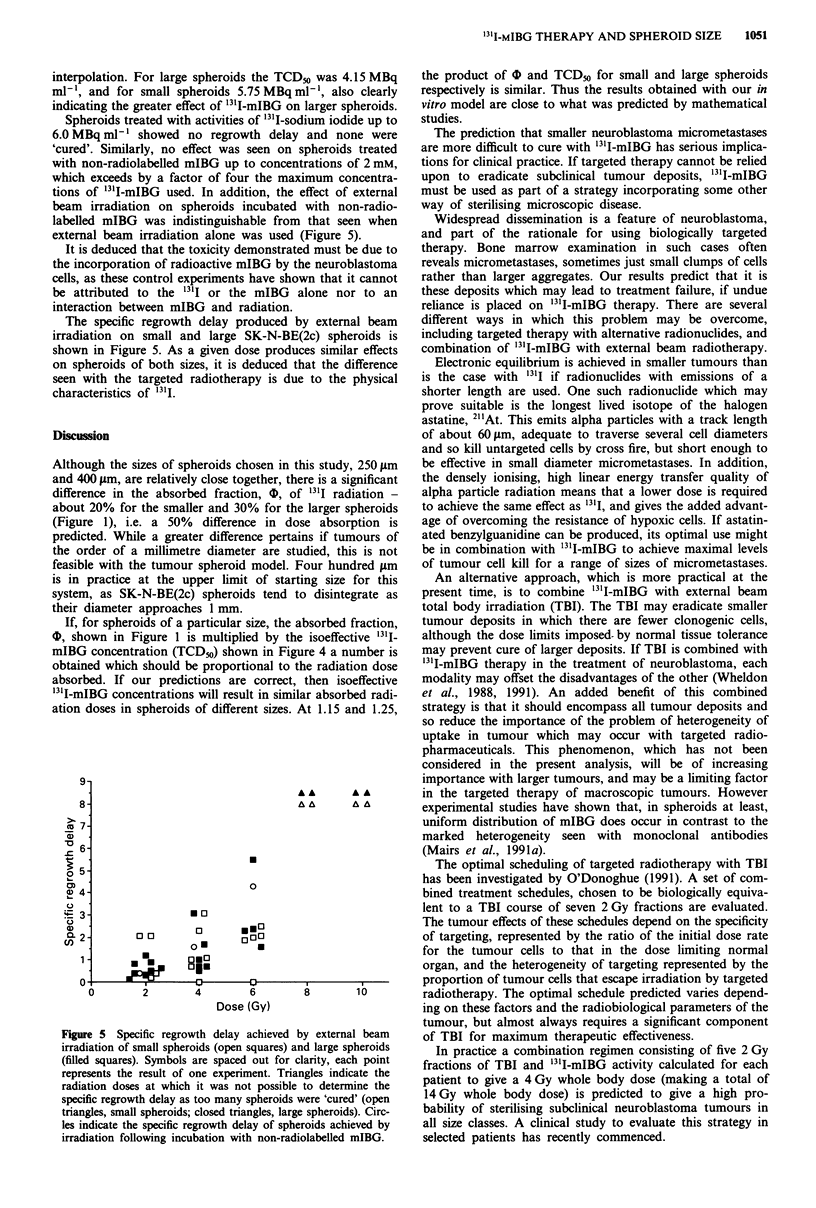
Mathematical models have predicted that targeted radiotherapy of neuroblastoma with metaiodobenzylguanidine (mIBG) is less likely to cure small rather than large micrometastases if 131I is the conjugated radionuclide. This study uses multicellular tumour spheroids as an in vitro model to test the hypothesis that smaller tumours of sub-millimetre dimensions are relatively resistant to 131I-mIBG. Spheroids of the human neuroblastoma cell line SK-N-BE(2c), either 250 microns or 400 microns diameter, were incubated with 131I-mIBG at concentrations of up to 6.0 MBq ml-1. Using both regrowth delay and spheroid 'cure' as endpoints, the greater vulnerability of larger spheroids was confirmed. From this in vitro result we conclude that when used in vivo 131I-mIBG may spare smaller micrometastases. Therefore, either a radionuclide such as 211At which emits a shorter path length radiation should be conjugated to mIBG, or targeted radiotherapy should be combined with a treatment such as total body irradiation, the efficacy of which is not reduced in smaller tumours.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biedler J. L., Roffler-Tarlov S., Schachner M., Freedman L. S. Multiple neurotransmitter synthesis by human neuroblastoma cell lines and clones. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 1):3751–3757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carachi R., Raza T., Robertson D., Wheldon T. W., Wilson L., Livingstone A., van Heyningen V., Spowart G., Middleton P., Gosden J. R. Biological properties of a tumour cell line (NB1-G) derived from human neuroblastoma. Br J Cancer. 1987 Apr;55(4):407–411. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefnagel C. A., Voûte P. A., de Kraker J., Marcuse H. R. Radionuclide diagnosis and therapy of neural crest tumors using iodine-131 metaiodobenzylguanidine. J Nucl Med. 1987 Mar;28(3):308–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humm J. L. Dosimetric aspects of radiolabeled antibodies for tumor therapy. J Nucl Med. 1986 Sep;27(9):1490–1497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lashford L. S., Hancock J. P., Kemshead J. T. Meta-iodobenzylguanidine (mIBG) uptake and storage in the human neuroblastoma cell line SK-N-BE(2C). Int J Cancer. 1991 Jan 2;47(1):105–109. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis I. J., Lashford L. S., Fielding S., Flower M. A., Ackery D., Kemshead J. A phase I/II study of 131I mIBG in chemo-resistant neuroblastoma. The United Kingdom Children's Cancer Study Group (UKCCSG). Prog Clin Biol Res. 1991;366:463–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mairs R. J., Angerson W., Gaze M. N., Murray T., Babich J. W., Reid R., McSharry C. The distribution of alternative agents for targeted radiotherapy within human neuroblastoma spheroids. Br J Cancer. 1991 Mar;63(3):404–409. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mairs R. J., Gaze M. N., Barrett A. The uptake and retention of metaiodobenzyl guanidine by the neuroblastoma cell line NB1-G. Br J Cancer. 1991 Aug;64(2):293–295. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montaldo P. G., Lanciotti M., Casalaro A., Cornaglia-Ferraris P., Ponzoni M. Accumulation of m-iodobenzylguanidine by neuroblastoma cells results from independent uptake and storage mechanisms. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 15;51(16):4342–4346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. V., West C. M., Hendry J. H. Deriving cell survival curves from the overall responses of irradiated tumours: analysis of published data for tumour spheroids. Br J Cancer. 1987 Sep;56(3):309–314. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyes J. S., Babich J. W., Carter R., Meller S. T., Agrawal M., McElwain T. J. Quantitative study of radioiodinated metaiodobenzylguanidine uptake in children with neuroblastoma: correlation with tumor histopathology. J Nucl Med. 1989 Apr;30(4):474–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donoghue J. A. Optimal scheduling of biologically targeted radiotherapy and total body irradiation with bone marrow rescue for the treatment of systemic malignant disease. