Abstract
Rotenone and rotenoid-containing botanicals, important insecticides and fish poisons, are reported to have anticancer activity in rats and mice. The toxic action of rotenone is attributed to inhibition of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity and the purported cancer chemopreventive effect of deguelin analogs has been associated with inhibition of phorbol ester-induced ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) activity. This study defines a possible relationship between these two types of activity important in evaluating the toxicology of rotenoid pesticides and the suitability of the anticancer model. Fractionation of cubé resin (the commercial rotenoid pesticide) establishes that the activity in both assays is due primarily to rotenone (IC50 = 0.8–4 nM), secondarily to deguelin, and in small part to rotenolone and tephrosin. In addition, the potency of 29 rotenoids from cubé insecticide for inhibiting NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase in vitro assayed with bovine heart electron transport particles satisfactorily predicts their potency in vivo in the induced ODC assay using noncytotoxic rotenoid concentrations with cultured MCF-7 human breast cancer cells (r = 0.86). Clearly the molecular features of rotenoids essential for inhibiting NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase are similar to those for blocking ODC induction. This apparent correlation extends to 11 flavonoids and stilbenoids from cubé resin (r = 0.98) and genistein and resveratrol except for lower potency and less selectivity than the rotenoids relative to cytotoxicity. These findings on cubé insecticide constituents and our earlier study comparing rotenone and pyridaben miticide indicate that inhibition of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity lowers the level of induced ODC activity leading to the antiproliferative effect and anticancer action.
Keywords: rotenone
Rotenone (compound 1) and deguelin (compound 11) (Fig. 1) and related compounds (rotenoids) are the active ingredients of botanical insecticides used for at least 150 years to control crop pests (1, 2). They have been used even longer as fish poisons by native tribes to obtain food (1, 2) and more recently in fish management to achieve the desired balance of species (e.g., the 1997 treatment of Lake Davis in California) (3). The acute toxicity of rotenone to insects, fish, and mammals is attributable to inhibition of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity as the primary target (4, 5).
Figure 1.
Rotenone (compound 1) and deguelin (compound 11), the major constituents of cubé (a botanical insecticide/piscicide), and the structurally unrelated pyridaben with similar biological activity. Letters and numbers on the structures designate the ring system (A–E) and position of substituents. Analogs of compound 1 in cubé studied herein are as follows: 12aβ-methoxy (compound 2), 13-homo-13-oxa-6a,12a-dehydro (dioxepin B ring) (compound 3), 12aβ-hydroxy (rotenolone) (compound 4), 12aβ-hydroxy-7′-nor-6′-oxo-4′,5′-dehydro (compound 5), 12aα-hydroxy (compound 6), 12aα-methoxy (compound 7), 6a,12a-dehydro (compound 8), 12aβ-hydroxyrot-2′-enonic acid (compound 9), and 6a,12a-dehydro-6-oxo (compound 10). Analogs of deguelin (compound 11) in cubé investigated herein are as follows: 11-hydroxy (α-toxicarol) (compound 12), 12aβ-methoxy (compound 13), 12aβ-hydroxy (compound 14), 4′,5′-dihydro-5′-hydroxy-7′-chloro (compound 15), 13-homo-13-oxa-6a,12a-dehydro (compound 16), 11,12aβ-dihydroxy (compound 17), 6a,12a-dehydro (compound 18), 13-homo-13-oxa-4′,5′-dihydro-4′,5′-dihydroxy-6a,12a-dehydro (compound 19), 12aα-methoxy (compound 20), 12aα-hydroxy (compound 21), 6a,12a-dehydro-6-oxo (compound 22), 6a,12a-dehydro-11-hydroxy (compound 23), 12aβ,5′,7′-trihydroxy (compound 24), 4′,5′-dihydro-12aβ,5′,7′-trihydroxy (compound 25), trans-4′,5′-dihydro-4′,5′-dihydroxy (compounds 26 and 27, 4′α,5′β, 4′β,5′α), and cis-4′,5′-dihydro-4′,5′-dihydroxy (compounds 28 and 29, 4′α,5′α and 4′β,5′β).
