Abstract
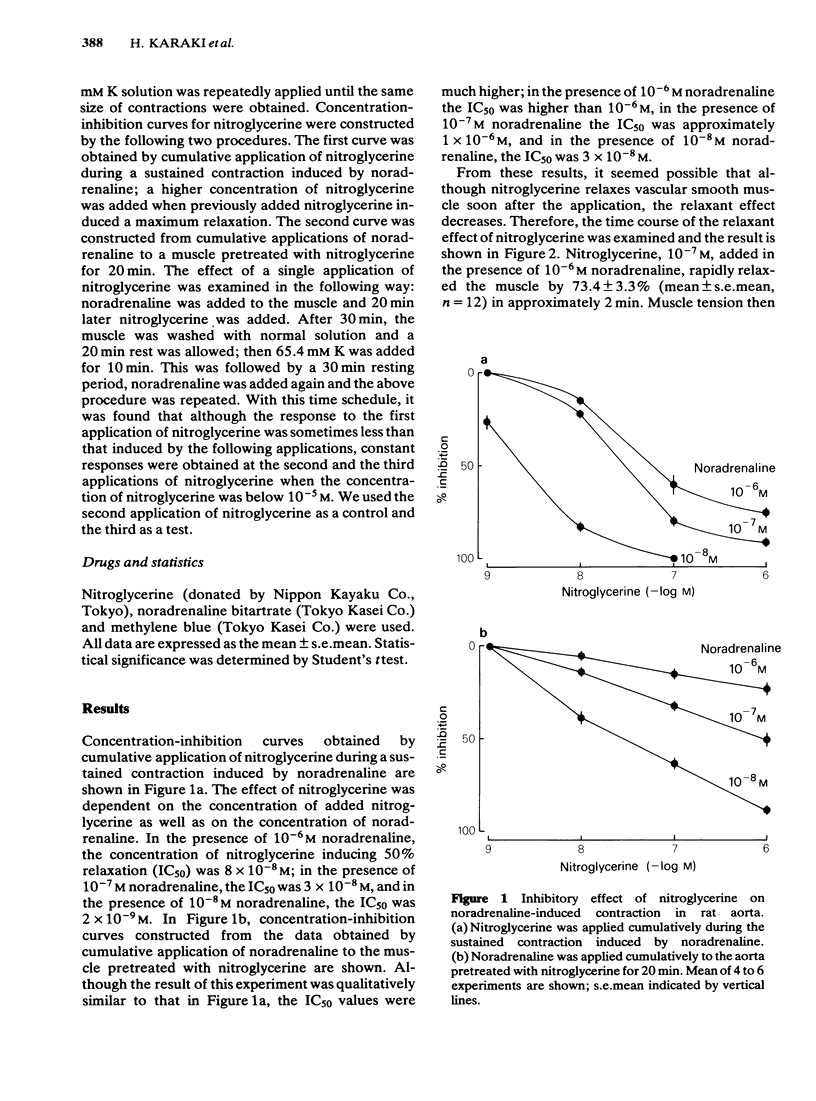
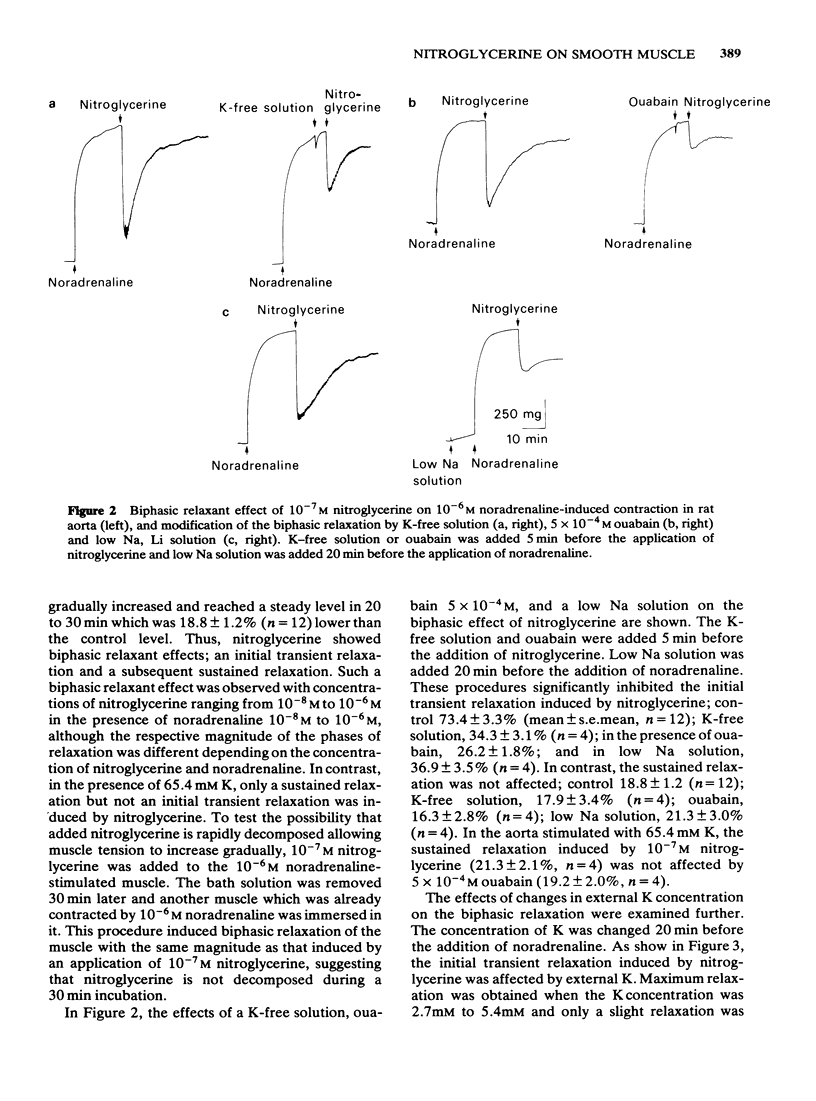
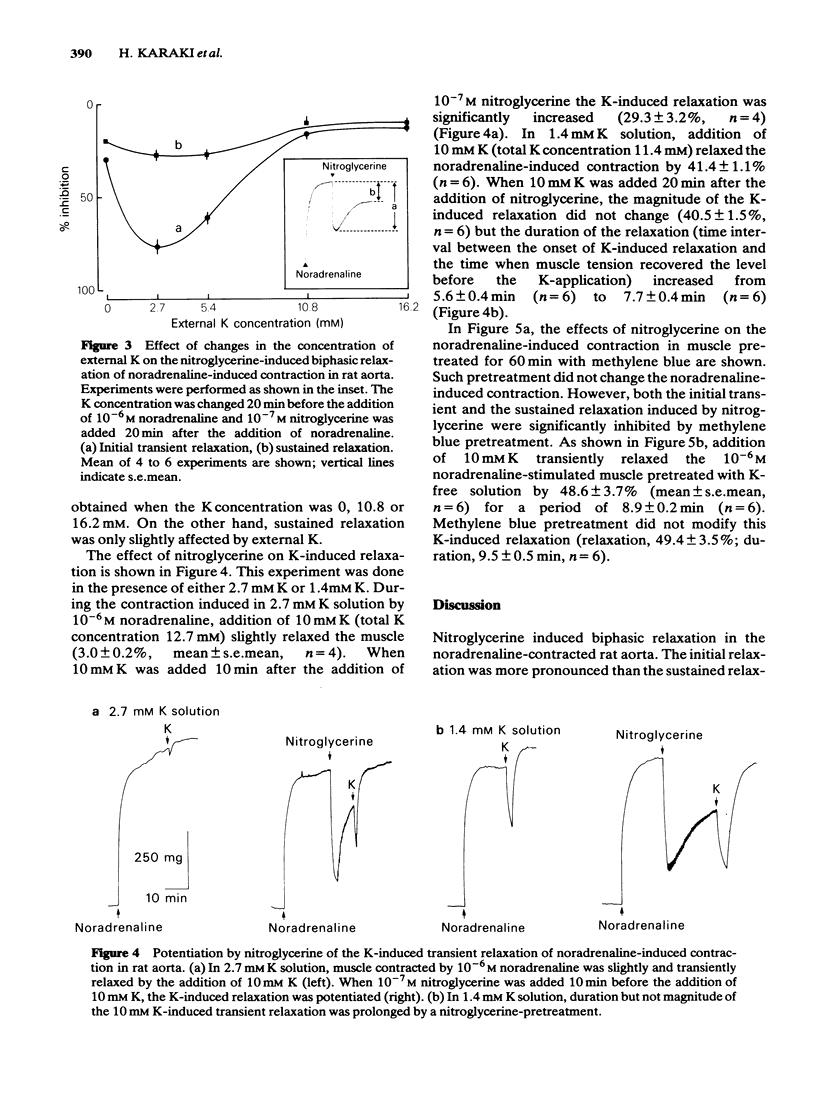
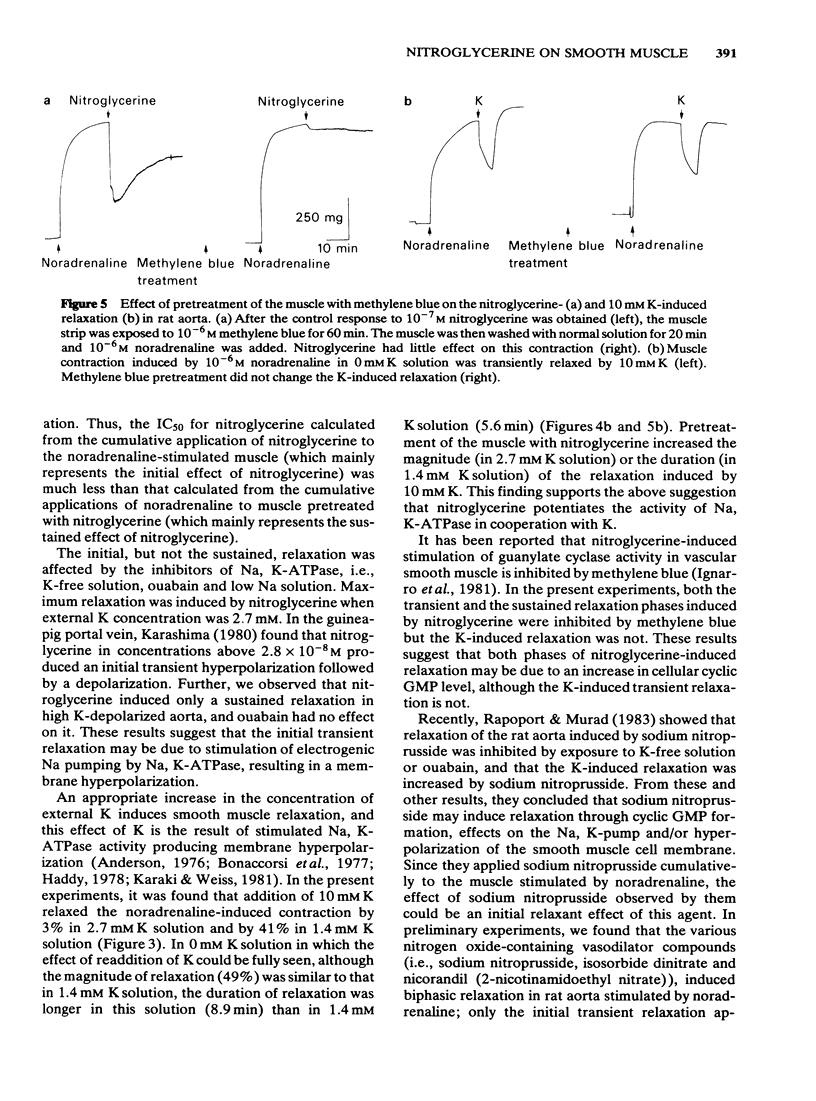
Nitroglycerine induced biphasic relaxation in the rat aorta, previously contracted by noradrenaline; a rapid decrease in tension was followed by a gradual increase reaching a steady level below the control contractile tension. No initial transient relaxation was induced by nitroglycerine in high K-stimulated muscle. The initial transient relaxation, but not the sustained relaxation, was dependent on the concentration of external K; maximum relaxation was observed in the presence of 2.7 mM K solution and only a slight relaxation was observed in 0 mM or 10.8 mM K solution. The initial transient relaxation was also inhibited by ouabain or low Na solution. On an appropriate increase in the concentration of external K, noradrenaline-induced contraction was transiently relaxed. Previous application of nitroglycerine potentiated this K-induced relaxation. Pretreatment of the muscle with methylene blue, an inhibitor of guanylate cyclase, inhibited both the initial transient and the sustained