Abstract
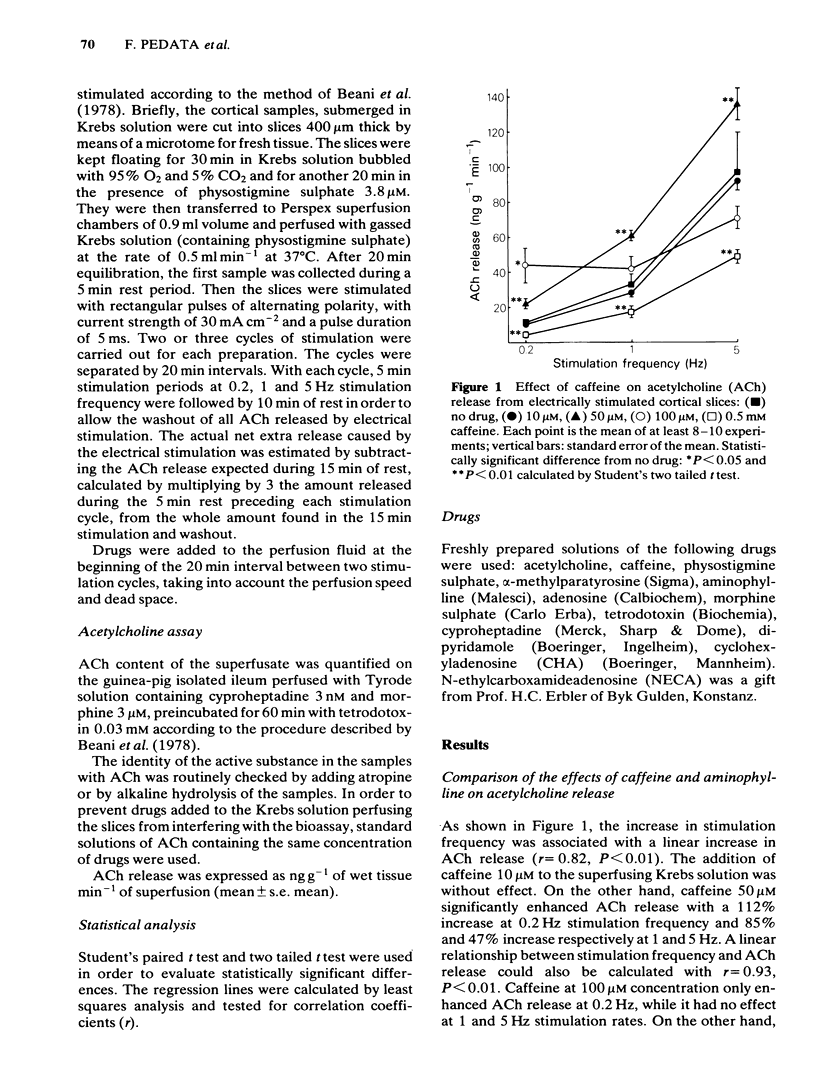
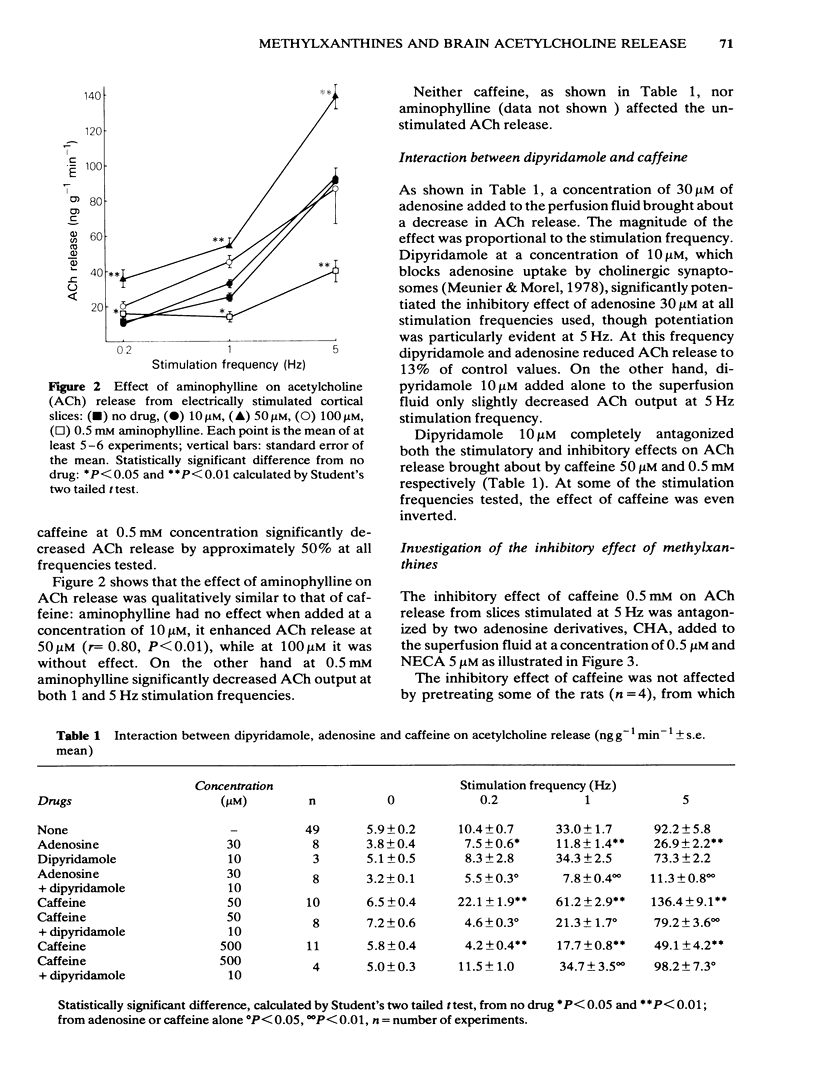
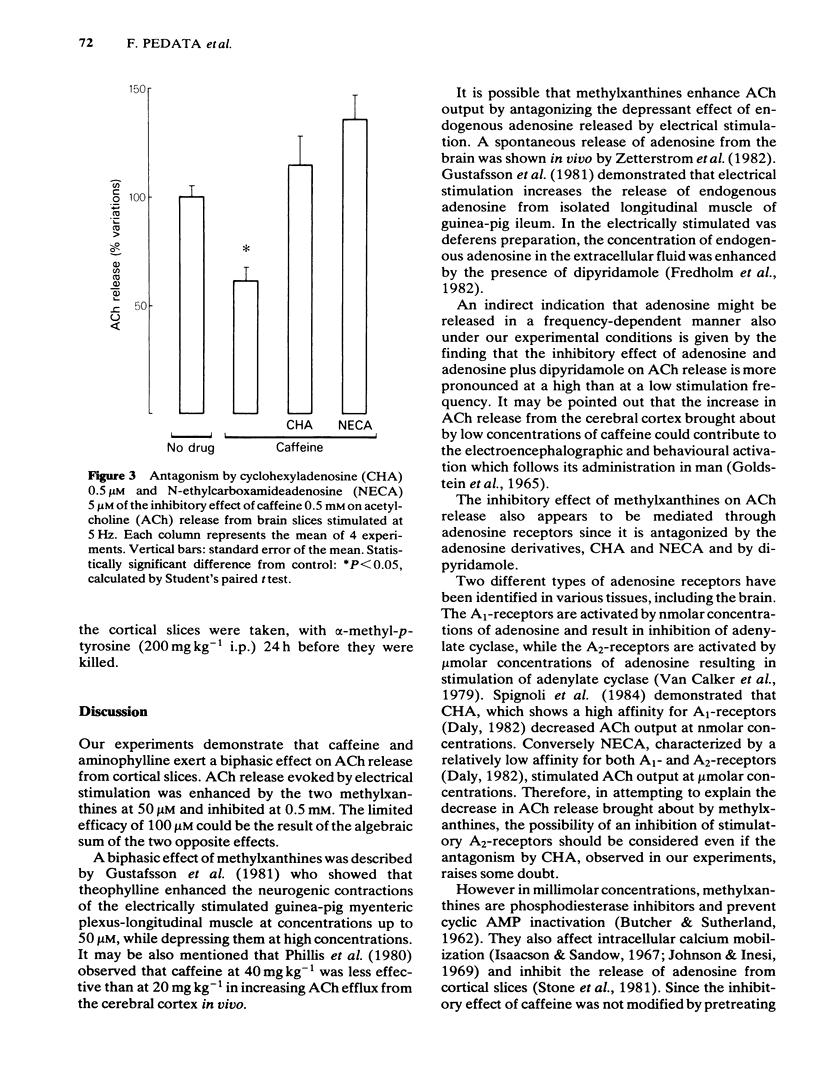
The effect of caffeine and aminophylline on the release of acetylcholine (ACh) was investigated in slices of rat cortex perfused with Krebs solution at rest and during electrical stimulation at frequencies of 0.2, 1 and 5 Hz. Both methylxanthines added to the superfusing Krebs solution at a concentration of 50 microM enhanced ACh release. Conversely, at a concentration of 0.5 mM both caffeine and aminophylline decreased ACh release. Neither caffeine nor aminophylline affected the unstimulated ACh release. Dipyridamole 10 microM potentiated the inhibitory effect of adenosine 30 microM on ACh release and antagonized both the stimulatory and inhibitory effects of caffeine on ACh release. The inhibitory effect of caffeine was antagonized by cyclohexyladenosine (CHA) 0.5 microM and N-ethylcarboxamideadenosine (NECA) 5 microM. The results indicate that methylxanthines exert both stimulatory and inhibitory effects on ACh release by acting on adenosine receptors. Methylxanthines may enhance the electrically-evoked ACh release by antagonizing the effect of endogenous adenosine on inhibitory adenosine receptors. On the other hand the mechanism through which methylxanthines decrease ACh release remains obscure.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTCHER R. W., SUTHERLAND E. W. Adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in biological materials. I. Purification and properties of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase and use of this enzyme to characterize adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in human urine. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1244–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beani L., Bianchi C., Giacomelli A., Tamberi F. Noradrenaline inhibition of acetylcholine release from guinea-pig brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Mar 15;48(2):179–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90327-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz B. A., Tarver J. H., Spector S. Release of norepinephrine in the central nervous system by theophylline and