Rotenoids are known not only as toxicants but also as candidate anticancer agents based on three observations: dietary rotenone reduces the background incidence of liver tumors in mice (6) and mammary tumors in rats (7), prevents cell proliferation induced by a peroxisome proliferator in mouse liver (6), and deguelin and three of its derivatives inhibit phorbol ester-induced ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) activity as a measure of cancer chemopreventive potency (8, 9). The commercial rotenone-containing botanicals or extracts thereof are complex mixtures of rotenoids and other natural products that provide the opportunity for action on multiple biochemical targets. One hypothesis is that rotenone and other rotenoids inhibit NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase and induced ODC activities by totally different mechanisms. On this basis there would be a unique structure–activity relationship for the two assays and probably different constituents of the botanical insecticide most active in the two systems. An alternative hypothesis is that the inhibition of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity is coupled to the cancer chemopreventive action (10, 11) and to the lowering of induced ODC activity (12, 13) so the same primary target may be involved.
Our recent study (13) with compounds 1 and 11 led to the proposal that inhibition of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity blocks multiple signal transduction pathways, possibly modulated by reactive oxygen species, that regulate ODC activity. Thus, rotenone is equally effective in blocking ODC induction by phorbol ester, insulin-like growth factor I, and 17β-estradiol (13). This hypothesis is not restricted to rotenoids because pyridaben, despite its totally different type of chemical structure (Fig. 1), is an exceptionally potent inhibitor of both NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase and induced ODC activities (13). A definitive test of this proposal would involve critical examination of the complex mixture of natural materials making up cubé resin, the commercial source of rotenone. Accordingly, this resin was fractionated and the bioactive rotenoids, flavonoids, and stilbenoids were isolated and identified, and their potency was examined as inhibitors of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase and induced ODC activities. The findings are related herein to the two hypotheses above and to the purported anticancer activity of rotenone.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cubé Resin.
The roots of Lonchocarpus utilis and Lonchocarpus urucu (14) from Peru were extracted by the SARPAP Company (Bergarac, France) to obtain cubé resin, designated as “brittle,” used as the commercial insecticide/piscicide (provided by AgrEvo Environmental Health, Montvale, NJ) and the starting material for the present study (15).
Analysis of the Four Principal Rotenoids.
HPLC involved a C18 column (1 × 25 cm, 5 μm) developed with 44% acetonitrile in water (40 min) and then 60% acetonitrile in water (20 min) at a flow rate of 4 ml/min; the eluent was monitored at 310 nm. Quantitation of the major constituents in cubé resin (150 μg) involved comparison of the areas for the four major HPLC peaks with those for authentic standards of compounds 1 and 11 and their 12aβ-hydroxy derivatives, compounds 4 and 14, respectively (Fig. 1).
Isolation and Identification of Rotenoids, Flavonoids, and Stilbenoids.
The cubé resin (650 g) was dissolved in warm methanol (60°C), and the mixture was then cooled to 0°C, leading to precipitation of the major component 1. The precipitate was treated the same way two more times to obtain higher purity compound 1, analyzed by HPLC. After removal of 86% of compound 1 from cubé resin as above, the soluble portion was separated into 20 fractions by chromatography on a silica gel column (200–425 mesh) developed with a gradient of hexane/ethyl acetate/methanol, 95:3.8:1.2 (vol/vol), to ethyl acetate/methanol, 3:1 (vol/vol). The fractions were examined chromatographically for purity by TLC on silica gel with two solvent systems (hexane/ethyl acetate and toluene/acetone in different ratios) and biologically for inhibitory potency in assays of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase and phorbol ester-induced ODC activities (see below). The bioactive fractions (fractions 2–16) were further purified by TLC (precoated silica gel GF plates; 2 mm thick; toluene/acetone, 7:3) followed by HPLC on a silica column (1 × 25 cm, 5 μm) from which material was eluted with hexane/ethyl acetate mixtures at 4 ml/min or on a C18 column as above with gradients of 20–50% acetonitrile in water over a period of 40 min. Twenty-nine rotenoids and 11 flavonoids and stilbenoids (Figs. 1 and 2) were isolated in this way with purities of 98% or greater on the basis of HPLC UV monitoring and proton NMR spectroscopy. Although not detailed herein, 20 of the compounds (compounds 1–4, 6–14, 16–18, 23, and 34–36) were known previously based on proton NMR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and/or UV spectroscopy comparisons (15, 16) with authentic standards or literature data. The 20 additional compounds (compounds 5, 15, 19–22, 24–33, and 38–41) were structurally assigned by proton and fully coupled 13C NMR data and high-resolution fast atom bombardment/mass spectrometry.
