Abstract
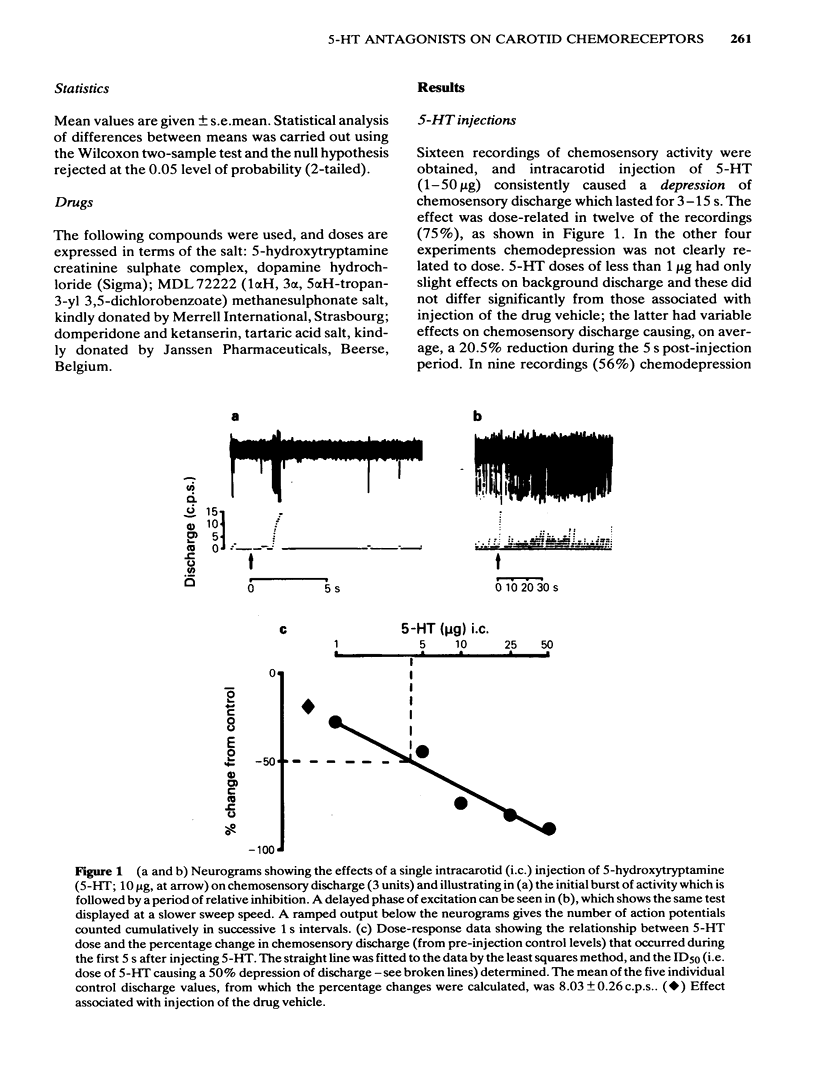
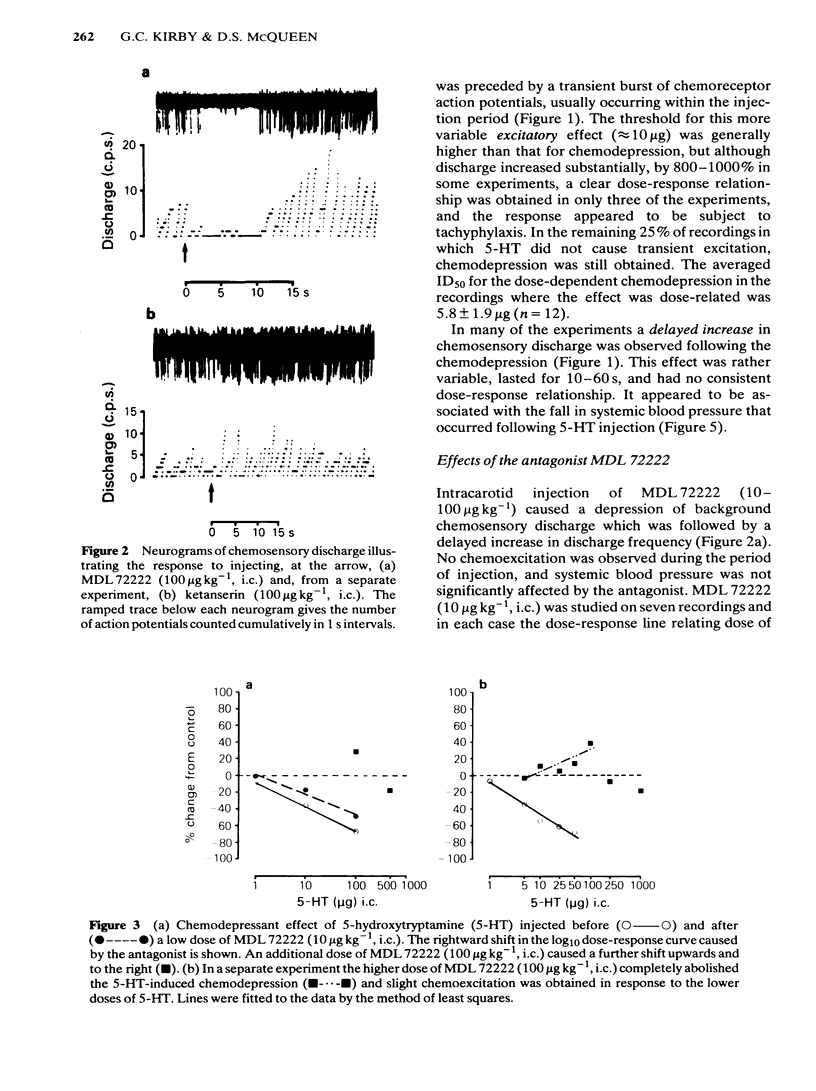
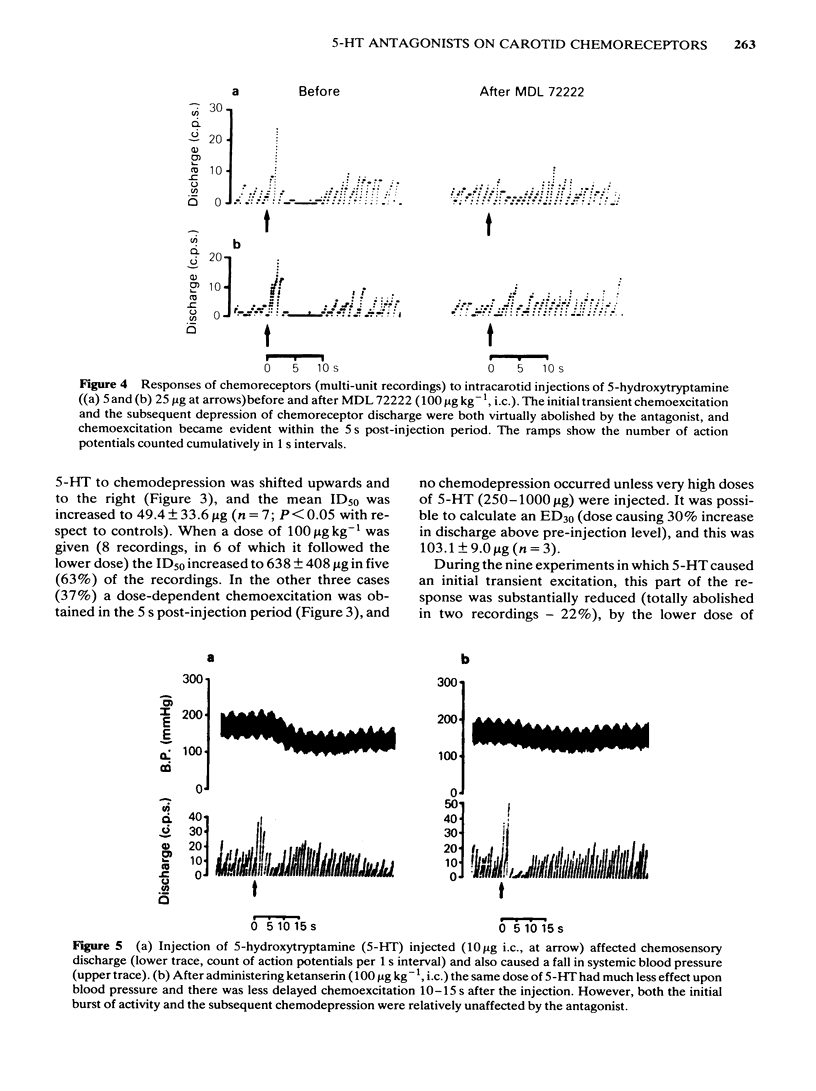
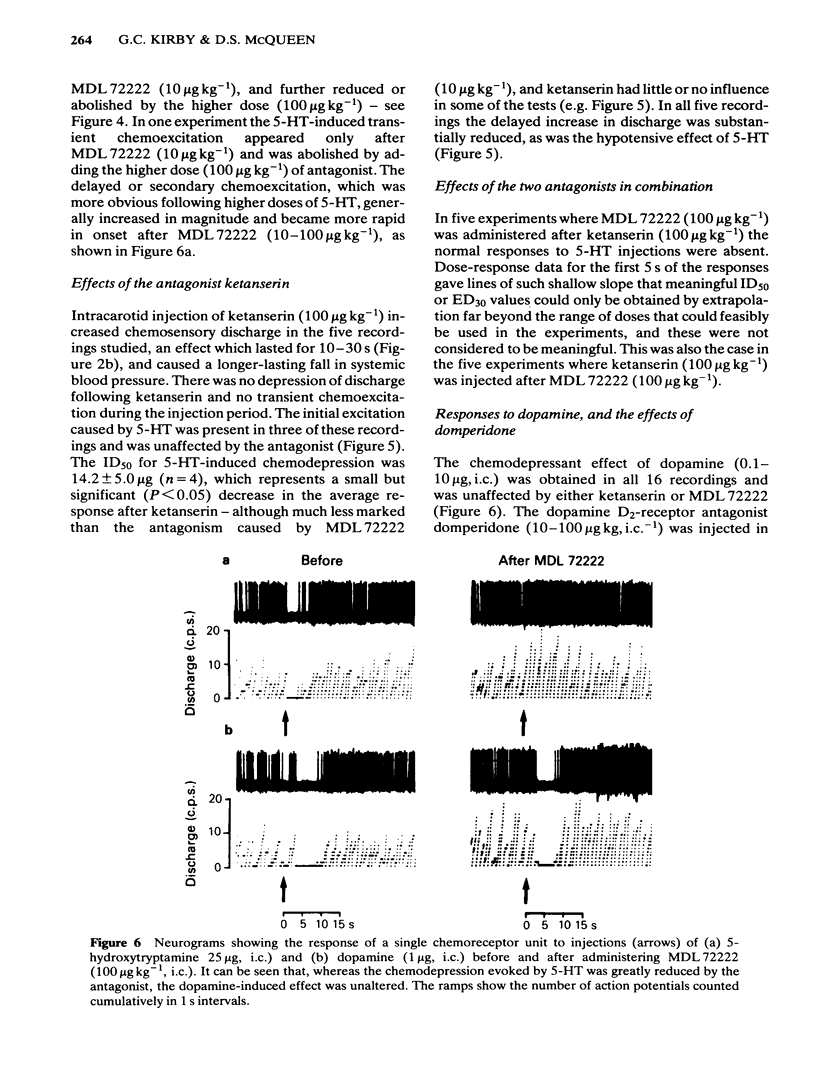
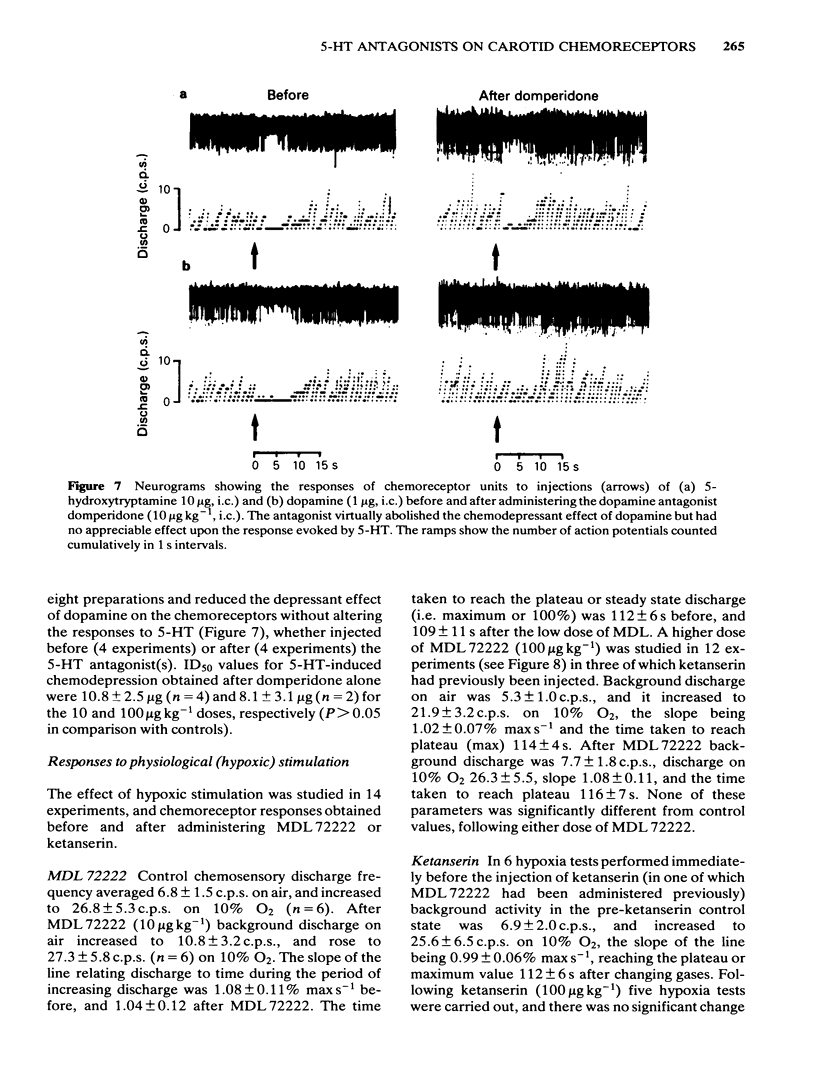
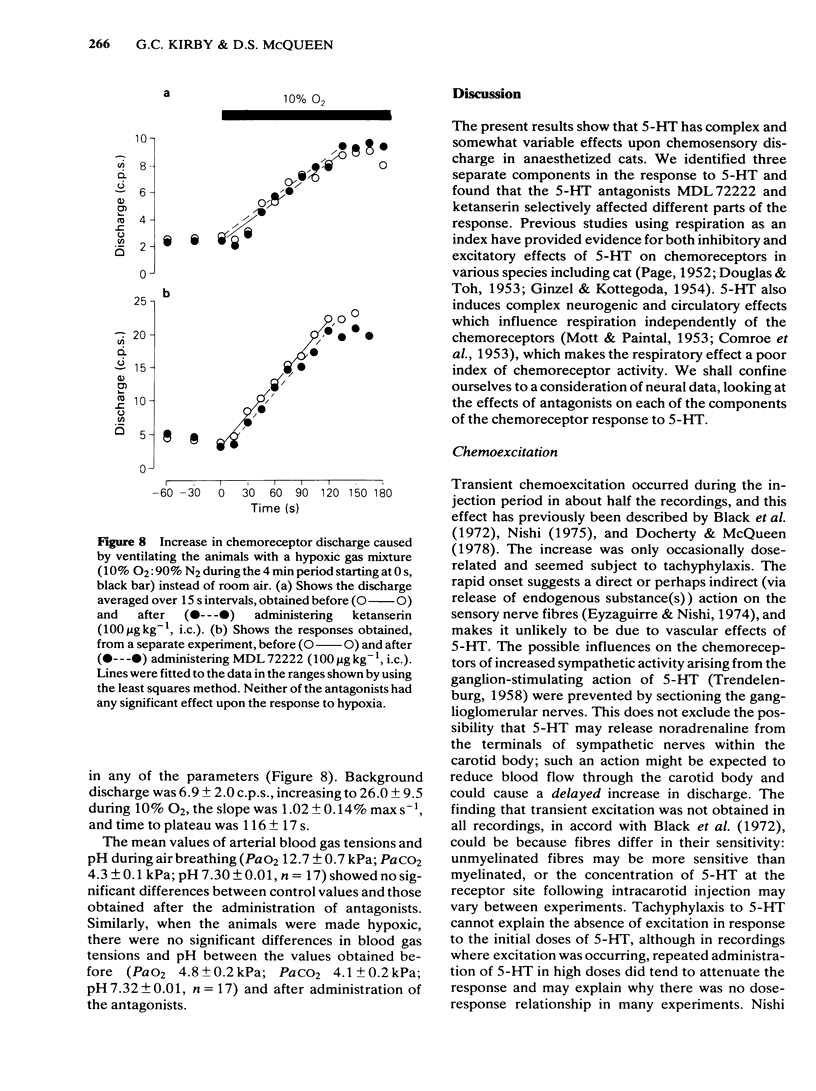
The effects of intracarotid (i.c.) injections of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT; 1-50 micrograms) on carotid chemoreceptor activity recorded from the carotid sinus nerve have been studied in anaesthetized cats. Three separate components in the complex response of the chemoreceptors to injected 5-HT were identified. Firstly, a transient burst of activity was obtained during the injection period in 56% of the recordings. Secondly, in all the recordings a period of chemodepression commenced a few seconds after completing the injection and was usually dose-related. Thirdly, a delayed longer-lasting chemoexcitation occurred in many experiments, concomitant with a fall in systemic blood pressure. The neuronal 5-HT receptor antagonist MDL 72222 (10-100 micrograms kg-1, i.c.) virtually abolished the transient chemoexcitation evoked during 5-HT injections and also significantly increased the mean ID50 for 5-HT-induced chemodepression; in 37% of recordings 5-HT caused a dose-related chemoexcitation after the high dose of MDL 