Annual influenza vaccination is recommended for immunocompromised patients.1,2 Rituximab, an anti‐CD20 monoclonal antibody, recently approved by American and European authorities for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients failing tumour necrosis factor (TNF)‐blocking agents, diminishes the number of circulating B cells for a period of six to nine months after infusion.3,4 Circulating plasma cells and immunoglobulin levels are not affected by this therapy. Based on data in lymphoma patients, the package insert states that patients should not be vaccinated from one month before the administration of rituximab until six months after.5,6 In those studies the underlying lymphoma and treatment with chemotherapy contributed to the diminished immunological response. The effect of rituximab on the outcome of influenza vaccination in RA is not known.
We examined the humoral response upon influenza vaccination in four RA patients (three women, age range 55–61 years) treated with rituximab (1000 mg intravenously on days 0 and 14) combined with methotrexate (5–20 mg a week) and additional prednisone (5 mg) in one patient. Nineteen RA patients treated with TNF‐blocking agents with or without disease‐modifying antirheumatic drugs (79% women, mean age 56 years, range 40–71), and 20 healthy individuals (50% women, mean age 45 years, range 19–77) acted as controls. The three groups were well matched with respect to sex, age, prevaccination titres and previous influenza vaccination. Both patient groups had high disease activity scores (mean DAS28 3.47 and 4.44 for RA patients treated with rituximab and anti‐TNF, respectively, p = 0.088, analysis of variance). Participants were vaccinated intramuscularly with a trivalent subunit vaccine (0.5 ml Influvac 2005–2006; Solvay, Weesp, the Netherlands). Haemagglutination‐inhibition titres were measured just before vaccination and 28 days later, as described before.7,8 Absolute lymphocyte counts were analysed using TruCOUNT tubes by flowcytometry. B cells were completely depleted (<1×106 cells/l) in all four patients from day 28 to day 84 after the first rituximab infusion. The vaccine was administered shortly after day 84, with only marginal B‐cell reconstitution at the time of vaccination (median B‐cell count <10×106 cells/l). As a result of low B‐cell and patient numbers no trends could be determined in B‐cell subsets.
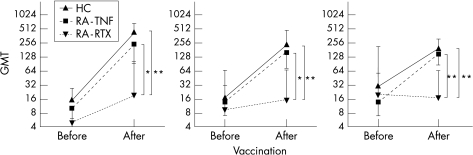
Even though only four RA patients treated with rituximab were evaluated, we found significantly lower postvaccination titres (fig. 1) and protection rates (the proportion of a group with a titre ⩾40) in comparison with both control groups for all three antigens. These findings could not be explained by differences in disease activity. One other study reported a significantly lower response rate for only one out of three antigens in RA patients treated with rituximab.9 The comparability with our results is limited because responses were poor in all groups and no information was provided on the dose of rituximab and number of B cells at the time of vaccination.
Figure 1 Pre and postvaccination serum geometric mean titres (GMT), with 95% confidence intervals, against influenza A/H3N2, A/H1N1 and influenza B for a group of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treated with rituximab (RA–RTX; n = 4), compared with RA patients treated with anti‐tumour necrosis factor (TNF; RA–TNF; n = 19) and healthy controls (HC; n = 20). *p⩽0.02; **p⩽0.001.
The present study shows that influenza vaccination, although not completely ineffective, will probably not protect rituximab‐treated RA patients sufficiently against influenza infection. Larger studies are warranted to confirm our findings.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ruud van Beek of the Department of Virology, Erasmus Medical Center, for his expert technical assistance. Solvay Pharma kindly provided the vaccines used in this study.
Abbreviations
RA - Rheumatoid arthritis
TNF - tumour necrosis factor
References
- 1.Smith N M, Bresee J S, Shay D K.et al Prevention and control of influenza: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep 2006551–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chalmers A, Scheifele D, Patterson C.et al Immunization of patients with rheumatoid arthritis against influenza: a study of vaccine safety and immunogenicity. J Rheumatol 1994211203–1206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Edwards J C, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J.et al Efficacy of B‐cell‐targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 20043502572–2581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Leandro M J, Cambridge G, Ehrenstein M R, Edwards J C. Reconstitution of peripheral blood B cells after depletion with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 200654613–620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Horwitz S M, Negrin R S, Blume K G.et al Rituximab as adjuvant to high‐dose therapy and autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation for aggressive non‐Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2004103777–783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.van der Kolk L E, Baars J W, Prins M H, van Oers M H. Rituximab treatment results in impaired secondary humoral immune responsiveness. Blood 20021002257–2259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Palmer D F, Dowdle W R, Coleman M T, Schild G C.Haemagglutination‐inhibition test. Advanced laboratory techniques for influenza diagnosis. Procedural guide. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health, Education and Welfare, Public Health Service, Center for Disease Control, 197525–62.
- 8.Masurel N, Ophof P, de Jong P. Antibody response to immunization with influenza A/USSR/77 (H1N1) virus in young individuals primed or unprimed for A/New Jersey/76 (H1N1) virus. J Hyg (Lond) 198187201–209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Oren C, Mendelbaum M, Paran D.et al Vaccination against influenza in rheumatoid arthritis patients: the effect of rituximab on the humoral response. ACR. 2006 abstract no. 1234