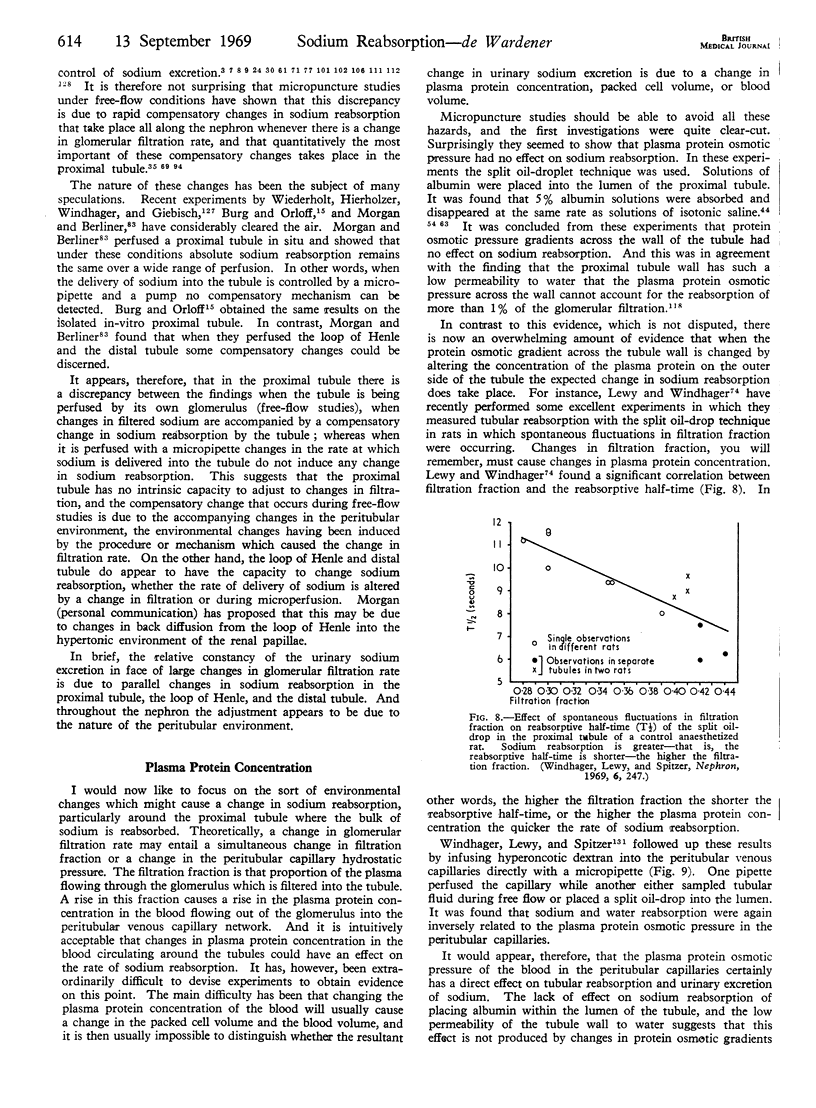
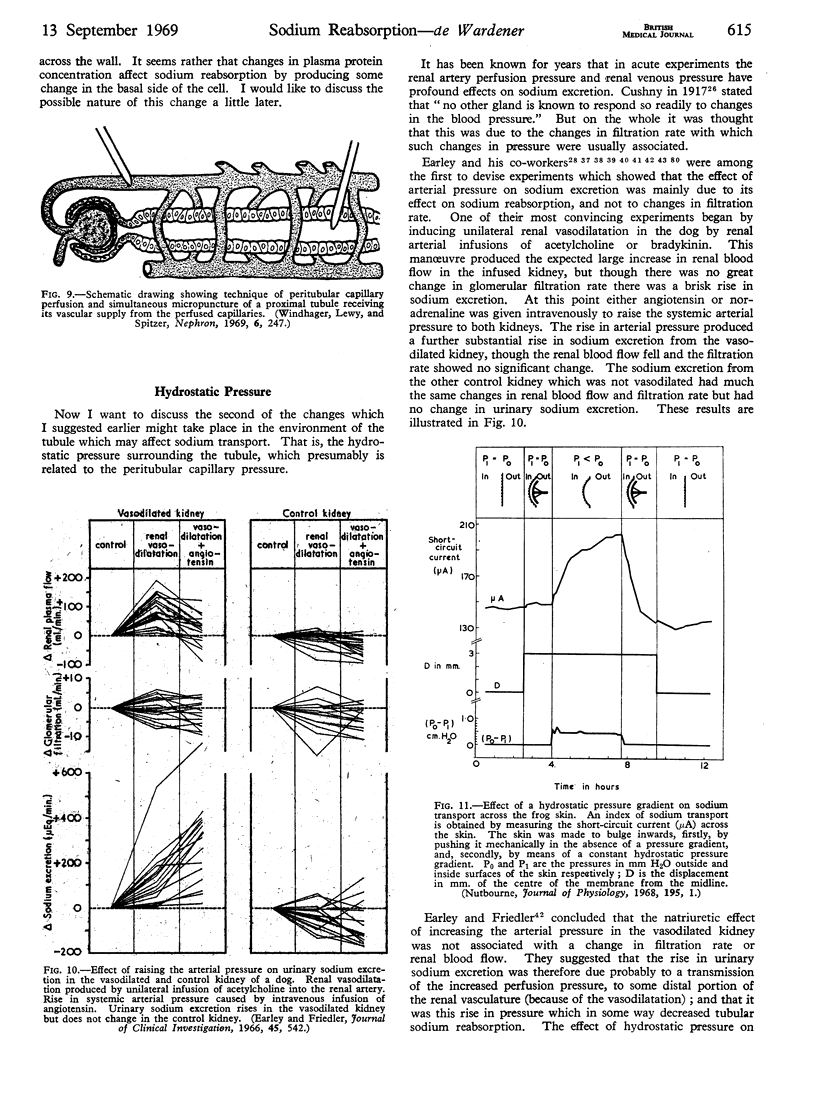
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burg M. B., Orloff J. Control of fluid absorption in the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2016–2024. doi: 10.1172/JCI105888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earley L. E., Friedler R. M. The effects of combined renal vasodilatation and pressor agents on renal hemodynamics and the tubular reabsorption of sodium. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):542–551. doi: 10.1172/JCI105368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisher C. C., Bulger R. E., Trump B. F. Human renal ultrastructure. I. Proximal tubule of healthy individuals. Lab Invest. 1966 Aug;15(8):1357–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windhager E. E., Lewy J. E., Spitzer A. Intrarenal control of proximal tubular reabsorption of sodium and water. Nephron. 1969;6(3):247–259. doi: 10.1159/000179732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




