Abstract
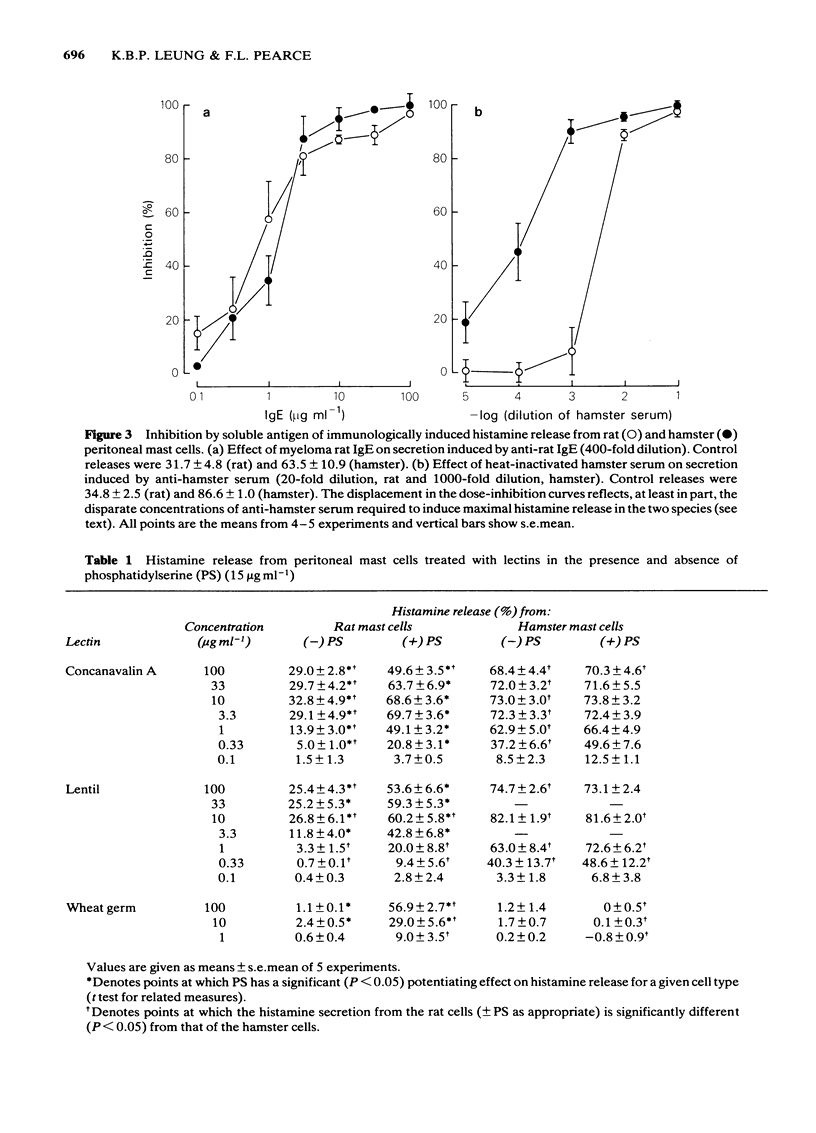
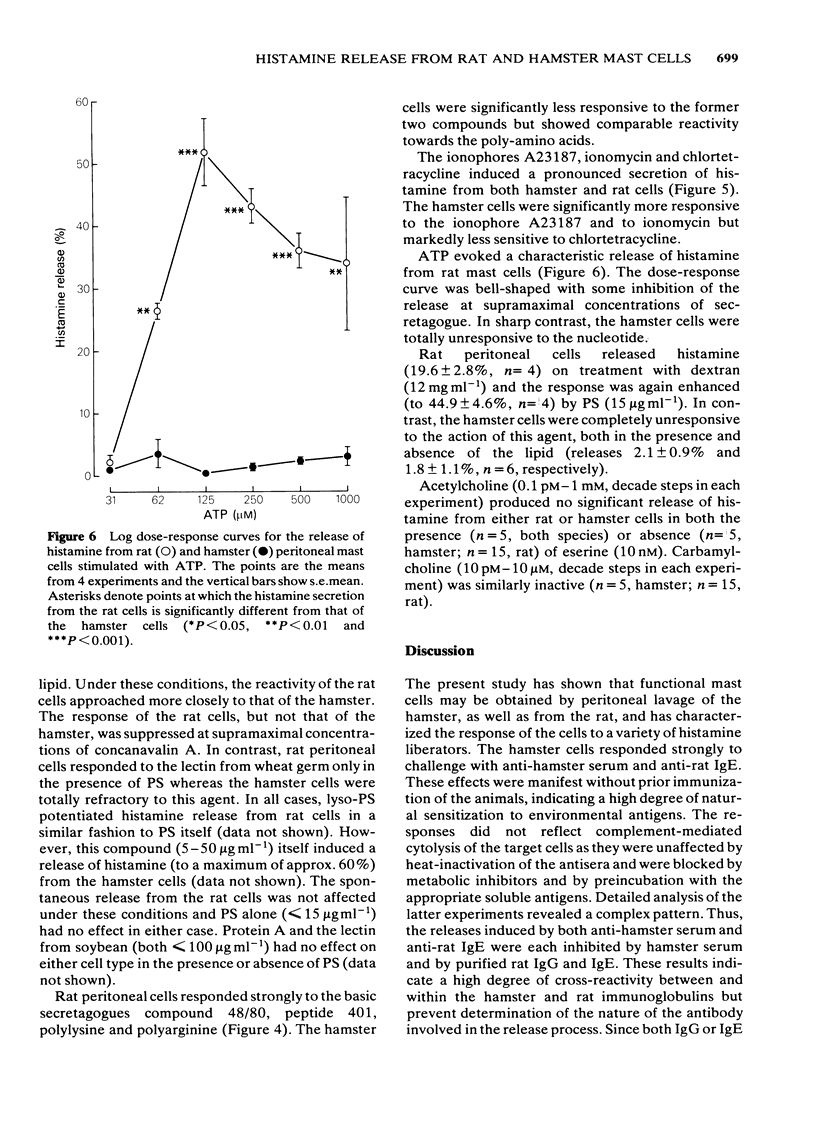
Functional mast cells have been obtained by peritoneal lavage of the rat and hamster. Both cell types released histamine on stimulation with appropriate dilutions of anti-rat IgE and anti-hamster serum. The maximum response evoked by each reagent was significantly greater for the hamster cells. The release was non-cytotoxic and was in each case blocked by the corresponding soluble antigen. The rat and hamster cells responded to concanavalin A and the lectin from lentil. Phosphatidylserine (PS) potentiated the release only from the rat cells. In the absence of the lipid, the hamster cells were more reactive. The lectin from wheat germ, in the presence of PS, evoked histamine secretion only from the rat cells. Both populations were refractory to the lectin from soybean and to protein A. Rat peritoneal cells were more responsive to the basic secretagogues compound 48/80 and peptide 401 (the MCD-peptide from bee venom). These differences were less marked in the case of polylysine and polyarginine. The two cell populations responded to the calcium ionophores A23187, ionomycin and chlortetracycline. The hamster cells were significantly more sensitive to the former two liberators but markedly less reactive to chlortetracycline. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) and dextran were potent histamine liberators from the rat cells but were totally ineffective against the hamster. Acetylcholine and carbamylcholine had no effect on either cell type. These results are discussed in terms of the functional heterogeneity of mast cells from different sources.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson G., Ennis M., Pearce F. L. The effect of alkaline earth cations on the release of histamine from rat peritoneal mast cells treated with compound 48/80 and peptide 401. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Mar;65(3):395–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb07843.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. The ATP4- receptor of rat mast cells. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):789–798. doi: 10.1042/bj1880789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis M. Histamine release from human pulmonary mast cells. Agents Actions. 1982 Apr;12(1-2):60–63. doi: 10.1007/BF01965108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis M., Pearce F. L. Differential reactivity of isolated mast cells from the rat and guinea pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Sep 5;66(4):339–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis M., Truneh A., Pearce F. L. Lectin-induced histamine secretion from isolated rat and guinea pig mast cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Aug 1;30(15):2179–2181. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantozzi R., Masini E., Blandina P., Mannaioni P. F., Bani-Sacchi T. Release of histamine from rat mast cells by acetylcholine. Nature. 1978 Jun 8;273(5662):473–474. doi: 10.1038/273473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman J. C., Lichtenstein L. M. Induction of histamine secretion by polycations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 22;629(3):587–603. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman J. C. The pharmacological control of immediate hypersensitivity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:63–81. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.000431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goth A., Adams H. R., Knoohuizen M. Phosphatidylserine: selective enhancer of histamine release. Science. 