Figure 2.
Structures of some flavonoids (compounds 30–36 and 38) and stilbenoids (compounds 39–41) in cubé insecticide and of two related botanicals, genistein (compound 37) and resveratrol (compound 42), with cancer chemopreventive activity. Numbers on the structures designate the position of substituents. Analogs of prenylisolonchocarpin are 5,3′-dihydroxy,5′-methoxy (compound 30), 5,4′-dihydroxy-3′-methoxy (compound 31), 5-hydroxy-3′,4′-dimethoxy (compound 32), and 3′,4′-dimethoxy (compound 33). Lonchocarpusone (compound 34) is present with its 4′,5′-dihydrodiol (compound 38). Analogs of lonchocarpin are 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy (compound 35) and 4-hydroxy (compound 36). Stilbene derivatives with a gem-dimethylpyran moiety are 3,4,5-trimethoxy (compound 39), 4-hydroxy-5′-methoxy (compound 40), and 4-hydroxy-3,5′-dimethoxy (compound 41).
Biology.
The cubé resin constituents were compared with rotenoid 11 (8, 13, 17), the flavonoid genistein (compound 37) (18) and the stilbenoid resveratrol (compound 42) (19) (Figs. 1 and 2) as standards with cancer chemopreventive activity. NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity was determined as NADH oxidation (loss of NADH absorbance at 340 nM) by a standard procedure (20) with bovine heart electron transport particles (ETP) (21). The inhibitor and enzyme (40 μg of ETP protein) in 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) with 0.25 M sucrose (1.0 ml) were incubated for 5 min at 25°C, then NADH (28 μM final concentration) was added, and the absorbance loss was monitored for 3 min. The concentration for 50% inhibition (IC50) value was determined from three experiments with at least five concentrations of test compound in a 1, 3, 10, and 30 nM series.
Inhibition of phorbol ester (phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate)-induced ODC activity was determined by a procedure based on Gerhäuser et al. (8). Human epithelial breast cancer cells (MCF-7, American Type Culture Collection) were cultured in minimum essential medium (S-MEM) supplemented with nonessential amino acids (1×, GIBCO/BRL), 10% fetal bovine serum, 0.05 mM calcium chloride, penicillin (100 units/ml), and streptomycin sulfate (100 μg/ml) at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% carbon dioxide/95% air. Cells in 24-well tissue culture plates at an initial density of 2 × 105 cells per ml per well were incubated for 24 h. Test compounds were added as solutions (2.5 μl) in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), with controls containing DMSO alone, immediately before the addition of phorbol ester (0 or 200 nM, final concentration) (13) in DMSO (2.5 μl). After a 6-h incubation, the medium was carefully removed by aspiration, and the cells were washed twice with PBS (10 mM potassium phosphate/2.7 mM potassium chloride/137 mM sodium chloride, pH 7.4) and stored at −80°C until assayed. ODC activity was determined directly in the 24-well plates as release of 14CO2 from l-[1-14C]ornithine hydrochloride (0.10 μCi, 400 μM; 1 Ci = 37 GBq) in a medium (100 μl) containing 1 mM EDTA, 2.5 mM DTT, 0.1 mM pyridoxal phosphate, 1.4 mM potassium chloride, 68 mM sodium chloride, and 50 mM sodium phosphate (pH 7.2), with incubation for 1 h at 37°C. Radioactivity captured in potassium hydroxide-impregnated filter discs (22) was determined by liquid scintillation counting and protein was measured by using the Folin reagent in microtiter plates. The 14CO2 liberated per mg of protein was compared for cells treated with 0 and 200 nM phorbol ester in the same 24-well tissue culture plate; the induced ODC activity was 9-fold greater on an average than that without phorbol ester. IC50 values were based on three experiments.
