Abstract
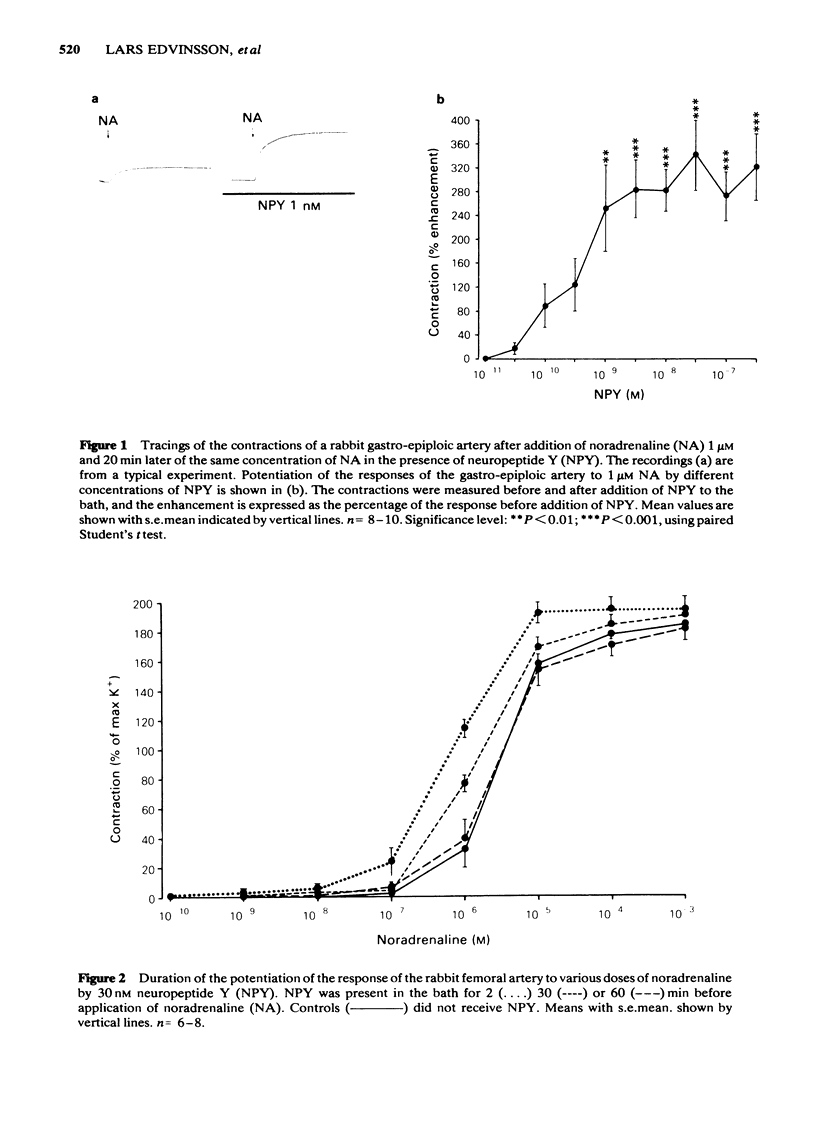
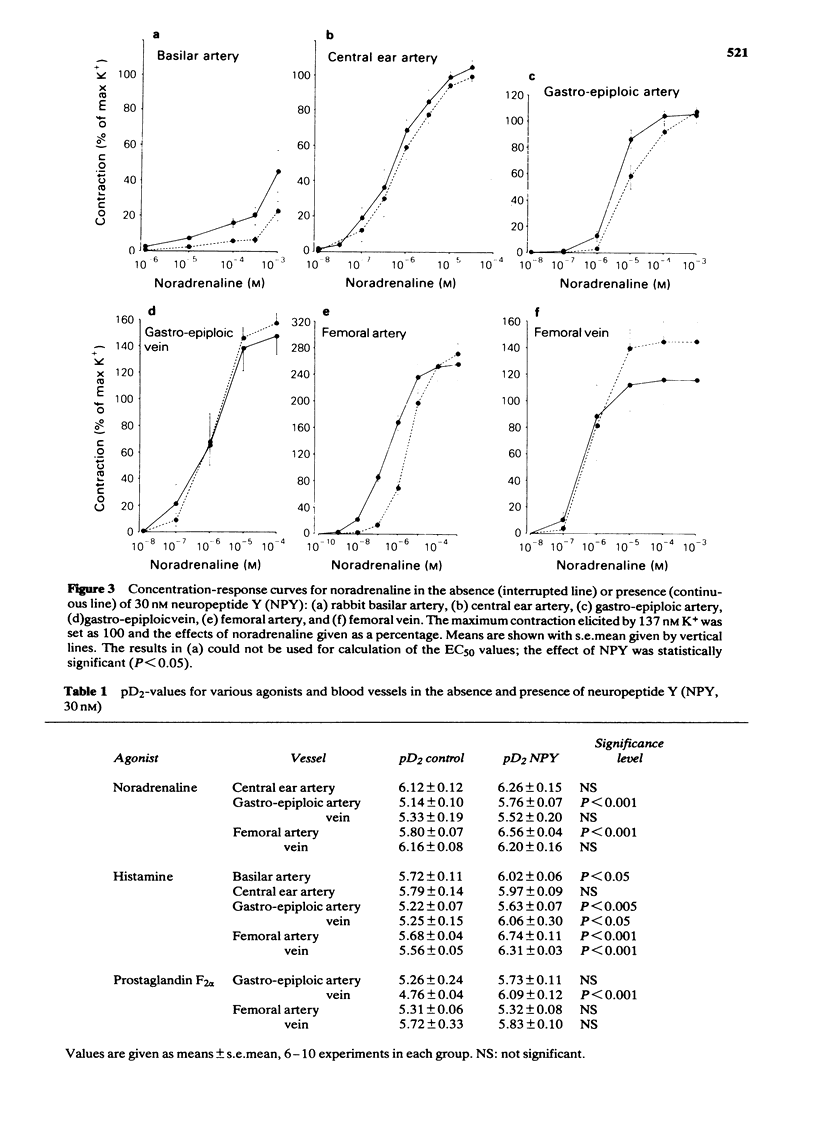
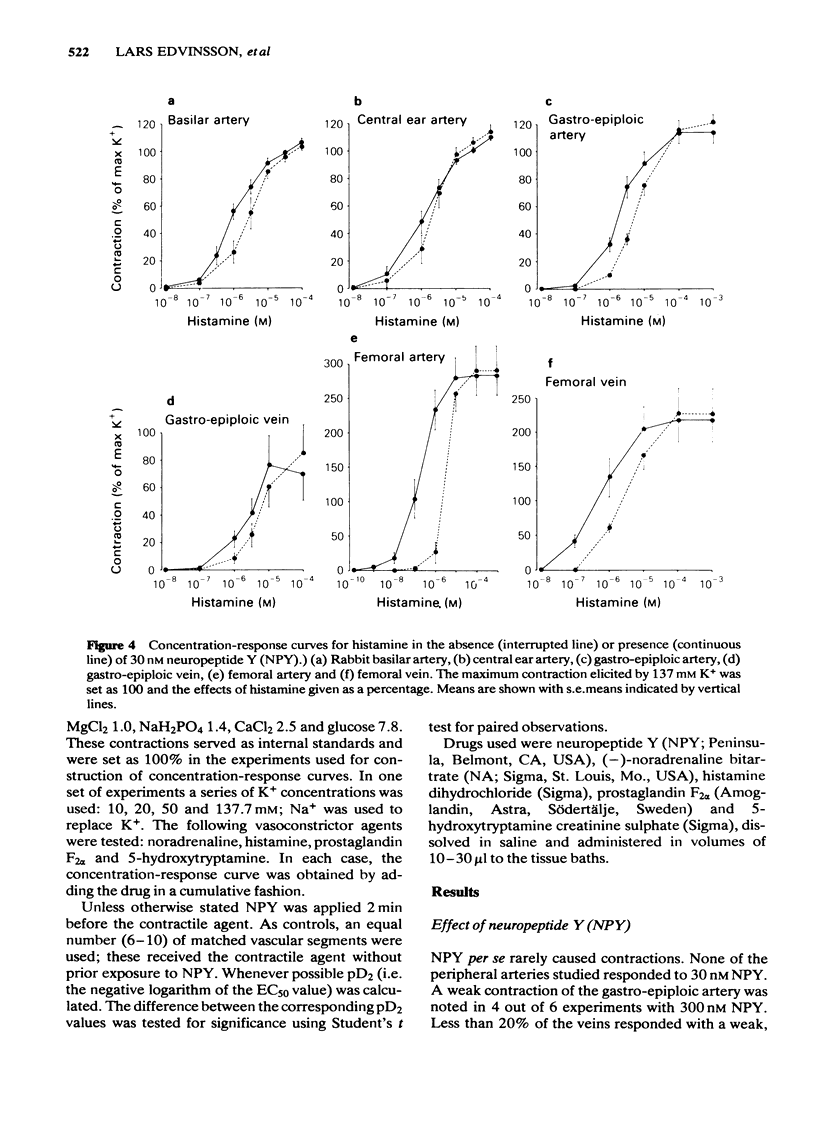
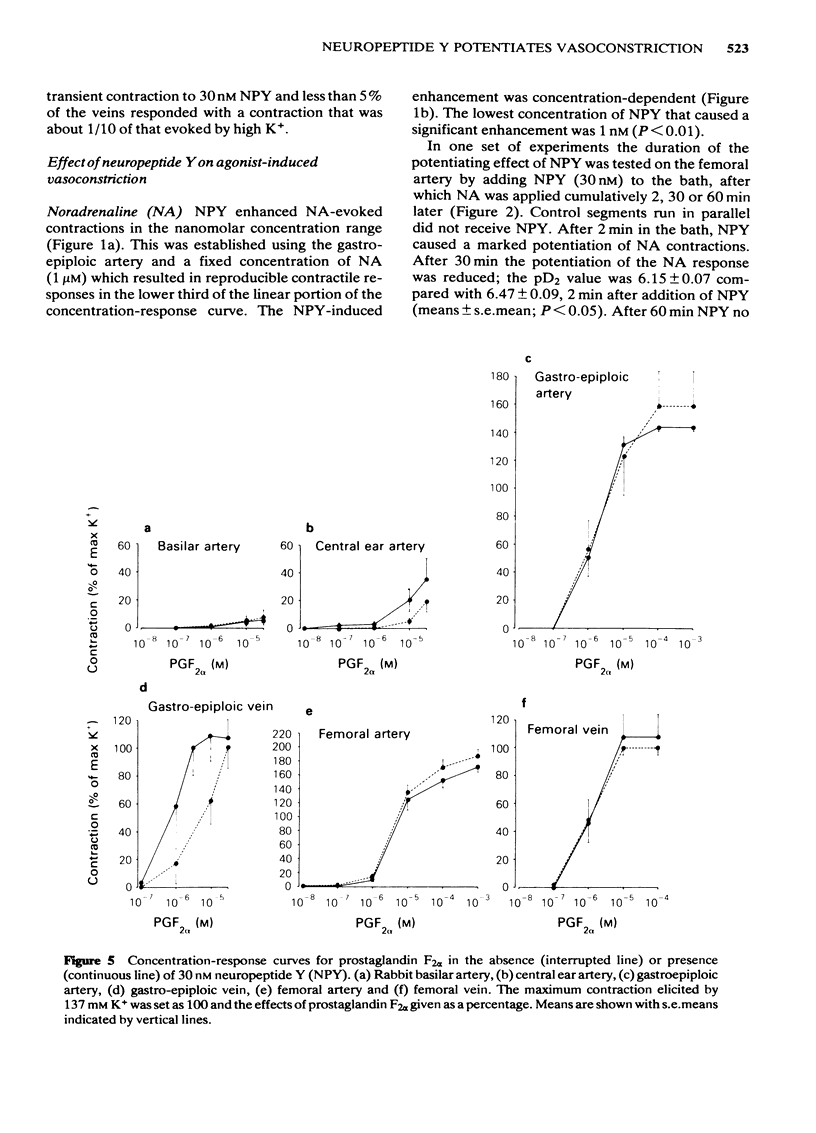
The contractile effect of neuropeptide Y (NPY) was tested on isolated segments of basilar artery, central ear artery, gastro-epiploic artery and vein, and femoral artery and vein from the rabbit. At 30 nM NPY did not evoke vasoconstriction; at 300 nM NPY evoked a weak and variable response. NPY greatly potentiated the response of the gastro-epiploic and femoral arteries to noradrenaline without affecting the maximum response. As tested on the gastro-epiploic artery NPY was effective at concentrations of 1 nM and higher. As tested on the femoral artery the potentiating effect of 30 nM NPY on noradrenaline-evoked contractions was apparent immediately and 30 min after the application of NPY, but not after one hour. NPY (30 nM) potentiated the contractile response to noradrenaline and histamine but not to 5-hydroxytryptamine or high K+. The response to histamine was augmented in both arteries and veins, whereas