1971 Sep 10;173(4001):1034–1035. doi: 10.1126/science.173.4001.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook W. A., Dougherty S. F., Oppenheim J. J. Release of histamine from hamster mast cells by concanavalin A and phytohemagglutinin. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):903–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.903-908.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. Interrelations between different types of cells. II. Histamine-release from the mast cells of various species by cationic polypeptides of polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomes and other cationic compounds. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;34(2):139–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOTA I., VUGMAN I. Effects of anaphylactic shock and compound 48/80 on the mast cells of the guinea pig lung. Nature. 1956 Mar 3;177(4505):427–429. doi: 10.1038/177427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magro A. M. Histamine release from fawn-hooded rat mast cells is not potentiated by phosphatidylserine. Immunology. 1981 Sep;44(1):1–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongar J. L., Svec P. The effect of phospholipids on anaphylactic histamine release. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Dec;46(4):741–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb06899.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodley I., Mongar J. L., Foreman J. C. Histamine release induced by dextran: the nature of the dextran receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Sep 10;83(1-2):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodley I., Mongar J. L. IgG receptors on the mast cells. Agents Actions. 1981 Apr;11(1-2):77–83. doi: 10.1007/BF01991464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARRATT J. R., WEST G. B. Histamine liberation in the hamster. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1957 Dec 1;113(1-2):209–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce F. L., Barrett K. E., White J. R. Histamine secretion from mast cells treated with chlortetracycline (aureomycin): a novel calcium ionophore. Agents Actions. 1983 Apr;13(2-3):117–122. doi: 10.1007/BF01967312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce F. L., Befus A. D., Gauldie J., Bienenstock J. Mucosal mast cells. II. Effects of anti-allergic compounds on histamine secretion by isolated intestinal mast cells. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2481–2486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce F. L. Calcium and histamine secretion from mast cells. Prog Med Chem. 1982;19:59–109. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70328-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce F. L. Functional heterogeneity of mast cells from different species and tissues. Klin Wochenschr. 1982 Sep 1;60(17):954–957. doi: 10.1007/BF01716954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmutzler W., Poblete-Freundt G., Rauch K., Schoenfeld W. Response to immunological or cholinergic stimulation of isolated mast cells from man, guinea pig and rat. Monogr Allergy. 1979;14:288–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian R. P., Hazard K. A. Mechanisms of mouse mast cell activation and inactivation for IgE-mediated histamine release. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1719–1725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. R., Pearce F. L. Characterization of chlortetracycline (aureomycin) as a calcium ionophore. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6309–6312. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