Cytotoxicity was assayed as inhibition of MCF-7 cell growth during a 72-h exposure to the test compound (16); MCF-7 cells were cultured as above.
RESULTS
Composition of Cubé Resin.
HPLC analysis of cubé resin on the C18 column revealed only four major peaks (Table 1), each consisting of a single pure compound based on silica HPLC and proton NMR, identified as compounds 1 and 11 as the principal ingredients and compounds 4 and 14 in lesser amount (Table 1). All other components were individually less than 0.5% of the resin based on UV response. Silica gel column chromatography of cubé (with 86% of compound 1 removed) gave 19 minor rotenoids (compounds 2, 3, 5–10, 12, 13, and 15–23) along with compounds 4 and 14 in fractions 6–10 and 6 others (compounds 24–29) in fractions 14–16; the intermediate region (fractions 11–13) consisted of predominantly compounds 1 and 11. Eleven flavonoids and stilbenoids were recovered from fractions 2–5. The chemical identity of these cubé constituents is given in Figs. 1 and 2 with designations 1–10 used for rotenone and its derivatives, 11–29 for deguelin and its derivatives, and 30–36 and 38–41 for the flavonoids and stilbenoids, respectively.
Table 1.
Contribution of the four major rotenoids to the biological activity of cubé resin
| Parameter | Rotenone (1) | Deguelin (11) | Rotenolone (4) | Tephrosin (14) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC retention time, min | 36.2 | 40.5 | 21.2 | 22.8 |
| Content in cubé resin, % | 44.0 ± 0.9 | 22.0 ± 0.2 | 6.7 ± 0.1 | 4.3 ± 0.1 |
| IC50, nM | ||||
| NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase | 4.4 ± 1.4 | 6.9 ± 0.9 | 285 ± 82 | 98 ± 7 |
| Induced ODC | 0.80 ± 0.10 | 11 ± 1 | 91 ± 3 | 147 ± 34 |
| Contribution to total cubé resin activity, % | ||||
| NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase | 75.0 | 23.8 | 0.17 | 0.32 |
| Induced ODC | 92.1 | 3.3 | 0.12 | 0.05 |
HPLC retention time and content in cubé resin are based on mass relative to authentic compounds using UV response from C18 column developed with 44% acetonitrile in water. The corresponding retention times for a silica column developed with hexane/ethyl acetate (84:16 for 35 min, 80:20 for 2 min, and 62:38 for 11 min) are 39.3, 36.2, 41.2, and 41.2 min for compounds 1, 11, 4 and 14, respectively. Data are the mean ± SEM (n = 3). IC50 values for NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase assay with ETP from bovine heart and induced ODC activity were determined with MCF-7 cells. Data are the mean ± SEM (n = 3). Contribution to total cubé resin activity was determined as (potency of resin/potency of rotenoid) × percentage of rotenoid in resin. IC50 values (ng/ml) for the resin were 2.95 and 0.67 for NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase and induced ODC activities, respectively.
Contribution of the Four Major Rotenoids to the Biological Activity of Cubé Resin (Table 1).
The two principal components are similar in potency for inhibition of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity, i.e., IC50 values of 4.4 nM for compound 1 and 6.9 nM for compound 11. However, there is a 14-fold difference in potency for inhibition of phorbol ester-induced ODC activity with IC50 values of 0.80 nM for compound 1 and 11 nM for compound 11. Rotenone (compound 1) contributes 75–92% of the overall cubé resin activity for inhibition of the two enzyme systems and essentially all of the remaining activity is attributable to deguelin (compound 11) with a minor contribution (0.05–0.32%) from compounds 4 and 14 due to their smaller amount and lower potency.
Contribution of Minor Rotenoids, Flavonoids, and Stilbenoids to the Biological Activity of Cubé Resin.
