Abstract
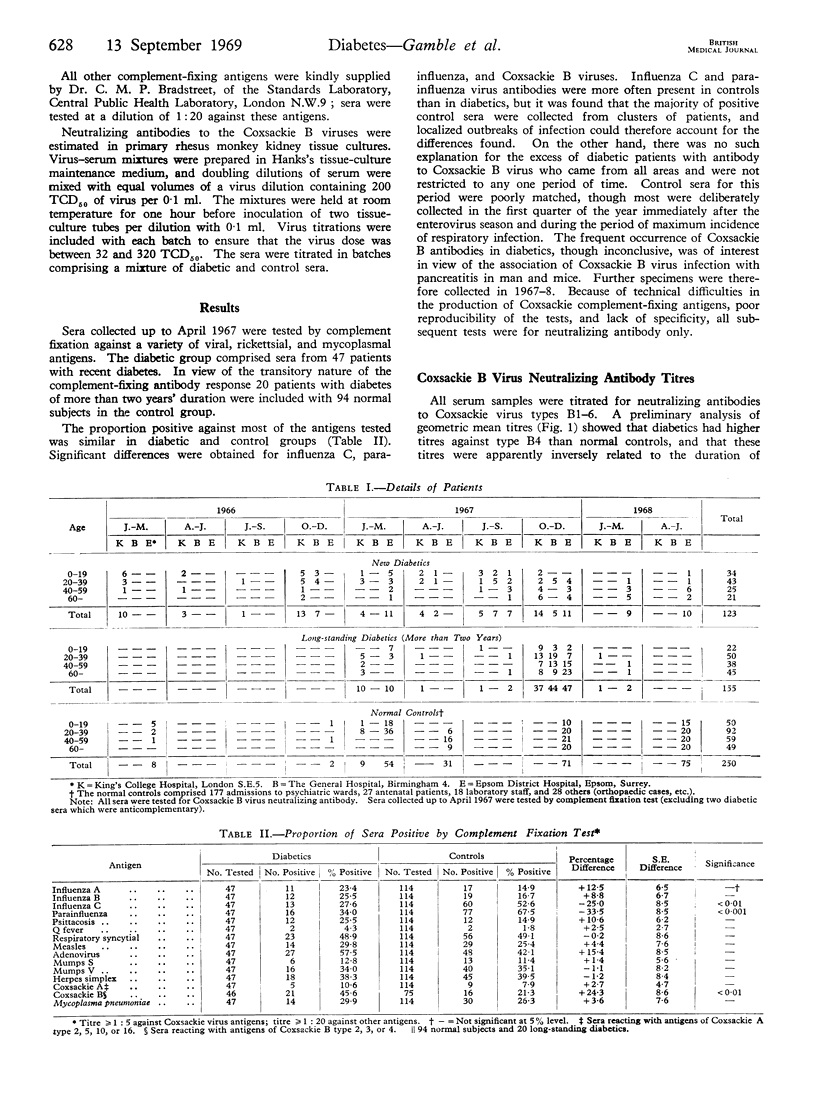
Sera from 123 patients with diabetes mellitus of recent onset, 155 patients with diabetes of more than two years' duration, and 250 normal persons were collected over a period of two and a half years. All sera were tested for neutralizing antibody to Coxsackie virus types B1–6, and a sample was tested for complement-fixing antibody to a number of viral, rickettsial, and mycoplasmal antigens.
In diabetics of recent onset no evidence was found of any excess of antibodies to mumps virus or some common respiratory viruses. Insulin-dependent diabetes within three months of onset were found to have higher antibody titres to Coxsackie B virus, particularly of type B4, than either normal subjects or patients with diabetes of longer duration.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENIRSCHKE K., KIBRICK S. Acute aseptic myocarditis and meningoencephalitis in the newborn child infected with coxsackle virus group B, type 3. N Engl J Med. 1956 Nov 8;255(19):883–889. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195611082551902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADSTREET C. M., TAYLOR C. E. Technique of complementfixation test applicable to the diagnosis of virus diseases. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1962 May;21:96–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craighead J. E., McLane M. F. Diabetes mellitus: induction in mice by encephalomyocarditis virus. Science. 1968 Nov 22;162(3856):913–914. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3856.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FECHNER R. E., SMITH M. G., MIDDLEKAMP J. N. Coxsackie B virus infection of the newborn. Am J Pathol. 1963 Apr;42:493–505. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIBRICK S., BENIRSCHKE K. Severe generalized disease (encephalohepatomyocarditis) occurring in the newborn period and due to infection with Coxsackie virus, group B; evidence of intrauterine infection with this agent. Pediatrics. 1958 Nov;22(5):857–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNETTE E. H., SHINOMOTO T. T., SCHMIDT N. J., MAGOFFIN R. L. Observations on the neutralizing antibody response to group B Coxsackie viruses in patients with central nervous system disease. J Immunol. 1961 Mar;86:257–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY A. M., SIMMUL R. COXSACKIE B4 VIRUS INFECTIONS IN NEW SOUTH WALES DURING 1962. Med J Aust. 1964 Sep 19;2:443–445. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1964.tb117911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPENHEIMER A. M., KUNZ L. J., RICHARDSON S. Passage of Coxsackie virus (Connecticut-5 strain) in adult mice with production of pancreatic disease. J Exp Med. 1951 Jul 1;94(1):45–64. doi: 10.1084/jem.94.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLATT H. A study of the pathological changes produced in young mice by the virus of foot-and-mouth disease. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1956 Jul;72(1):299–312. doi: 10.1002/path.1700720135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANLEY N. F., DORMAN D. C., PONSFORD J. Studies on the pathogenesis of a hitherto undescribed virus (hepato-encephalomyelitis) producing unusual symptoms in suckling mice. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1953 Apr;31(2):147–159. doi: 10.1038/icb.1953.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD E. M., SNIESZKO S. F., YASUTAKE W. T. Infectious pancreatic necrosis in brook trout. AMA Arch Pathol. 1955 Jul;60(1):26–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