the response to noradrenaline was enhanced in arteries but not in veins. NPY failed to potentiate the prostaglandin F2 alpha-evoked contraction except in the gastro-epiploic vein.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnati L. F., Fuxe K., Benfenati F., Battistini N., Härfstrand A., Tatemoto K., Hökfelt T., Mutt V. Neuropeptide Y in vitro selectivity increases the number of alpha 2-adrenergic binding sites in membranes of the medulla oblongata of the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Jul;118(3):293–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Bircham P. M., Edwards A. V., Tatemoto K., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) reduces myocardial perfusion and inhibits the force of contraction of the isolated perfused rabbit heart. Regul Pept. 1983 Jul;6(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. Mechanisms of action of transmitters and other substances on smooth muscle. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):606–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Emson P., McCulloch J., Tatemoto K., Uddman R. Neuropeptide Y: cerebrovascular innervation and vasomotor effects in the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Dec 23;43(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K. Pancreatic polypeptide family (APP, BPP, NPY and PYY) in relation to sympathetic vasoconstriction resistant to alpha-adrenoceptor blockade. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):393–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Polak J., Bloom S., Goldstein M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in peripheral noradrenergic neurons and effects of NPY on sympathetic function. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):477–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Carlquist M., Mutt V. Neuropeptide Y--a novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):659–660. doi: 10.1038/296659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Neuropeptide Y: complete amino acid sequence of the brain peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5485–5489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


