Abstract
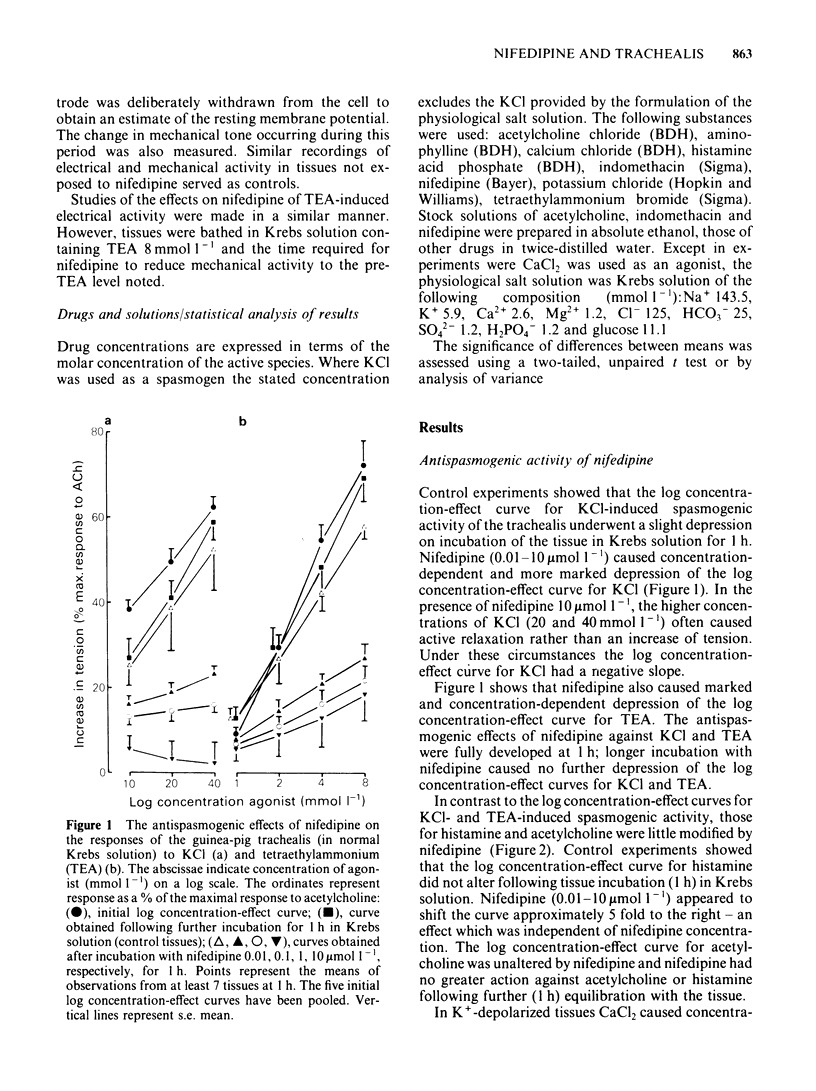
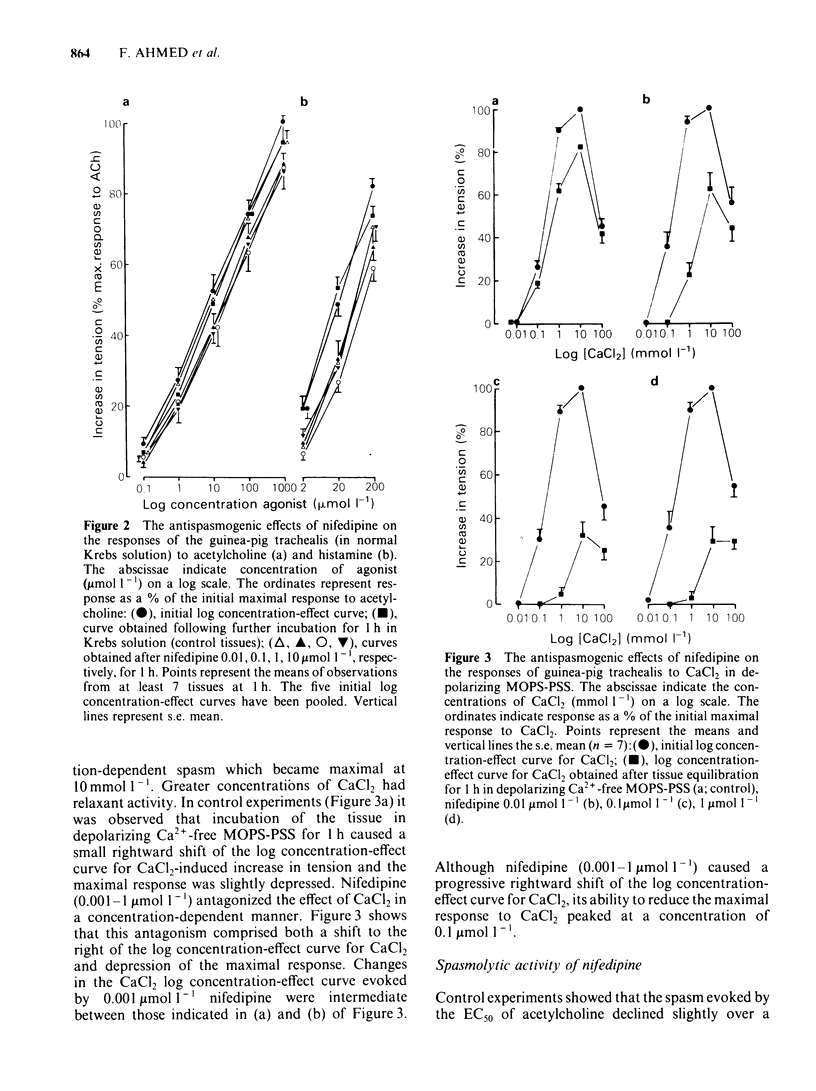
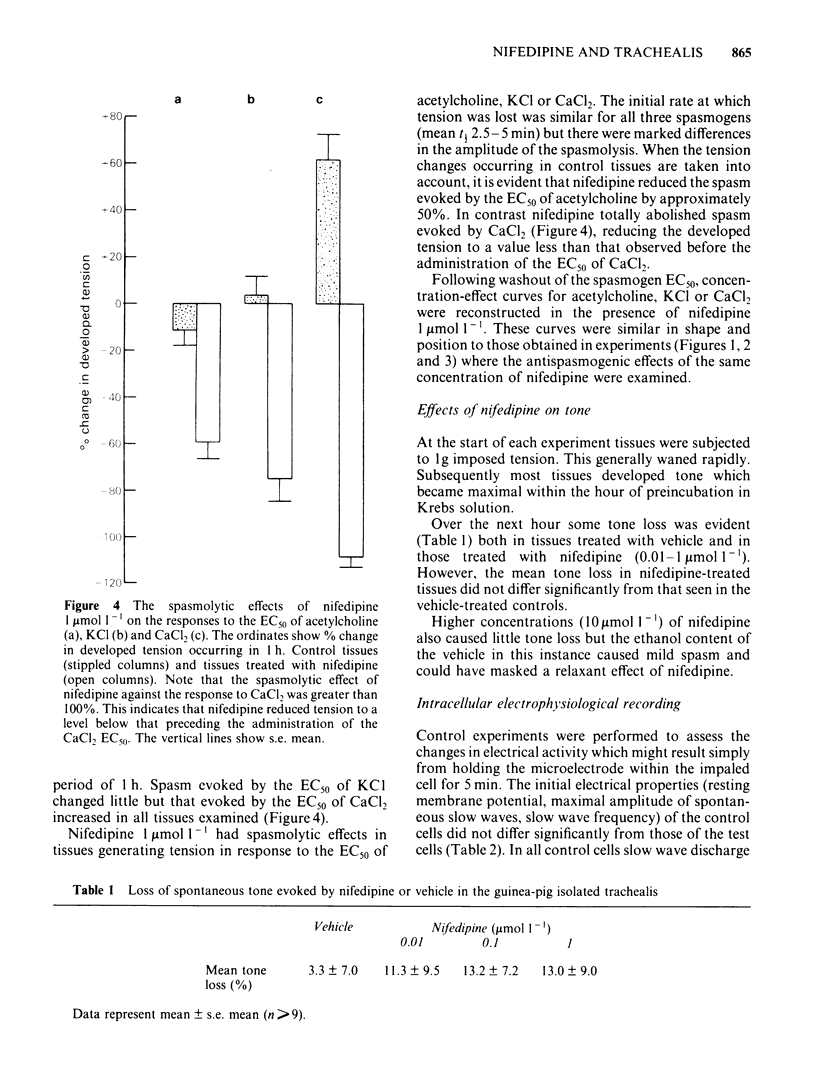
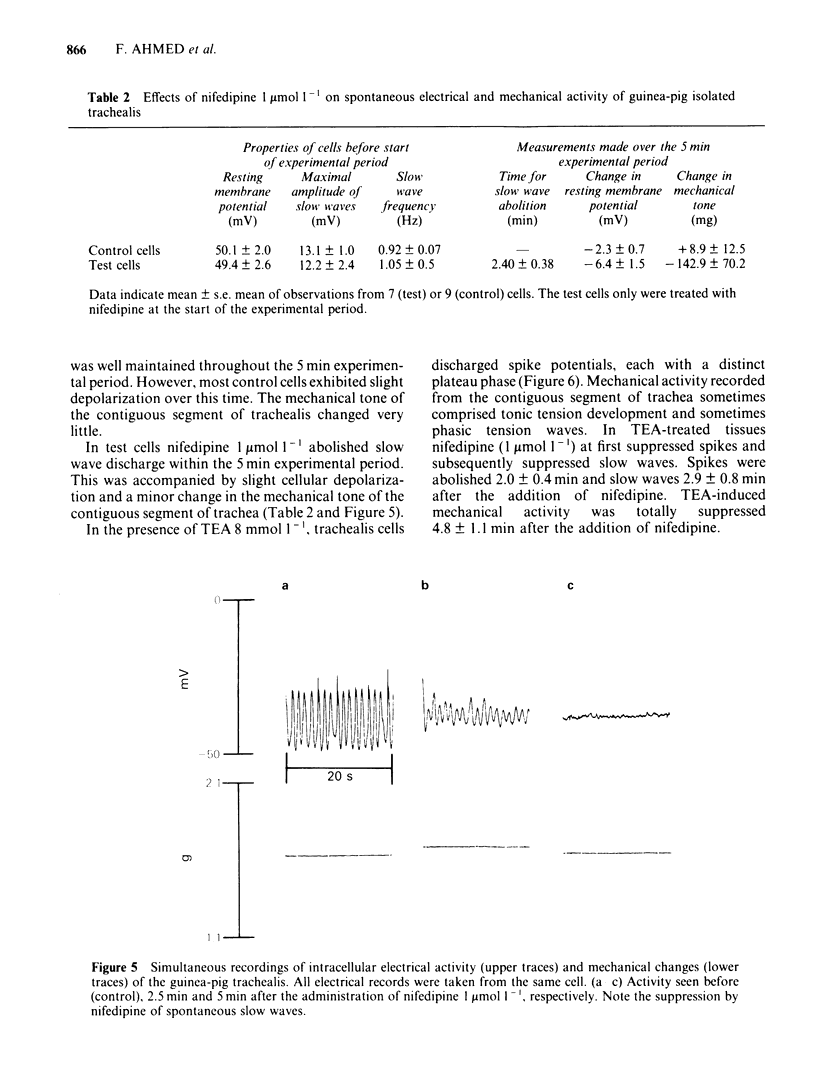
In trachealis depolarized by a K+-rich medium, nifedipine (0.001-1 mumol 1(-1) caused concentration-dependent antagonism of CaCl2-induced increase in tension, moving the CaCl2 log concentration-effect curve to the right and depressing the maximal response. In trachealis in normal Krebs solution, similar concentrations of nifedipine had marked antispasmogenic activity against the responses to potassium chloride (KCl) and tetraethylammonium (TEA). However, nifedipine had little, if any, antispasmogenic activity against the responses to acetylcholine or histamine. Nifedipine 1 mumol 1(-1) was tested for spasmolytic activity in tissues generating tension in response to the EC50 of acetylcholine, KCl or CaCl2. In producing spasmolysis nifedipine was most effective against CaCl2 and least effective against acetylcholine. Nifedipine (0.01-1 mumol-1) had little or no effect on the tone of trachealis in normal Krebs solution. Intracellular electrophysiological recording showed that nifedipine 1 mumol 1(-1) could abolish spontaneous slow wave activity. This was associated with very minor depolarization and little or no loss of mechanical tone. In tissues treated with TEA (8 mmol 1(-1) nifedipine abolished spike and slow wave discharge and reduced mechanical activity to the pre-TEA level. It is concluded that nifedipine prevents KCl- or TEA-induced spasm by inhibition of Ca2+ influx. Spasm evoked by acetylcholine or histamine and the maintenance of spontaneous tone depend largely on mechanisms for increasing the cytoplasmic concentration of free Ca2+ which are resistant to nifedipine.