72222. Neither the delayed chemoexcitation nor the hypotension caused by 5-HT were much affected by the antagonist. MDL 72222 itself had a biphasic effect on chemosensory discharge, causing depression followed by a delayed excitation. The 5-HT2-receptor antagonist ketanserin (100 micrograms kg-1, i.c.) had no appreciable effect on the transient chemoexcitation evoked during 5-HT injections and caused a slight but significant increase in the mean ID50 for 5-HT-induced chemodepression. The delayed chemoexcitation and accompanying hypotension associated with 5-HT were both substantially reduced or abolished by the antagonist. Ketanserin itself caused a short-lasting period of chemoexcitation. All the effects of injected 5-HT on chemosensory discharge could be abolished by the combination of MDL 72222 and ketanserin (100 micrograms kg-1, i.c.). Neither MDL 72222 nor ketanserin had any significant effect upon the response of the carotid chemoreceptors to hypoxia. The rate at which discharge increased, and also the steady-state discharge before and during hypoxia, were unaffected by the antagonists, alone or in combination. At least two types of 5-HT receptor appeared to be involved in the response of carotid body chemoreceptors to 5-HT. Transient excitation and chemodepression were mediated via MDL 72222-sensitive (peripheral neuronal) receptors whereas the delayed chemoexcitation and associated hypotension involved a ketanserin-sensitive, presumably 5-HT2-, receptor. It appears unlikely that 5-HT plays a crucial role in chemoreception.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black A. M., Comroe J. H., Jr, Jacobs L. Species difference in carotid body response of cat and dog to dopamine and serotonin. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1097–1102. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMROE J. H., Jr, VAN LINGEN B., STROUD R. C., RONCORONI A. Reflex and direct cardiopulmonary effects of 5-OH-tryptamine (serotonin); their possible role in pulmonary embolism and coronary thrombosis. Am J Physiol. 1953 Jun;173(3):379–386. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.173.3.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiocchio S. R., Biscardi A. M., Tramezzani J. H. 5-hydroxytryptamine in the carotid body of the cat. Science. 1967 Nov 10;158(3802):790–791. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3802.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuello A. C., McQueen D. S. Substance P: a carotid body peptide. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Apr;17(1-2):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., TOH C. C. The respiratory stimulant action of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) in the dog. J Physiol. 1953 May 28;120(3):311–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty R. J., McQueen D. S. Inhibitory action of dopamine on cat carotid chemoreceptors. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:425–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyzaguirre C., Nishi K. Further study on mass receptor potential of carotid body chemosensors. J Neurophysiol. 1974 Jan;37(1):156–169. doi: 10.1152/jn.1974.37.1.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fozard J. R. MDL 72222: a potent and highly selective antagonist at neuronal 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 May;326(1):36–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00518776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINZEL K. H., KOTTEGODA S. R. The action of 5-hydroxytryptamine and tryptamine on aortic and carotid sinus receptors in the cat. J Physiol. 1954 Feb 26;123(2):277–288. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GYERMEK L. 5-hydroxytryptamine antagonists. Pharmacol Rev. 1961 Sep;13:399–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönblad M., Liesi P., Rechardt L. Serotonin-like immunoreactivity in rat carotid body. Brain Res. 1983 Oct 16;276(2):348–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90745-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Ljungdahl A., Lundberg J. M., Schultzberg M. Peptidergic neurones. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):515–521. doi: 10.1038/284515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Calne D. B. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. doi: 10.1038/277093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leysen J. E., Awouters F., Kennis L., Laduron P. M., Vandenberk J., Janssen P. A. Receptor binding profile of R 41 468, a novel antagonist at 5-HT2 receptors. Life Sci. 1981 Mar 2;28(9):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90747-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAJNO G., PALADE G. E. Studies on inflammation. 1. The effect of histamine and serotonin on vascular permeability: an electron microscopic study. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:571–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOTT J. C., PAINTAL A. S. The action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on pulmonary and cardiovascular vagal afferent fibres and its reflex respiratory effects. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1953 Jun;8(2):238–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1953.tb00786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen D. S. A quantitative study of the effects of cholinergic drugs on carotid chemoreceptors in the cat. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):515–532. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi K. The action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on chemoreceptor discharges of the cat's carotid body. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Sep;55(1):27–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAGE I. H. The vascular action of natural serotonin, 5- and 7-hydroxytryptamine and tryptamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1952 May;105(1):58–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele R. H., Hinterberger H. Catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the carotid body in vascular, respiratory, and other diseases. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Jul;80(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis D. Neuronal 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors outside the central nervous system. Life Sci. 1981 Dec 7;29(23):2345–2355. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90470-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


