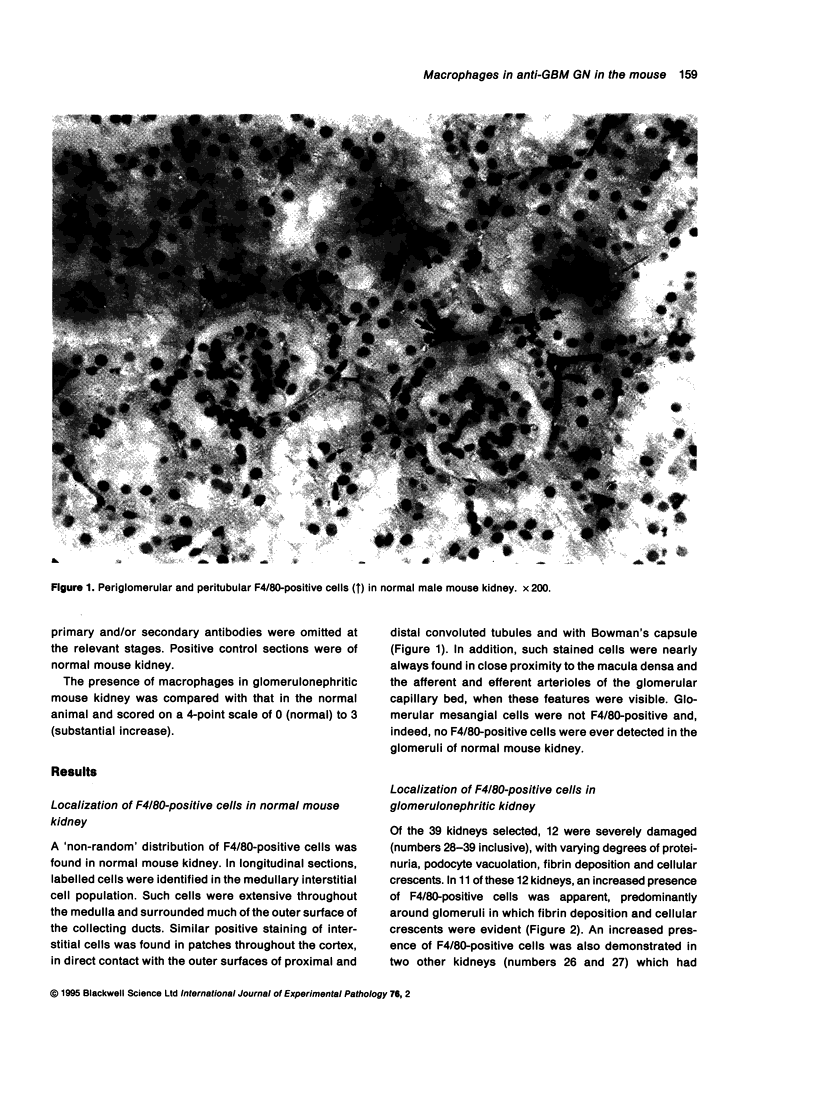
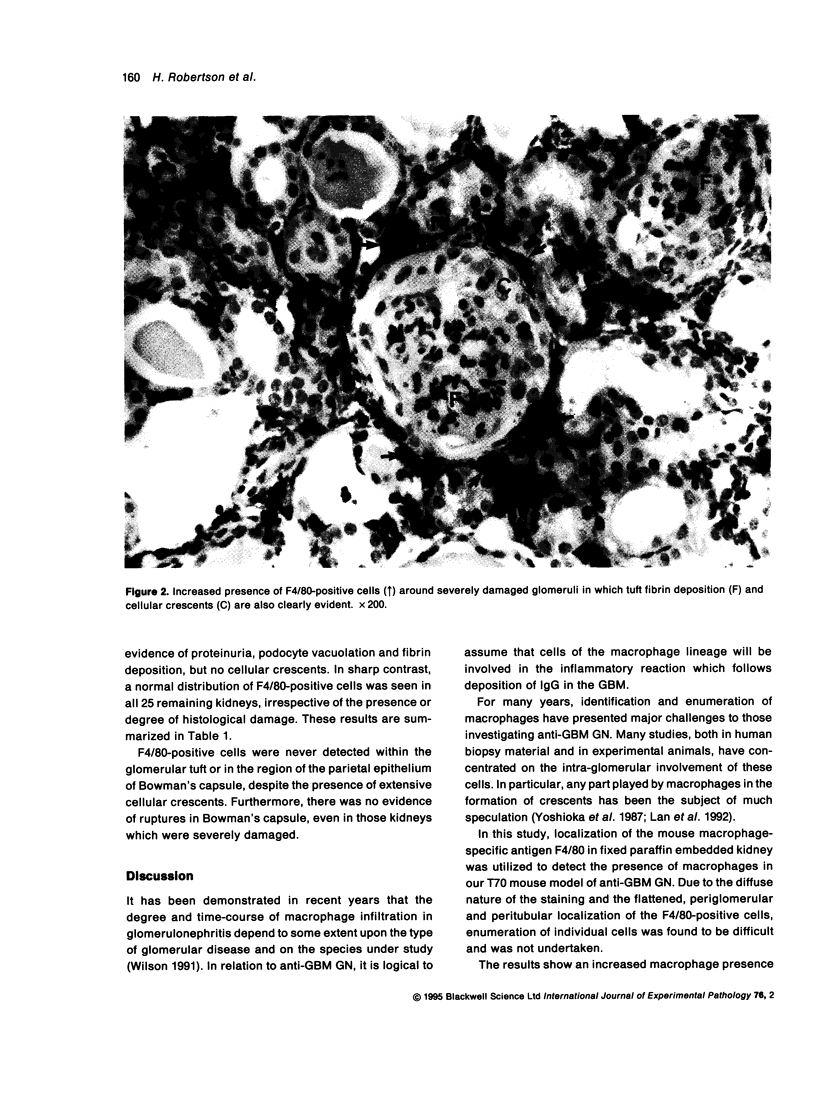
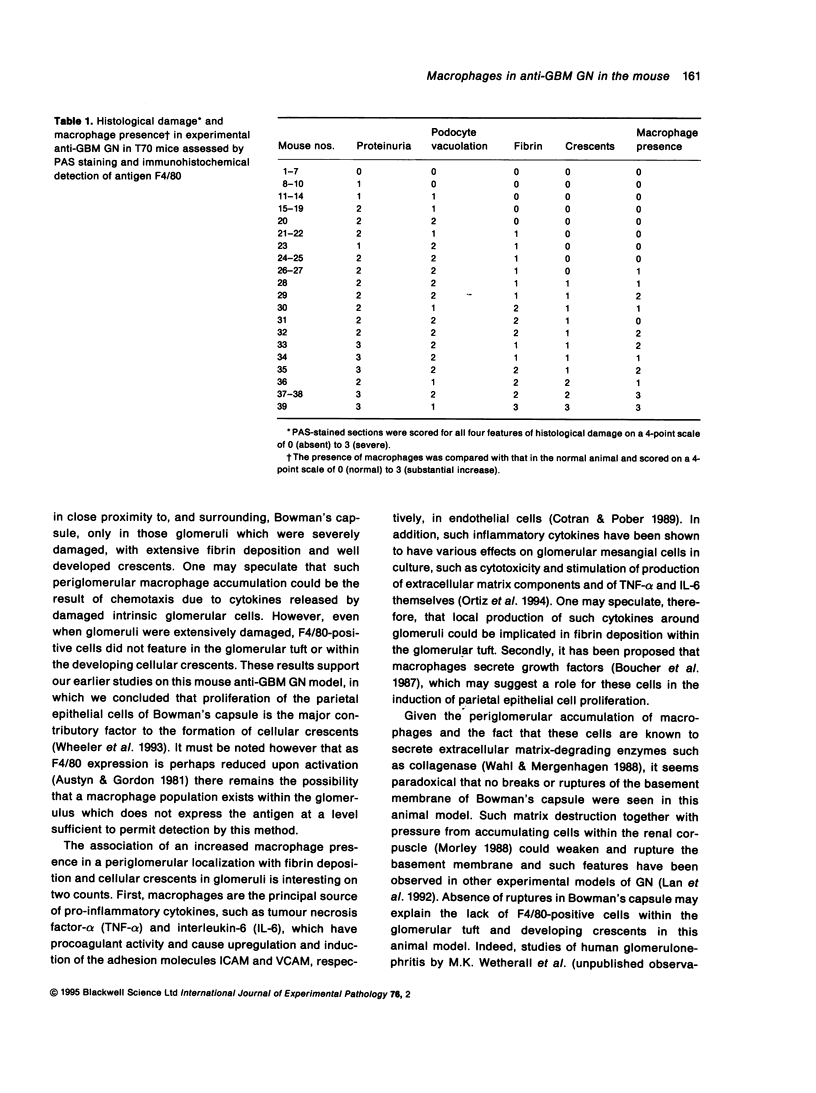
Abstract
An immunohistochemical study was undertaken on fixed, paraffin-embedded mouse kidney in order to elucidate the role and significance of infiltrating macrophages in a mouse model of anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis (anti-GBM GN). Tissue was available representing the full gamut of histological features seen in this model. The mouse macrophage-specific antigen F4/80 was detected in tissue sections of glomerulonephritic kidney and the pattern and extent of staining was compared with normal mouse kidney. In glomerulonephritic kidney, an increase in the number of F4/80-positive cells was evident in close proximity to and surrounding Bowman's capsule of those glomeruli which were severely damaged, with extensive fibrin deposition and well developed cellular crescents. F4/80-positive cells did not feature in the glomerular tuft or in the region of the parietal epithelium of Bowman's capsule even when extensive cellular crescents were present. Breaks in Bowman's capsule were not demonstrated. We conclude that F4/80-positive macrophages are not a major constitutive cell type of developing crescents in this mouse model of anti-GBM GN but, by virtue of their peri-glomerular localization, may be involved in the destructive process, perhaps producing signalling molecules which contribute to the inflammatory reaction.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abboud H. E. Platelet-derived growth factor and mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1992 Mar;41(3):581–583. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austyn J. M., Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Oct;11(10):805–815. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher A., Droz D., Adafer E., Noël L. H. Relationship between the integrity of Bowman's capsule and the composition of cellular crescents in human crescentic glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1987 May;56(5):526–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotran R. S., Pober J. S. Effects of cytokines on vascular endothelium: their role in vascular and immune injury. Kidney Int. 1989 Apr;35(4):969–975. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume D. A., Gordon S. Mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localization of antigen F4/80. Identification of resident macrophages in renal medullary and cortical interstitium and the juxtaglomerular complex. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1704–1709. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume D. A., Robinson A. P., MacPherson G. G., Gordon S. The mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localization of antigen F4/80. Relationship between macrophages, Langerhans cells, reticular cells, and dendritic cells in lymphoid and hematopoietic organs. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1522–1536. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraal G., Rep M., Janse M. Macrophages in T and B cell compartments and other tissue macrophages recognized by monoclonal antibody MOMA-2. An immunohistochemical study. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Dec;26(6):653–661. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan H. Y., Nikolic-Paterson D. J., Atkins R. C. Involvement of activated periglomerular leukocytes in the rupture of Bowman's capsule and glomerular crescent progression in experimental glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1992 Dec;67(6):743–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Starkey P. M., Gordon S. Quantitative analysis of total macrophage content in adult mouse tissues. Immunochemical studies with monoclonal antibody F4/80. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):475–489. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malorny U., Michels E., Sorg C. A monoclonal antibody against an antigen present on mouse macrophages and absent from monocytes. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;243(2):421–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00251059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz A., Gómez-Chiarri M., Alonso J., Bustos C., Gómez-Guerrero C., López-Armada M. J., Gómez-Garre D., Palacios I., Ruíz-Ortega M., Gutierrez S. The potential role of inflammatory and fibrogenic cytokines in the glomerular diseases. J Lipid Mediat Cell Signal. 1994 Feb;9(1):55–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F. The role of the macrophage in glomerular injury. Semin Nephrol. 1991 May;11(3):268–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T., Galfrè G., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Monoclonal xenogeneic antibodies to murine cell surface antigens: identification of novel leukocyte differentiation antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):539–551. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl L. M., Mergenhagen S. E. Regulation of monocyte/macrophage collagenase. J Oral Pathol. 1988 Nov;17(9-10):452–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1988.tb01314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler J., Morley A. R., Appleton D. R. Anti-glomerular basement membrane (GBM) glomerulonephritis in the mouse: development of disease and cell proliferation. J Exp Pathol (Oxford) 1990 Jun;71(3):411–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler J., Robertson H., Morley A. R., Appleton D. R. Anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis (anti-GBM GN) in the mouse: BrdU-labelling indices and histological damage. Int J Exp Pathol. 1993 Feb;74(1):9–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka K., Takemura T., Akano N., Miyamoto H., Iseki T., Maki S. Cellular and non-cellular compositions of crescents in human glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1987 Aug;32(2):284–291. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]