Abstract
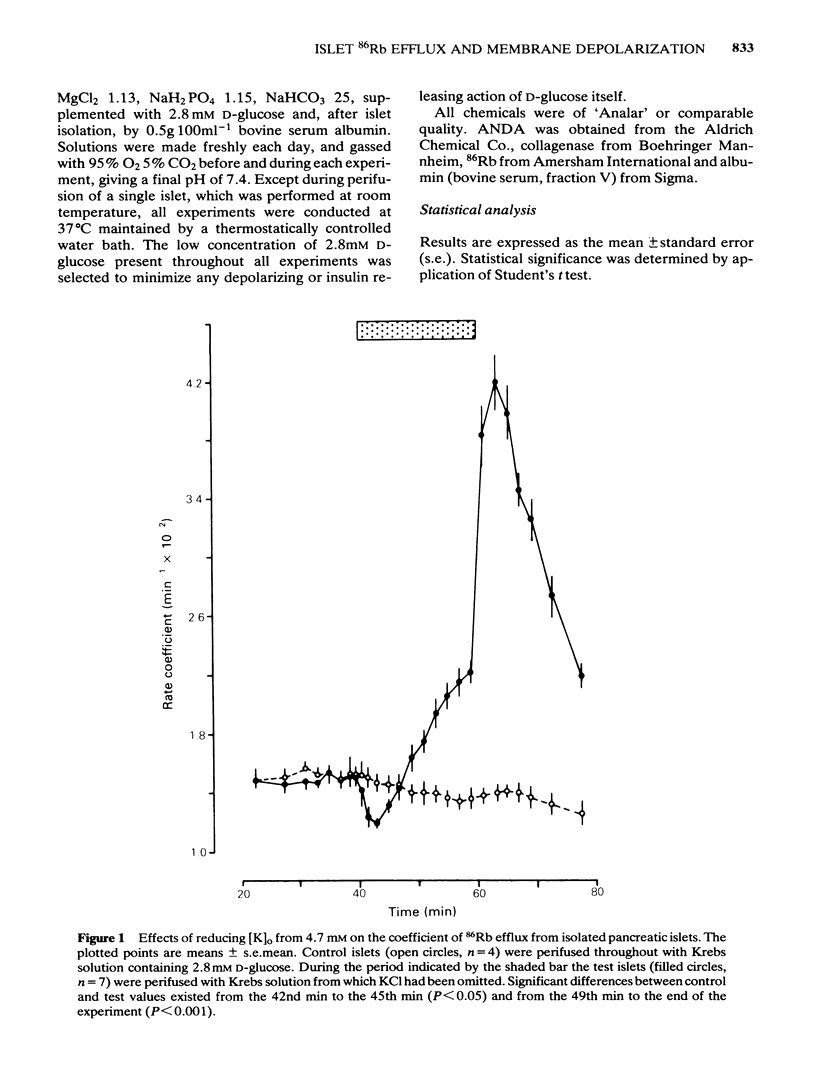
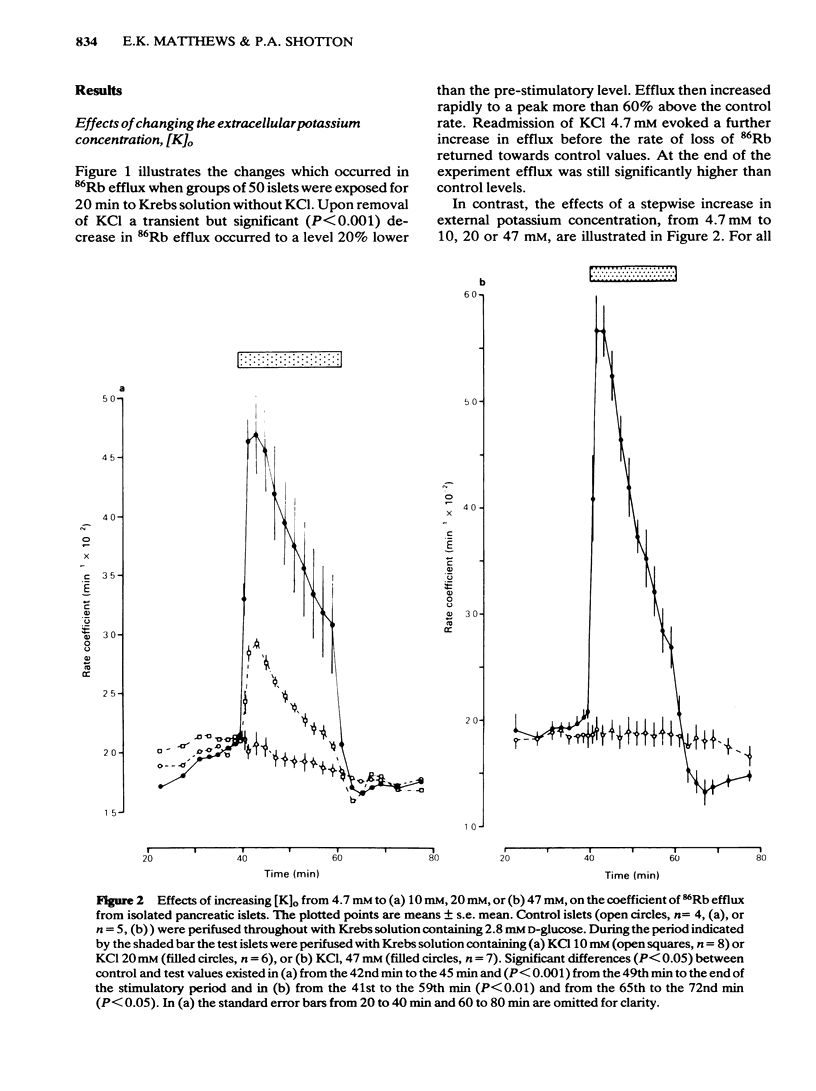
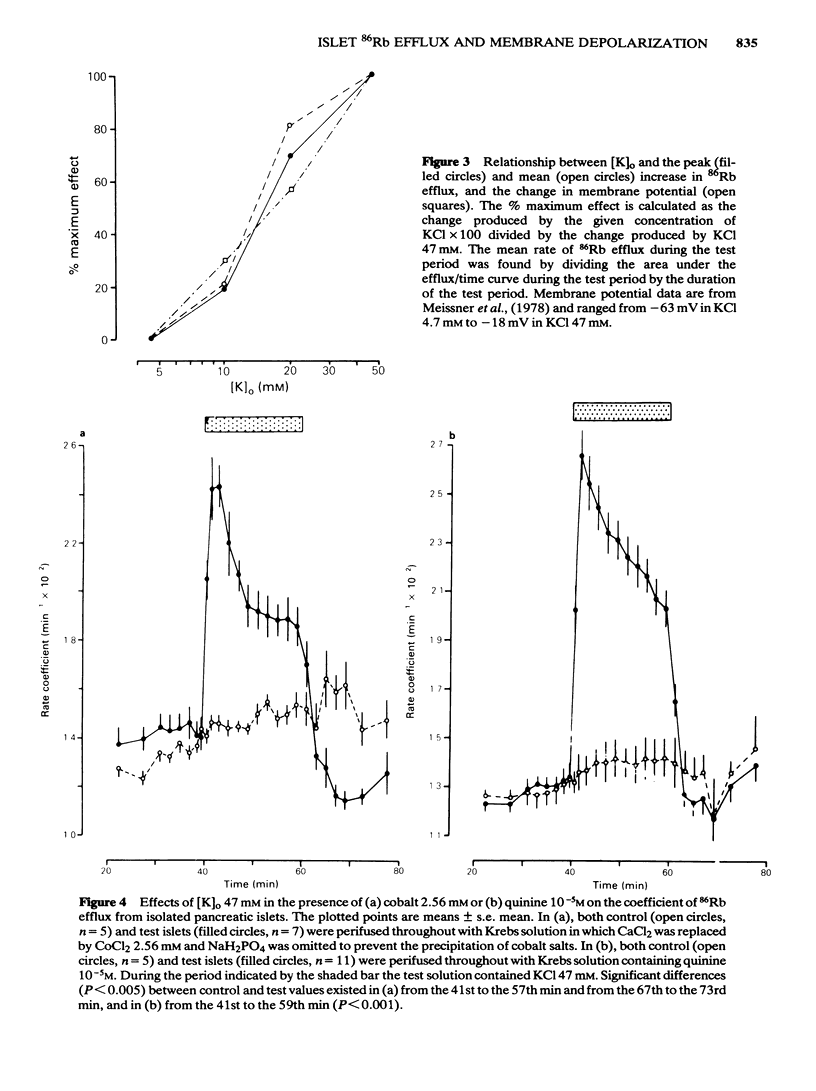
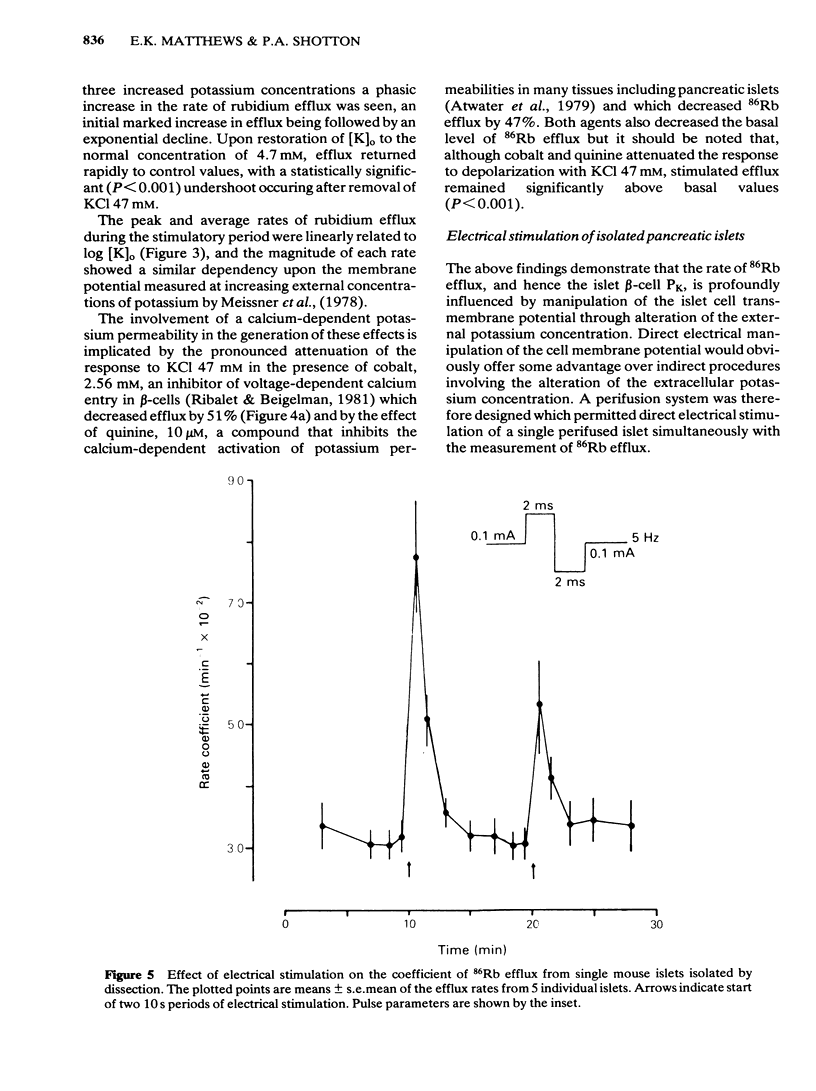
The efflux of 86Rb from rat or mouse perifused islets preloaded with the isotope has been used as an index of the potassium permeability of the islet beta-cell membrane. Cellular transmembrane potentials were altered by changing [K]O or by direct electrical stimulation and the effects on potassium permeability examined. Omission of KCl from the medium perifusing rat islets induced a biphasic change in 86Rb efflux, a brief decline being superseded by a pronounced increase in efflux. Re-introduction of KCl, 4.7 mM, caused a further increase in 86Rb efflux preceding a return to control values. Increasing [K]O from 4.7 mM to 10 mM, 20 mM or 47 mM caused a phasic increase in 86Rb efflux with the magnitude of both the peak and average rate of efflux being dependent upon the extent of the change in [K]O. The increase in 86Rb efflux produced by [K]O, 47 mM, was attenuated by Co2+, 2.56 mM (51% inhibition) or quinine, 10 microM (47% inhibition), but efflux remained significantly (P less than 0.001) above control values. Electrical stimulation of single microdissected mouse pancreatic islets by currents of 0.1 to 0.5 mA evoked a rapid, phasic increase in 86Rb efflux. The magnitude of the response was unaffected by EGTA, 2 mM, or nupercaine, 100 microM. These observations are discussed in relation to the mechanisms controlling the potassium permeability, membrane potential and insulin secretion of the pancreatic islet beta-cell.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armando-Hardy M., Ellory J. C., Ferreira H. G., Fleminger S., Lew V. L. Inhibition of the calcium-induced increase in the potassium permeability of human red blood cells by quinine. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;250(1):32P–33P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Beigelman P. M. Dynamic characteristics of electrical activity in pancreatic beta-cells. I. - Effects of calcium and magnesium removal. J Physiol (Paris) 1976 Nov;72(6):769–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Potassium permeability activated by intracellular calcium ion concentration in the pancreatic beta-cell. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:575–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Cyclic changes in potential and resistance of the beta-cell membrane induced by glucose in islets of Langerhans from mouse. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:117–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Meves H., Ridgway E. B. Calcium entry in response to maintained depolarization of squid axons. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):527–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschero A. C., Kawazu S., Duncan G., Malaisse W. J. Effect of glucose on K+ handling by pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1977 Nov 1;83(1):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80662-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschero A. C., Malaisse W. J. Stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XXIX. Regulation of 86Rb+ efflux from perfused islets. Am J Physiol. 1979 Feb;236(2):E139–E146. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.2.E139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpinelli A., Malaisse W. J. Regulation of 86Rb+ outflow from pancreatic islets. I. Reciprocal changes in the response to glucose, tetraethylammonium and quinine. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1980 Feb;17(2):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(80)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Porte D., Jr, Crill W. E. Voltage dependence of rhythmic plateau potentials of pancreatic islet cells. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):E290–E296. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.3.E290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson C. M., Atwater I., Rojas E. Potassium-induced insulin release and voltage noise measurements in single mouse islets of Langerhans. J Membr Biol. 1982;64(1-2):33–43. doi: 10.1007/BF01870766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1968 Jul 27;219(5152):389–390. doi: 10.1038/219389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells: effect of ions. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):265–275. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Glucose-induced electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):255–264. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donatsch P., Lowe D. A., Richardson B. P., Taylor P. The functional significance of sodium channels in pancreatic beta-cell membranes. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):357–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formby B., Capito K., Egeberg J., Hedeskov C. J. Ca-activated ATPase activity in subcellular fractions of mouse pancreatic islets. Am J Physiol. 1976 Feb;230(2):441–448. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.2.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez M., Curry D. L. Potassium stimulation of insulin release by the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1973 Apr;92(4):1126–1134. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-4-1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Bennett L. L. Cation requirements for insulin secretion in the isolated perfused pancreas. Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):910–913. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales C. N., Milner R. D. The role of sodium and potassium in insulin secretion from rabbit pancreas. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(3):725–743. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. D-glucose inhibits potassium efflux from pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):271–273. doi: 10.1038/271271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Horemans B., Nenquin M., Verniers J., Lambert A. E. Quinine-induced modifications of insulin release and glucose metabolism by isolated pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 1;57(3):280–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Lambert A. E. Cationic environment and dynamics of insulin secretion. II. Effect of a high concentration of potassium. Diabetes. 1974 Dec;23(12):933–942. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.12.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Lambert A. E. Cationic environment and dynamics of insulin secretion. III. Effect of the absence of potassium. Diabetologia. 1974 Dec;10(6):789–794. doi: 10.1007/BF01219542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Opposite effects of intracellular Ca2+ and glucose on K+ permeability of pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):66–68. doi: 10.1038/280066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Relative importance of extracellular and intracellular calcium for the two phases of glucose-stimulated insulin release: studies with theophylline. Endocrinology. 1978 Mar;102(3):723–730. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-3-723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Tetraethylammonium potentiation of insulin release and inhibition of rubidium efflux in pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):551–556. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herchuelz A., Malaisse W. J. Regulation of calcium fluxes in rat pancreatic islets: dissimilar effects of glucose and of sodium ion accumulation. J Physiol. 1980 May;302:263–280. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSKALEWSKI S. ISOLATION AND CULTURE OF THE ISLETS OF LANGERHANS OF THE GUINEA PIG. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1965 Jun;5:342–353. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(65)90059-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse-Lagae F., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. 3. Uptake of 45 calcium by isolated islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 1971 Jan;88(1):72–80. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-1-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Boschero A. C., Kawazu S., Hutton J. C. The stimulus secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XXVII. Effect of glucose on K+ fluxes in isolated islets. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Mar 20;373(3):237–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00580830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Sakamoto Y. Electrical characteristics of pancreatic islet cells. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(2):421–437. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Shotton P. A. The control of 86Rb efflux from rat isolated pancreatic islets by the sulphonylureas tolbutamide and glibenclamide. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;82(3):689–700. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10808.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Henquin J. C., Preissler M. Potassium dependence of the membrane potential of pancreatic B-cells. FEBS Lett. 1978 Oct 1;94(1):87–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80912-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Tsuchiya W., Yada T. Calcium channel and calcium pump involved in oscillatory hyperpolarizing responses of L-strain mouse fibroblasts. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:449–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. S., Tarvin J. T., Neighbors A. S., Pirkle J. A., Greider M. H. Use of a high voltage technique to determine the molecular requirements for exocytosis in islet cells. Diabetes. 1980 Nov;29(11):911–918. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.11.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Beigelman P. M. Calcium action potentials and potassium permeability activation in pancreatic beta-cells. Am J Physiol. 1980 Sep;239(3):C124–C133. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1980.239.3.C124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehlin J., Taljedal I. B. Glucose-induced decrease in Rb+ permeability in pancreatic beta cells. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):635–636. doi: 10.1038/253635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Transport of rubidium and sodium in pancreatic islets. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(2):505–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