relaxations induced by nitroglycerine, but not the K-induced transient relaxation. It is suggested that the nitroglycerine-induced initial transient relaxation, but not the sustained relaxation, may be due to a stimulation of an electrogenic Na pump. Both relaxation phases may be mediated by cyclic GMP.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. K. Cell potential and the sodium-potassium pump in vascular smooth muscle. Fed Proc. 1976 May 1;35(6):1294–1297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaccorsi A., Hermsmeyer K., Aprigliano O., Smith C. B., Bohr D. F. Mechanism of potassium relaxation of arterial muscle. Blood Vessels. 1977;14(5):261–276. doi: 10.1159/000158133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mey J., Vanhoutte P. M. Effect of removal and substitution of potassium ions on the adrenergic and cholinergic reactivity in canine femoral artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 3;67(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Lippton H., Edwards J. C., Baricos W. H., Hyman A. L., Kadowitz P. J., Gruetter C. A. Mechanism of vascular smooth muscle relaxation by organic nitrates, nitrites, nitroprusside and nitric oxide: evidence for the involvement of S-nitrosothiols as active intermediates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Sep;218(3):739–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Suzuki T., Urakawa N. Tris does not inhibit isolated vascular or intestinal smooth muscle contraction. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):H337–H341. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1981.241.3.H337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Weiss G. B. Effect of transmembrane pH gradient changes on potassium-induced relaxation in vascular smooth muscle. Blood Vessels. 1981;18(1-2):36–44. doi: 10.1159/000158336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karashima T. Actions of nitroglycerine on smooth muscles of the guinea-pig and rat portal veins. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(2):489–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10962.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuki S., Arnold W. P., Murad F. Effects of sodium nitroprusside, nitroglycerin, and sodium azide on levels of cyclic nucleotides and mechanical activity of various tissues. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977 Aug;3(4):239–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler M. F., Webb R. C., Jones A. W., Bohr D. F. In vitro effects of desoxycorticosterone on vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1979 Aug;237(2):H197–H203. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.237.2.H197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockette W. E., Webb R. C., Bohr D. F. Prostaglandins and potassium relaxation in vascular smooth muscle of the rat. The role of Na-K ATPase. Circ Res. 1980 May;46(5):714–720. doi: 10.1161/01.res.46.5.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Effect of ouabain and alterations in potassium concentration on relaxation induced by sodium nitroprusside. Blood Vessels. 1983;20(5):255–264. doi: 10.1159/000158478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Haeusler G., Somlyo A. P. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate: potassium-dependent action on vascular smooth muscle membrane potential. Science. 1970 Jul 31;169(3944):490–491. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3944.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