Each of the 25 minor rotenoids and the 11 flavonoids and stilbenoids (each <0.1% of the resin) is of lower activity than compound 1 or 11.
Correlation of Potency for Cubé Rotenoids, Flavonoids, and Stilbenoids as Inhibitors of NADH:Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase and Phorbol Ester-Induced ODC Activities.
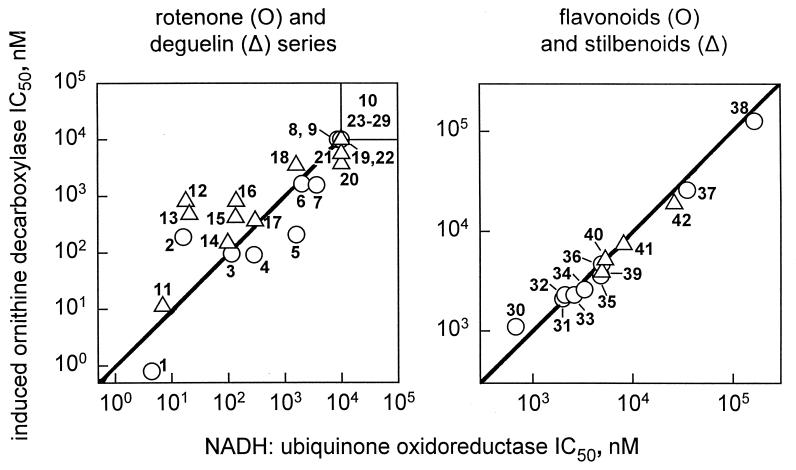
Twenty-nine rotenoids and 11 flavonoids and stilbenoids from cubé, plus genistein (compound 37) and resveratrol (compound 42), were compared for their potency as inhibitors of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity in bovine heart ETP and phorbol ester-induced ODC activity in MCF-7 cells (Fig. 3). Importantly, the potency of the 29 rotenoids in the oxidoreductase assay satisfactorily predicts their potency in the induced ODC system. Clearly, the molecular substituents and conformation essential for inhibiting NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity are the same as those for blocking ODC induction. More specifically, the deguelin type compounds are generally a little less active than the rotenone type, but within each series there is a similar potency order for the derivatives. This relationship extends to the 11 flavonoids and stilbenoids and to the comparison compounds genistein and resveratrol, which fit the same overall correlation line although they are generally less active than the rotenoids.
Figure 3.
Correlation of potency for rotenoids, flavonoids, and stilbenoids from cubé insecticide as inhibitors of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase and phorbol ester-induced ODC activities. Compounds in each series [rotenone (compounds 1–10), deguelin (compounds 11–29), flavonoid (compounds 30–36 and 38), and stilbenoid (compounds 39–41)] are numbered separately in the order of decreasing potency as inhibitors of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase. Eight rotenoids inactive in both assays (IC50 >10,000 nM) are shown in the upper right box. Compounds with discrete values in one assay but >10,000 nM in the other are arbitrarily plotted as 10,000 in the latter case. Rotenoid IC50 values of >10,000 nM are assigned the value of 10,000 in deriving the correlation coefficient. Correlation coefficients are 0.86 (n = 29) for the rotenoids, 0.98 (n = 11) for the flavonoids and stilbenoids from cubé, and 0.98 (n = 13) for the latter compounds plus genistein (compound 37) and resveratrol (compound 42). The flavonoids and stilbenoids are generally less potent than the rotenoids but fall on the same overall correlation line (composite figure not shown).
The major rotenoids (compounds 1, 4, 11, and 14) inhibit phorbol ester-induced ODC activity in MCF-7 cells in the 6-h assay at concentrations from 10- to 700-fold lower than those inhibiting cell growth at 72 h (data not shown). By comparison, the active flavonoids and stilbenes are less selective and their ratio is about 3-fold, under these assay conditions.
