Abstract
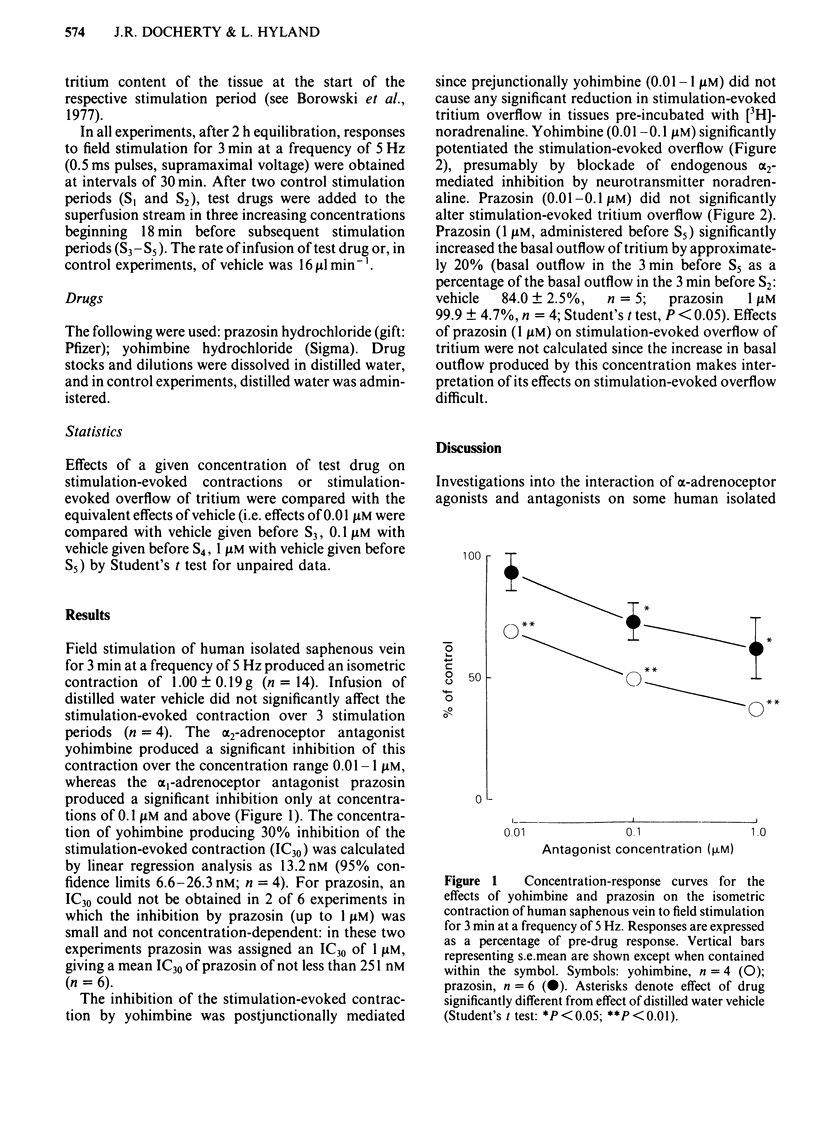
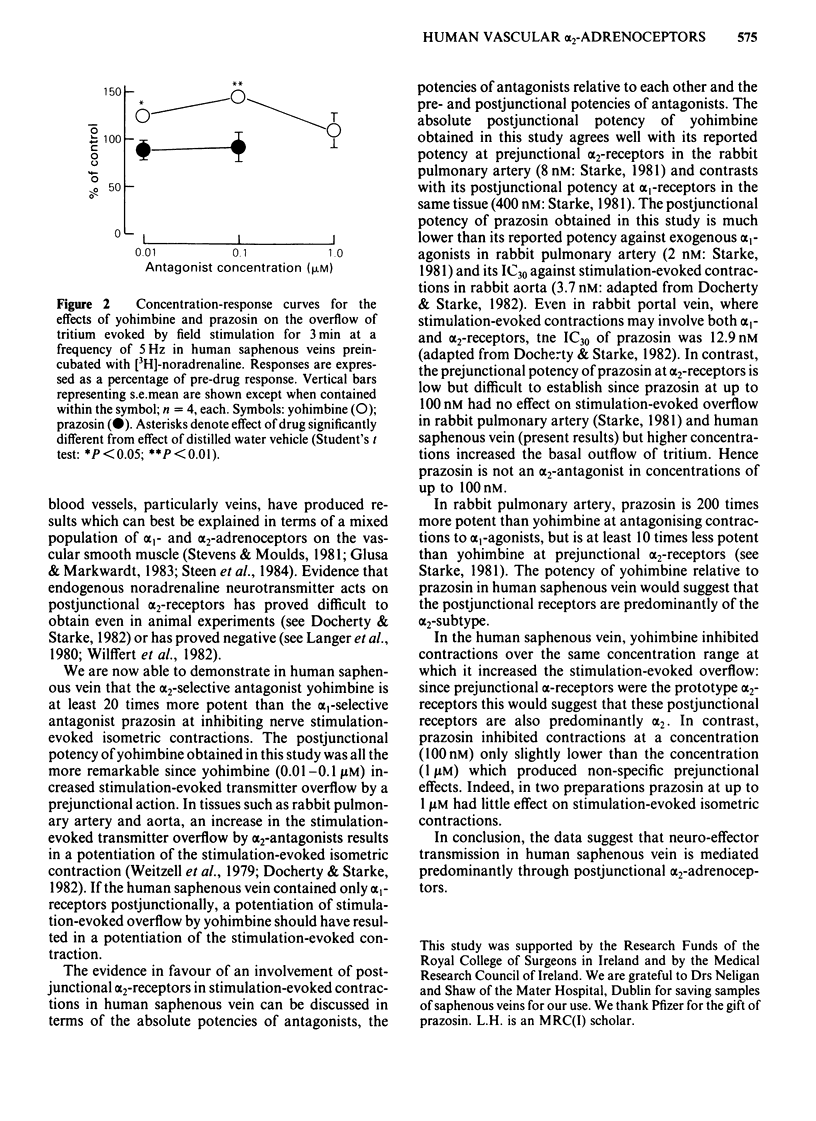
The effects of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist prazosin and the alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist yohimbine were examined against stimulation-evoked contractions in human isolated saphenous veins. The concentration of yohimbine producing 30% inhibition of stimulation-evoked contractions (IC30) was 13.2 nM, whereas the IC30 of prazosin was greater than 250 nM. The inhibition of stimulation-evoked contractions by yohimbine was not prejunctionally mediated since yohimbine (0.01-0.1 microM) significantly potentiated the stimulation-evoked overflow of tritium in tissues pre-incubated with [3H]-noradrenaline. The high potency of yohimbine and the low potency of prazosin indicate that neuro-effector transmission in human saphenous vein is mediated predominantly by postjunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borowski E., Starke K., Ehrl H., Endo T. A comparison of pre- and postsynaptic effects of alpha-adrenolytic drugs in the pulmonary artery of the rabbit. Neuroscience. 1977;2(2):285–296. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambridge D., Davey M. J., Massingham R. Prazosin, a selective antagonist of post-synaptic alpha-adrenoceptors [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;59(3):514P–515P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantine J. W., Lebel W., Archer R. Functional postsynaptic alpha 2- but not alpha 1-adrenoceptors in dog saphenous vein exposed to phenoxybenzamine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 3;85(3-4):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., McGrath J. C. A comparison of pre- and post-junctional potencies of several alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the cardiovascular system and anococcygeus muscle of the rat. Evidence for two types of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;312(2):107–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00569718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., Starke K. An examination of the pre- and postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors involved in neuroeffector transmission in rabbit aorta and portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jun;76(2):327–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M., Whiting S. B. Evidence for two distinct types of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in vascular smooth muscle in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;67(2):207–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott H. L., Reid J. L. Evidence for postjunctional vascular alpha 2-adrenoceptors in peripheral vascular regulation in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Sep;65(3):237–241. doi: 10.1042/cs0650237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glusa E., Markwardt F. Characterisation of postjunctional alpha-adrenoceptors in isolated human femoral veins and arteries. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;323(2):101–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00634256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z., Massingham R., Shepperson N. B. Presence of postsynaptic alpha 2-adrenoreceptors of predominantly extrasynaptic location in the vascular smooth muscle of the dog hind limb. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Dec;59 (Suppl 6):225s–228s. doi: 10.1042/cs059225s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Evidence for more than one type of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):467–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schümann H. J., Lues I. Postjunctional alpha-adrenoceptors in the isolated saphenous vein of the rabbit. Characterization and influence of angiotensin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Aug;323(4):328–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00512471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha-adrenoceptor subclassification. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;88:199–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steen S., Skärby T. V., Norgren L., Andersson K. E. Pharmacological characterization of postjunctional alpha-adrenoceptors in isolated human omental arteries and veins. Acta Physiol Scand. 1984 Jan;120(1):109–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1984.tb07379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens M. J., Moulds R. F. Heterogeneity of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptors in human vascular smooth muscle. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1981 Nov;254(1):43–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzell R., Tanaka T., Starke K. Pre- and postsynaptic effects of yohimbine stereoisomers on noradrenergic transmission in the pulmonary artery of the rabbit. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;308(2):127–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00499054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilffert B., Timmermans P. B., van Zwieten P. A. Extrasynaptic location of alpha-2 and noninnervated beta-2 adrenoceptors in the vascular system of the pithed normotensive rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Jun;221(3):762–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


