Abstract
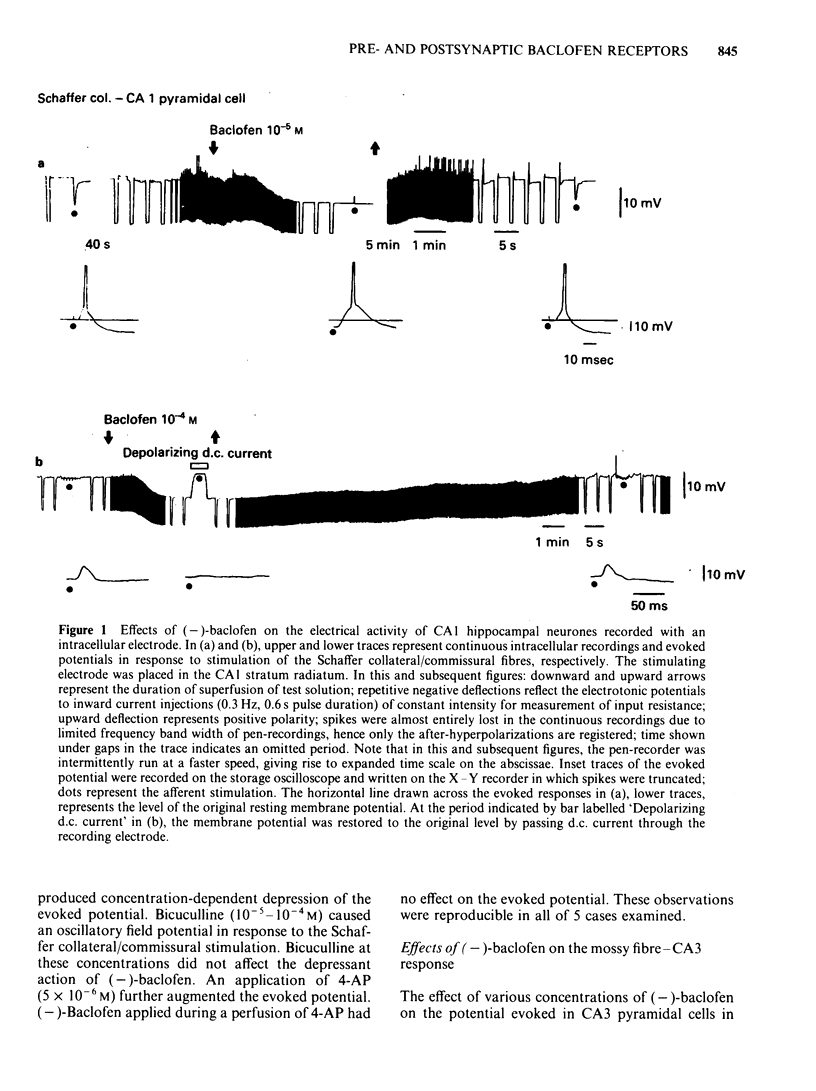
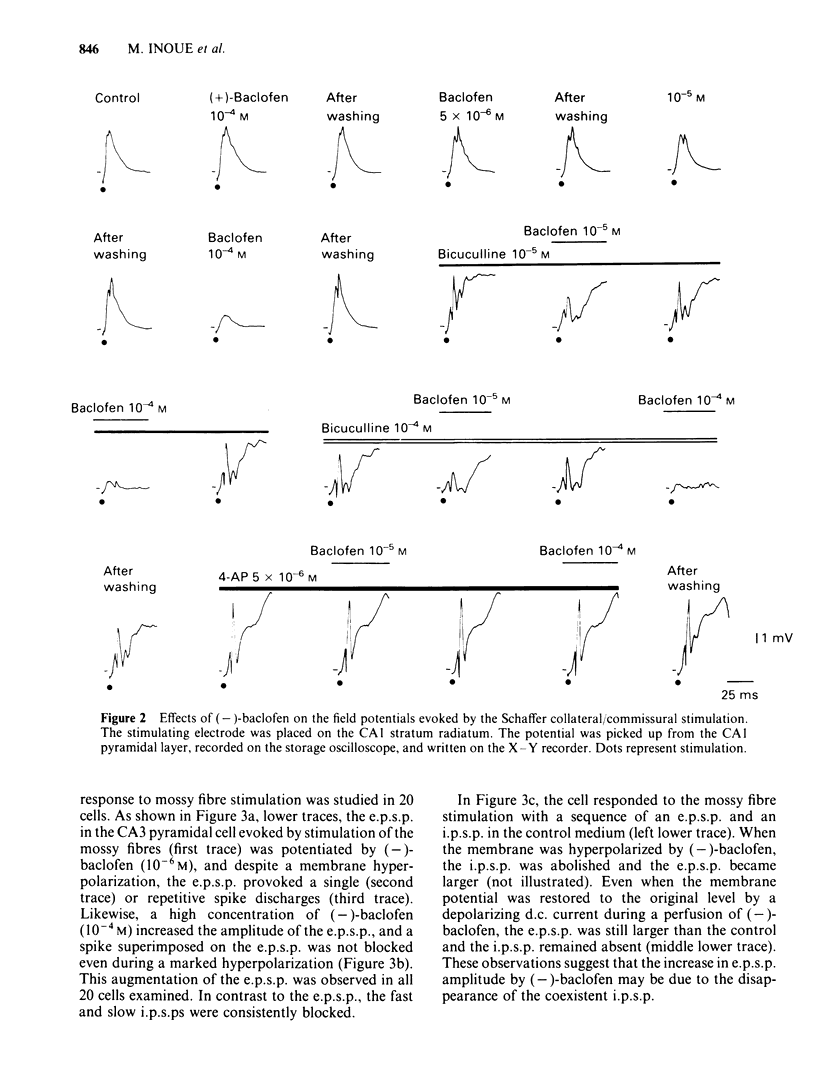
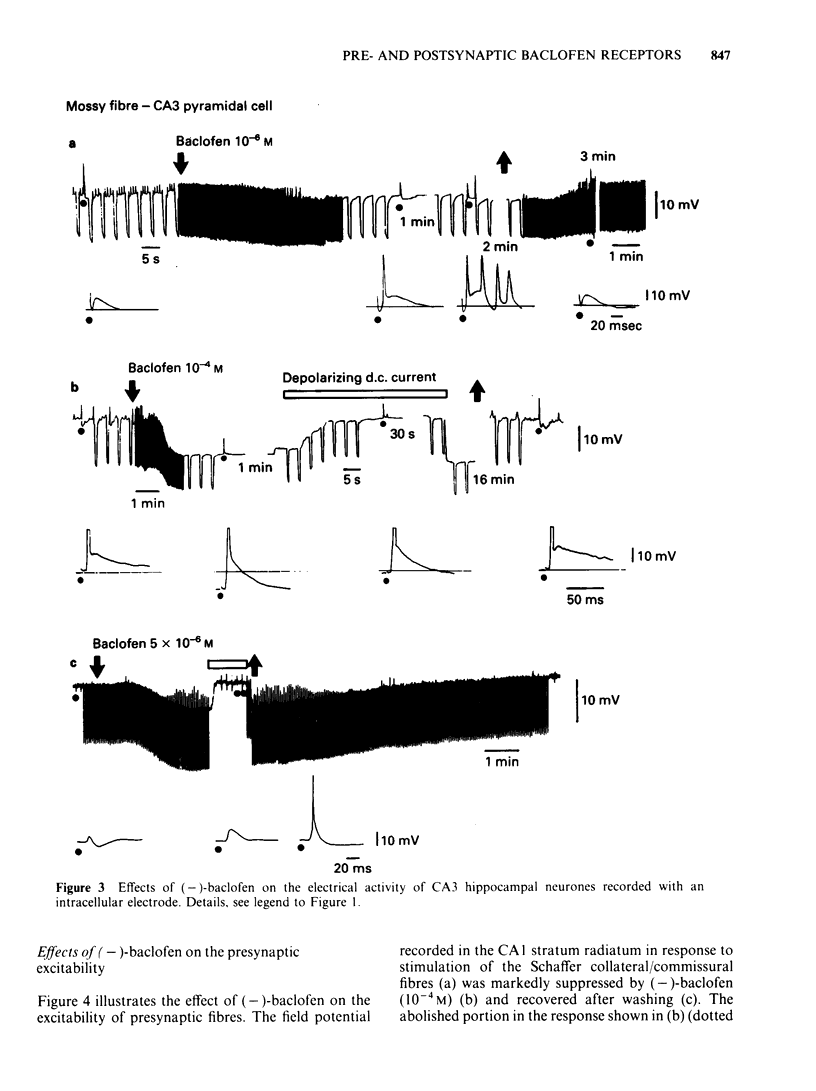
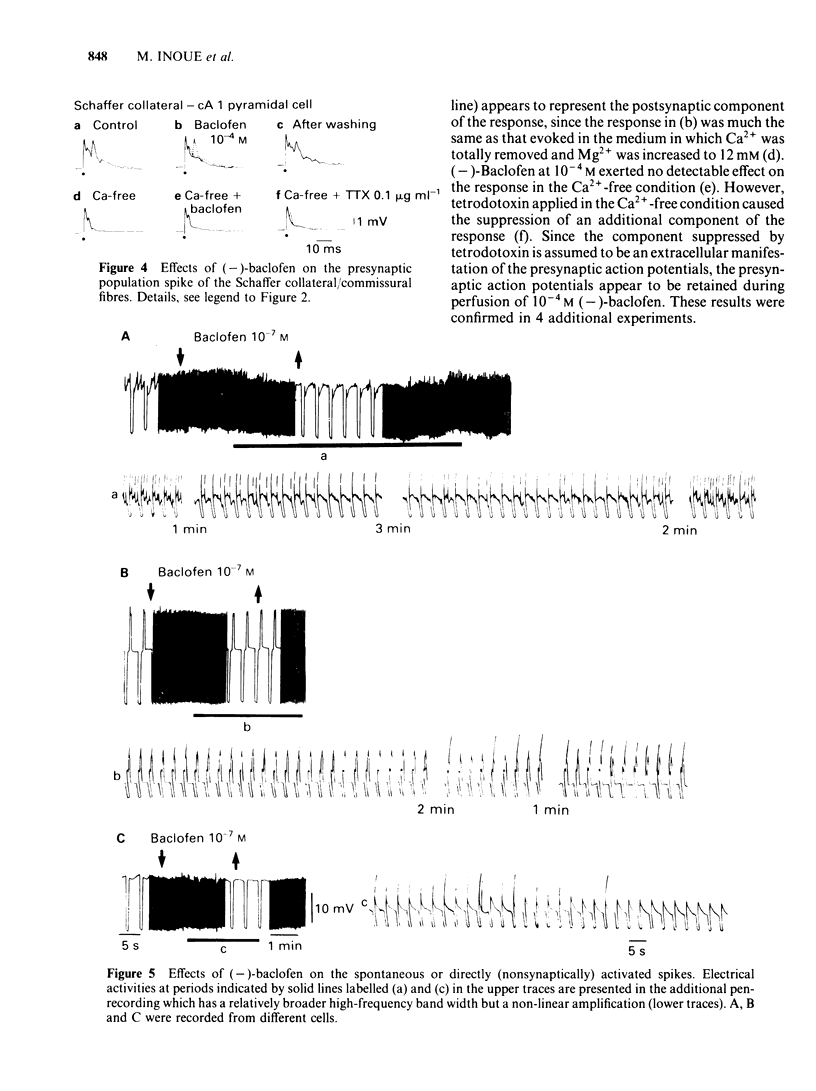
The effects of (-)-baclofen on evoked potentials in the hippocampus were examined through intracellular recordings from guinea-pig brain slices. The evoked responses were recorded in two fibre connections within the hippocampus: the Schaffer collateral/commissural-CA1 pyramidal cell, and the mossy fibre-CA3 pyramidal cell. The Schaffer collateral/commissural-CA1 response was suppressed by (-)-baclofen in concentrations over 2 X 10(-5)M, whereas (+)-baclofen, an inactive isomer, in a concentration of 10(-4)M had no effect on the response. A compound action potential of Schaffer collateral/commissural axons was unaffected by (-)-baclofen even at 10(-4)M, a concentration that almost completely depressed the evoked response in the CA1 pyramidal cell. The mossy fibre-CA3 response was not inhibited by (-)-baclofen (10(-4)M). The depressant action of (-)-baclofen on the Schaffer collateral/commissural-CA1 response was unaffected by bicuculline (10(-4)M), whereas the direct membrane effects of (-)-baclofen were antagonized by bicuculline (10(-5)M). It is suggested that (-)-baclofen may modulate neuronal transmission through presynaptic recognition sites possibly by decreasing transmitter release from nerve terminals and also may directly regulate the endogenous neuronal excitability through an activation of the postsynaptic recognition sites.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe H., Ogata N. Ionic mechanism for the osmotically-induced depolarization in neurones of the guinea-pig supraoptic nucleus in vitro. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:157–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Nadler J. V. Baclofen selectively inhibits transmission at synapses made by axons of CA3 pyramidal cells in the hippocampal slice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):291–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Nadler J. V. Effects of baclofen on synaptically-induced cell firing in the rat hippocampal slice. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Sep;80(1):211–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11068.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackstad T. W., Brink K., Hem J., Jeune B. Distribution of hippocampal mossy fibers in the rat. An experimental study with silver impregnation methods. J Comp Neurol. 1970 Apr;138(4):433–449. doi: 10.1002/cne.901380404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Doble A., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L., Shaw J. S., Turnbull M. J., Warrington R. Bicuculline-insensitive GABA receptors on peripheral autonomic nerve terminals. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 24;71(1):53–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L., Doble A., Middlemiss D. N., Shaw J., Turnbull M. (-)Baclofen decreases neurotransmitter release in the mammalian CNS by an action at a novel GABA receptor. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):92–94. doi: 10.1038/283092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins G. G., Anson J., Kelly E. P. Baclofen: effects on evoked field potentials and amino acid neurotransmitter release in the rat olfactory cortex slice. Brain Res. 1982 Apr 29;238(2):371–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. Selective depression of synaptic excitation in cat spinal neurones by baclofen: an iontophoretic study. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;72(2):373–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K. Two types of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor on embryonic sensory neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;74(3):579–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb D. I., Cowan W. M. Autoradiographic studies of the commissural and ipsilateral association connection of the hippocampus and detentate gyrus of the rat. I. The commissural connections. J Comp Neurol. 1973 Jun 15;149(4):393–422. doi: 10.1002/cne.901490402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry J. L. Pharmacological studies on the prolonged depressant effects of baclofen on lumbar dorsal horn units in the cat. Neuropharmacology. 1982 Nov;21(11):1085–1093. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(82)90165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Matsuo T., Ogata N. Baclofen activates voltage-dependent and 4-aminopyridine sensitive K+ conductance in guinea-pig hippocampal pyramidal cells maintained in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr;84(4):833–841. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb17377.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. A., Hailstone M. H., Freeman C. G. Baclofen: stereoselective inhibition of excitant amino acid release. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;32(3):230–231. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1980.tb12902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanthorn T. H., Cotman C. W. Baclofen selectively inhibits excitatory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 23;225(1):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90326-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. A bicuculline-resistant inhibitory post-synaptic potential in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:239–254. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. Direct hyperpolarizing action of baclofen on hippocampal pyramidal cells. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):450–452. doi: 10.1038/308450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata N., Abe H. Neuropharmacology in the brain slice: effects of substance P on neurons in the guinea-pig hypothalamus. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1982;72(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0306-4492(82)90081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olpe H. R., Baudry M., Fagni L., Lynch G. The blocking action of baclofen on excitatory transmission in the rat hippocampal slice. J Neurosci. 1982 Jun;2(6):698–703. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-06-00698.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potashner S. J. Baclofen: effects on amino acid release and metabolism in slices of guinea pig cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1979 Jan;32(1):103–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogawski M. A., Barker J. L. Effects of 4-aminopyridine on calcium action potentials and calcium current under voltage clamp in spinal neurons. Brain Res. 1983 Nov 28;280(1):180–185. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K., Konishi S., Otsuka M. Antagonism between Lioresal and substance P in rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1975 Oct 24;97(1):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90928-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Wyss J. M., Cowan W. M. An autoradiographic study of the organization of intrahippocampal association pathways in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Oct 15;181(4):681–715. doi: 10.1002/cne.901810402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