DISCUSSION
The four major rotenoids in cubé resin (rotenone, deguelin, rotenolone, and tephrosin in decreasing amounts) are normal constituents in plants of the family Leguminosae used in pesticidal preparations (1, 2). Many rotenoids have been isolated after the isolation of rotenone almost a century ago (23), yet cubé resin has recently provided the 13-homo-13-oxa-6a,12a-dehydro derivatives of rotenone (compound 3) and deguelin (compound 16) (15) and an additional 12 compounds in the present study. One of these is related to rotenone with a modified E ring (compound 5) and the others are related to deguelin with modifications in the 12aα position (compounds 20 and 21), the 6,6a,12a region (compound 22), or the E ring (compounds 15, 19, and 24–29). These compounds include a chlorine-containing rotenoid (compound 15) from a plant extract. Although these rotenoids were isolated from an extract of Lonchocarpus root, some of the minor constituents may not be natural products but instead originate from structural modification of major components during extraction and processing of the cubé resin. All of the flavonoids and stilbenes isolated here contain the gem-dimethylpyran moiety as in the rotenoid deguelin and the biosynthetic link or coexistence of isoflavones, flavanones, chalcones, and stilbenoids with the corresponding rotenoids is commonly noted in Leguminosae (24–27).
The insecticidal and piscicidal activities of rotenoid-bearing plants are usually attributable to rotenone and deguelin (1, 2). This also applies in the present study to the inhibitory effects of cubé resin on NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase and phorbol ester-induced ODC activities. The identified minor components (<0.5% of cubé resin in each case) are all less active than compounds 1 and 11 and, therefore, contribute little to the overall activity. There is some structural specificity between the two assays. Thus, rotenone-type compounds 1 and 4 are more potent than the corresponding deguelin series (compounds 11 and 14) in the induced ODC system whereas compound 14 is more active than compound 4 in the NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase assay. This difference is also reflected in cytotoxicity studies with Hepa-1clc7 cells with a greater potency of compounds 1 than 11 that is not related to specificity at the NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase target but instead to the more rapid piperonyl butoxide-sensitive oxidative detoxification of compound 11 than compound 1 (16).
The potency of the identified cubé resin rotenoids as inhibitors of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity generally correlates with their potency in blocking ODC induction. This involves a comparison of bovine heart oxidoreductase in vitro with MCF-7 ODC induction within 6 h in cultured cells. Apparent discrepancies in this correlation may be due in part to metabolic detoxification in the cell assay for enzyme induction not relevant in the in vitro enzyme assay for intrinsic potency. The observation that essentially the same structure–activity relationships apply to both systems strongly supports two proposals: (i) inhibition of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity is the initial step leading to inhibition of induced ODC activity and (ii) the oxidoreductases of bovine heart and MCF-7 cells are of essentially the same sensitivity to the rotenoids [as shown for compounds 1 and 11 comparing enzymes of bovine heart and Hepa-1clc7 cells (16)]. This relationship is not restricted to rotenoids because, as noted, 11 flavonoids and stilbenoids from cubé resin that are similar to deguelin in the gem-dimethylbenzopyran moiety and a second aromatic substituent still fit the same correlation line, albeit with reduced activity. Lower potency but the same relationship is found for the cancer chemopreventive agents genistein and resveratrol. Strongly supporting these correlations, the highly active miticide and NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase inhibitor pyridaben (5, 28) is also very potent as an inhibitor of induced ODC activity (13).
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase inhibition leads to a block in induced ODC activity in MCF-7 cells, shown earlier for compounds 1 and 11 and pyridaben (13) and expanded herein to a general phenomenon for the other rotenoids and perhaps some of the flavonoids and stilbenoids in cubé resin. Proliferation of normal mammalian cells is dependent on ODC activity, which is highly inducible by growth-promoting stimuli and is overexpressed in various cancer cells (8, 29). On this basis the inhibition of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity and thereby the induced ODC activity may lead to the antiproliferative effect and anticancer action.
Acknowledgments
Discussions with our laboratory colleague J. Craig Rowlands provided the conceptual basis for the biological aspects of this study. We also thank Gary Quistad, Phillip Jefferies, Weiwei Li, and Motohiro Tomizawa of this laboratory for advice and assistance, and Lester Packer and Martyn Smith of the Berkeley campus for useful comments. The project described was supported by Grant P01 ES00049 from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health.
