Abstract
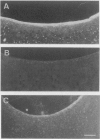
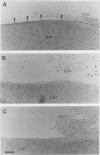
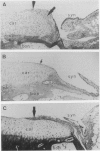
In rheumatoid arthritis, pannus formation resulting from synovial inflammation is a major factor in cartilage destruction. The ability of arthritic synovial cells to undergo pannus formation depends upon their initial adhesion to the partially deformed cartilage surfaces. Our recent studies using various lipid-derivatized glycosaminoglycans have revealed a preeminent inhibitory activity of phosphatidyl ethanol amine-derivatized chondroitin sulphate (CS-PE) toward cell-matrix adhesion. Here we evaluate whether CS-PE may protect articular cartilage from pannus extension in different in vitro and in vivo model systems using Escherichia coli 0:14-induced arthritis in rabbits and the articular cartilage explants, synovial tissues, and synovial cells obtained from them. These studies showed that CS-PE suppressed the in vivo pannus-like extension on cartilage surfaces, as well as the in vitro extension of the synovial cell layer on both CS-PE treated culture plates and cartilage explants. The results suggest that native chondroitin sulphate proteoglycans in the surface of normal articular cartilage play an important role in protecting the tissues from pannus extension and that the CS-PE immobilized onto partially eroded cartilage can mimic the inhibitory action of native chondroitin sulphate proteoglycans.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki S., Ikuta K., Aoyama G. Induction of chronic polyarthritis in rabbits. Nature. 1972 May 19;237(5351):168–169. doi: 10.1038/237168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki S., Ikuta K., Nonogaki T., Ito Y. Induction of chronic polyarthritis in rabbits by hyperimmunization with Escherichia coli. I. Pathologic and serologic features in two breeds of rabbits. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 May;28(5):522–528. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensouyad A., Hollander A. P., Dularay B., Bedwell A. E., Cooper R. A., Hutton C. W., Dieppe P. A., Elson C. J. Concentrations of glycosaminoglycans in synovial fluids and their relation with immunological and inflammatory mediators in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 May;49(5):301–307. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.5.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidanset D. J., LeBaron R., Rosenberg L., Murphy-Ullrich J. E., Hook M. Regulation of cell substrate adhesion: effects of small galactosaminoglycan-containing proteoglycans. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1523–1531. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. J., Oldberg A., Hayman E. G., Ruoslahti E. Effect of a proteoglycan produced by rat tumor cells on their adhesion to fibronectin-collagen substrata. Cancer Res. 1983 Sep;43(9):4302–4307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fell H. B., Jubb R. W. The effect of synovial tissue on the breakdown of articular cartilage in organ culture. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Sep-Oct;20(7):1359–1371. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander D. R., Milev P., Karthikeyan L., Margolis R. K., Margolis R. U., Grumet M. The neuronal chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan neurocan binds to the neural cell adhesion molecules Ng-CAM/L1/NILE and N-CAM, and inhibits neuronal adhesion and neurite outgrowth. J Cell Biol. 1994 May;125(3):669–680. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Tateishi H., Ziff M. Surface ultrastructure of rheumatoid articular cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jun;20(5):1085–1094. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella M. G., Wight T. N. Modulation of sulfated proteoglycan synthesis by bovine aortic endothelial cells during migration. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):679–687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martel-Pelletier J., Pelletier J. P., Cloutier J. M., Rebert N., Malemud C. J. Proteoglycan structural changes in human rheumatoid articular cartilage. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992 Mar-Apr;10(2):151–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed-Ali H. Influence of synovial cells on cartilage in vitro: induction of breakdown and inhibition of synthesis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1992;62(4):227–236. doi: 10.1007/BF02899686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogamo A., Matsuzaki K., Uchiyama H., Nagasawa K. Preparation and properties of fluorescent glycosaminoglycuronans labeled with 5-aminofluorescein. Carbohydr Res. 1982 Jul 1;105(1):69–85. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)81855-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perris R., Johansson S. Amphibian neural crest cell migration on purified extracellular matrix components: a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan inhibits locomotion on fibronectin substrates. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2511–2521. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. The Walter Herbert Lecture. Control of cell motility and tumour invasion by extracellular matrix interactions. Br J Cancer. 1992 Aug;66(2):239–242. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J. Tumour necrosis factor alpha stimulates resorption and inhibits synthesis of proteoglycan in cartilage. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):547–549. doi: 10.1038/322547a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinmei M., Miyauchi S., Machida A., Miyazaki K. Quantitation of chondroitin 4-sulfate and chondroitin 6-sulfate in pathologic joint fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Nov;35(11):1304–1308. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozawa S., Yoshihara R., Kuroki Y., Fujita T., Shiozawa K., Imura S. Pathogenic importance of fibronectin in the superficial region of articular cartilage as a local factor for the induction of pannus extension on rheumatoid articular cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Jul;51(7):869–873. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.7.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow D. M., Letourneau P. C. Neurite outgrowth on a step gradient of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (CS-PG). J Neurobiol. 1992 Apr;23(3):322–336. doi: 10.1002/neu.480230311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow D. M., Watanabe M., Letourneau P. C., Silver J. A chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan may influence the direction of retinal ganglion cell outgrowth. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1473–1485. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus A. H., Carter W. G., Wayner E. A., Hakomori S. Mechanism of fibronectin-mediated cell migration: dependence or independence of cell migration susceptibility on RGDS-directed receptor (integrin). Exp Cell Res. 1989 Jul;183(1):126–139. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90423-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura N., Sakurai K., Hori Y., Karasawa K., Suzuki S., Kimata K. Preparation of lipid-derivatized glycosaminoglycans to probe a regulatory function of the carbohydrate moieties of proteoglycans in cell-matrix interaction. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15779–15787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiku M. L., Teodorescu M., Skosey J. L. Immunobiological function of normal rabbit synovial cells. Cell Immunol. 1985 Apr 1;91(2):415–424. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90239-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winnemöller M., Schmidt G., Kresse H. Influence of decorin on fibroblast adhesion to fibronectin. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;54(1):10–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witter J., Roughley P. J., Webber C., Roberts N., Keystone E., Poole A. R. The immunologic detection and characterization of cartilage proteoglycan degradation products in synovial fluids of patients with arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 May;30(5):519–529. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata M., Saga S., Kato M., Bernfield M., Kimata K. Selective distributions of proteoglycans and their ligands in pericellular matrix of cultured fibroblasts. Implications for their roles in cell-substratum adhesion. J Cell Sci. 1993 Sep;106(Pt 1):55–65. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata M., Suzuki S., Akiyama S. K., Yamada K. M., Kimata K. Regulation of cell-substrate adhesion by proteoglycans immobilized on extracellular substrates. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8012–8018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]