caffeine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1970 Apr;10(1):64–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(70)90158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W. Adenosine receptors: targets for future drugs. J Med Chem. 1982 Mar;25(3):197–207. doi: 10.1021/jm00345a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Fried G., Hedqvist P. Origin of adenosine released from rat vas deferens by nerve stimulation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Apr 23;79(3-4):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90629-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Hedqvist P. Modulation of neurotransmission by purine nucleotides and nucleosides. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Jun 15;29(12):1635–1643. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Kaizer S., Warren R. Psychotropic effects of caffeine in man. II. Alertness, psychomotor coordination, and mood. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Oct;150(1):146–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson L., Fredholm B. B., Hedqvist P. Theophylline interferes with the modulatory role of endogenous adenosine on cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea pig ileum. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Mar;111(3):269–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson A., Sandow A. Quinine and caffeine effects on 45Ca movements in frog sartorius muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Sep;50(8):2109–2128. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.8.2109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. N., Inesi G. The effect of methylxanthines and local anesthetics on fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Oct;169(2):308–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier F. M., Morel N. Adenosine uptake by cholinergic synaptosomes from Torpedo electric organ. J Neurochem. 1978 Oct;31(4):845–851. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb00119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray T. F., Blaker W. D., Cheney D. L., Costa E. Inhibition of acetylcholine turnover rate in rat hippocampus and cortex by intraventricular injection of adenosine analogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Sep;222(3):550–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedata F., Antonelli T., Lambertini L., Beani L., Pepeu G. Effect of adenosine, adenosine triphosphate, adenosine deaminase, dipyridamole and aminophylline on acetylcholine release from electrically-stimulated brain slices. Neuropharmacology. 1983 May;22(5):609–614. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Jiang Z. G., Chelack B. J., Wu P. H. The effect of morphine on purine and acetylcholine release from rat cerebral cortex: evidence for a purinergic component in morphine's action. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1980 Sep;13(3):421–427. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(80)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spignoli G., Pedata F., Pepeu G. A1 and A2 adenosine receptors modulate acetylcholine release from brain slices. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jan 27;97(3-4):341–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90475-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Hollins C., Lloyd H. Methylxanthines modulate adenosine release from slices of cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1981 Mar 2;207(2):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90374-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Physiological roles for adenosine and adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the nervous system. Neuroscience. 1981;6(4):523–555. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S., Knoll J. The inhibitory effect of adenosine and related nucleotides on the release of acetylcholine. Neuroscience. 1976;1(5):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterström T., Vernet L., Ungerstedt U., Tossman U., Jonzon B., Fredholm B. B. Purine levels in the intact rat brain. Studies with an implanted perfused hollow fibre. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Apr 16;29(2):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90338-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Calker D., Müller M., Hamprecht B. Adenosine regulates via two different types of receptors, the accumulation of cyclic AMP in cultured brain cells. J Neurochem. 1979 Nov;33(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