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1991 Nov;21(6):1587–1594. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(91)90336-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donoghue J. A., Wheldon T. E., Babich J. W., Moyes J. S., Barrett A., Meller S. T. Implications of the uptake of 131I-radiolabelled meta-iodobenzylguanidine (mIBG) for the targeted radiotherapy of neuroblastoma. Br J Radiol. 1991 May;64(761):428–434. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-64-761-428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pourreau-Schneider N., Malaise E. P. Relationship between surviving fractions using the colony methods, the LD50, and the growth delay after irradiation of human melanoma cells grown as multicellular spheroids. Radiat Res. 1981 Feb;85(2):321–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwachöfer J. H., Crooijmans R. P., van Gasteren J. J., Hoogenhout J., Jerusalem C. R., Kal H. B., Theeuwes A. G. Radiosensitivity of different human tumor cells lines grown as multicellular spheroids determined from growth curves and survival data. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989 Nov;17(5):1015–1020. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(89)90149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twentyman P. R. Growth delay in small EMT6 spheroids induced by cytotoxic drugs and its modification by misonidazole pretreatment under hypoxic conditions. Br J Cancer. 1982 Apr;45(4):565–570. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voûte P. A., Hoefnagel C. A., de Kraker J., Valdes Olmos R., Bakker D. J., van de Kleij A. J. Results of treatment with 131 I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (131 I-MIBG) in patients with neuroblastoma. Future prospects of zetotherapy. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1991;366:439–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker K. A., Murray T., Hilditch T. E., Wheldon T. E., Gregor A., Hann I. M. A tumour spheroid model for antibody-targeted therapy of micrometastases. Br J Cancer. 1988 Jul;58(1):13–16. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West C. M., Sandhu R. R., Stratford I. J. The radiation response of V79 and human tumour multicellular spheroids--cell survival and growth delay studies. Br J Cancer. 1984 Aug;50(2):143–151. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheldon T. E., Brunton G. F. Relation of growth delay to cure for experimental tumour systems conforming to Poisson cure statistics. Br J Cancer. 1982 Jan;45(1):1–9. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheldon T. E., Livingstone A., Wilson L., O'Donoghue J., Gregor A. The radiosensitivity of human neuroblastoma cells estimated from regrowth curves of multicellular tumour spheroids. Br J Radiol. 1985 Jul;58(691):661–664. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-58-691-661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheldon T. E., O'Donoghue J. A., Barrett A., Michalowski A. S. The curability of tumours of differing size by targeted radiotherapy using 131I or 90Y. Radiother Oncol. 1991 Jun;21(2):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0167-8140(91)90080-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheldon T. E., O'Donoghue J. A., Hilditch T. E., Barrett A. Strategies for systemic radiotherapy of micrometastases using antibody-targeted 131I. Radiother Oncol. 1988 Feb;11(2):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-8140(88)90249-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland D. M., Wu J., Brown L. E., Mangner T. J., Swanson D. P., Beierwaltes W. H. Radiolabeled adrenergi neuron-blocking agents: adrenomedullary imaging with [131I]iodobenzylguanidine. J Nucl Med. 1980 Apr;21(4):349–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