ABBREVIATIONS
- DMSO
dimethyl sulfoxide
- ETP
electron transport particles
- ODC
ornithine decarboxylase
References
- 1.Negherbohn W O. Handbook of Toxicology. III. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1959. pp. 661–673. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fukami H, Nakajima M. In: Naturally Occurring Insecticides. Jacobson M, Crosby D G, editors. New York: Dekker; 1971. pp. 71–97. [Google Scholar]
- 3.California Department of Fish and Game. Lake Davis Northern Pike Eradication Project, January 1997, Final Environmental Impact Report. Sacramento, CA: The Resources Agency; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fukami J-I. In: Insecticide Biochemistry and Physiology. Wilkinson C F, editor. New York: Plenum; 1976. pp. 353–396. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hollingworth R M, Ahammadsahib K I. Rev Pestic Toxicol. 1995;3:277–302. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cunningham M L, Soliman M S, Badr M Z, Matthews H B. Cancer Lett. 1995;95:93–97. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(95)03869-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hansen W H, Davis K J, Fitzhugh O G. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1965;7:535–542. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(65)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gerhäuser C, Mar W, Lee S K, Suh N, Luo Y, Kosmeder J, Luyengi L, Fong H H S, Kinghorn A D, Moriarty R M, et al. Nat Med. 1995;1:260–266. doi: 10.1038/nm0395-260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Luyengi L, Lee I-S, Mar W, Fong H H S, Pezzuto J M, Kinghorn A D. Phytochemistry. 1994;36:1523–1526. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Figueras M J, Gosalvez M. Eur J Cancer. 1973;9:529–531. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(73)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gosálvez M, García-Cañero R, Blanco M, Gurucharri-Lloyd C. Cancer Treat Rep. 1976;60:1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gerhäuser, C., Kosmeder, J. W., II, Lee, S. K., Mar, W., Moriarity, R. M. & Pezzuto, J. M. (1996) Am. Chem. Soc. Abstr. 211 (1–2), MEDI 81.
- 13.Rowlands J C, Casida J E. The Toxicologist. 1997;36:235. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Killip E P, Smith A C. J Washington Acad Sci. 1930;20:74–81. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fang N, Casida J E. J Org Chem. 1997;62:350–353. doi: 10.1021/jo961604h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fang N, Rowlands J C, Casida J E. Chem Res Toxicol. 1997;10:853–858. doi: 10.1021/tx9700432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Udeani G O, Gerhäuser C, Thomas C F, Moon R C, Kosmeder J W, Kinghorn A D, Moriarty R M, Pezzuto J M. Cancer Res. 1997;57:3424–3428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lamartiniere C A, Moore J, Holland M, Barnes S. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1995;208:120–123. doi: 10.3181/00379727-208-43843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jang M, Cai L, Udeani G O, Slowing K V, Thomas C F, Beecher C W W, Fong H H S, Farnsworth N R, Kinghorn A D, Mehta R G, et al. Science. 1997;275:218–220. doi: 10.1126/science.275.5297.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wood E, Latli B, Casida J E. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 1996;54:133–145. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Crane F L, Glenn J L, Green D E. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956;22:475–487. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lichti U, Gottesman M M. J Cell Physiol. 1982;113:433–439. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Geoffroy E. Ann Inst Colon Marseille. 1895;2:1–86. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kaouadji M, Agban A, Mariotte A-M. J Nat Prod. 1986;49:281–285. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Magalhães A F, Azevedo Tozzi A M G, Noronha Sales B H L, Magalhães E G. Phytochemistry. 1996;42:1459–1471. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Crombie L, Dewick P M, Whiting D A. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans. 1973;1:1285–1294. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bhandari P, Crombie L, Daniels P, Holden I, Van Bruggen N, Whiting D A. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans. 1992;1:839–849. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Igarashi H, Sakamoto S. J Pestic Sci. 1994;19:S243–S251. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Law G L, Li R-S, Morris D R. In: Polyamines: Regulation and Molecular Interaction. Casero R A Jr, editor. Austin, TX: Landes; 1995. pp. 5–26. [Google Scholar]