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed F., Foster R. W., Small R. C., Weston A. H. Some features of the spasmogenic actions of acetylcholine and histamine in guinea-pig isolated trachealis. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;83(1):227–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. Mechanisms of action of transmitters and other substances on smooth muscle. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):606–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. B., Townley R. G. Pharmacological characterization of effects of nifedipine on isolated guinea-pig and rat tracheal smooth muscle. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1983 Jun;263(2):228–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coburn R. F. Electromechanical coupling in canine trachealis muscle: acetylcholine contractions. Am J Physiol. 1979 Mar;236(3):C177–C184. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.236.3.C177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coburn R. F., Yamaguchi T. Membrane potential-dependent and-independent tension in the canine tracheal muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 May;201(2):276–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. S., Small R. C. Evidence of poor conduction of muscle excitation in the longitudinal axis of guinea-pig isolated trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 May;79(1):75–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10498.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanta C. H., Venugopalan C. S., Lacouture P. G., Drazen J. M. Inhibition of bronchoconstriction in the guinea pig by a calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Jan;125(1):61–66. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J. M., Miles P. R. Role of depolarization in acetylcholine-induced contractions of dog trachealis muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Apr;201(1):199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R. W., Okpalugo B. I., Small R. C. Antagonism of Ca2+ and other actions of verapamil in guinea-pig isolated trachealis. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;81(3):499–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10103.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R. W., Small R. C., Weston A. H. Evidence that the spasmogenic action of tetraethylammonium in guinea-pig trachealis is both direct and dependent on the cellular influx of calcium ion. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 May;79(1):255–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R. W., Small R. C., Weston A. H. The spasmogenic action of potassium chloride in guinea-pig trachealis. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Nov;80(3):553–559. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10728.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. F., Heaton R. W., Dunlop L. S., Costello J. F. Effects of nifedipine on antigen-induced bronchoconstriction. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5):549–553. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetley M., Weston A. H. Some effects of sodium nitroprusside, methoxyverapamil (D600) and nifedipine on rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;68(2):311–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10420.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick C. T. Excitation and contraction in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):263–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaig D. J., Souhrada J. F. Alteration of electrophysiological properties of airway smooth muscle from sensitized guinea-pigs. Respir Physiol. 1980 Jul;41(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(80)90022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeburn D., Rodger I. W. Lack of effect of leukotriene D4 on Ca-uptake in airway smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):499–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small R. C. Electrical slow waves and tone of guinea-pig isolated trachealis muscle: effects of drugs and temperature changes. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;77(1):45–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens N. L., Kroeger E. Effect of hypoxia on airway smooth muscle mechanics and electrophysiology. J Appl Physiol. 1970 May;28(5):630–635. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.5.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Morita K., Kuriyama H. Innervation and properties of the smooth muscle of the dog trachea. Jpn J Physiol. 1976;26(3):303–320. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.26.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weichman B. M., Muccitelli R. M., Tucker S. S., Wasserman M. A. Effect of calcium antagonists on leukotriene D4-induced contractions of the guinea-pig trachea and lung parenchyma. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 May;225(2):310–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


