Abstract
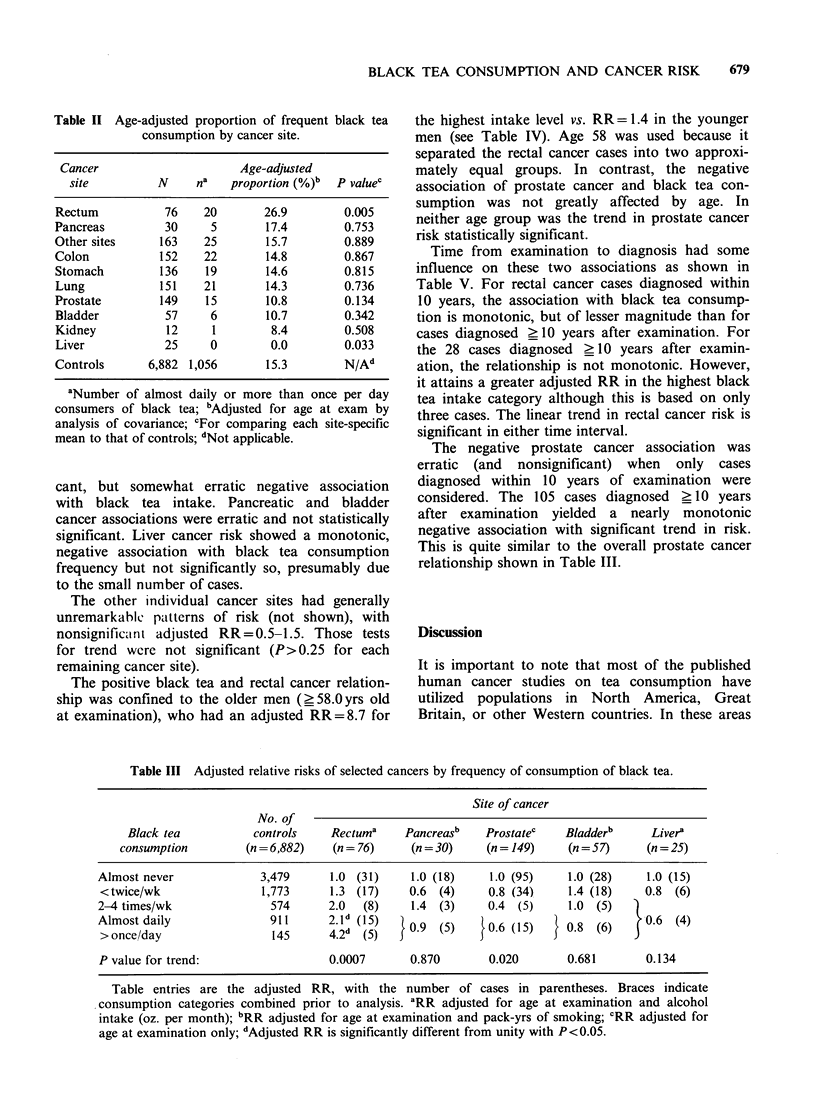
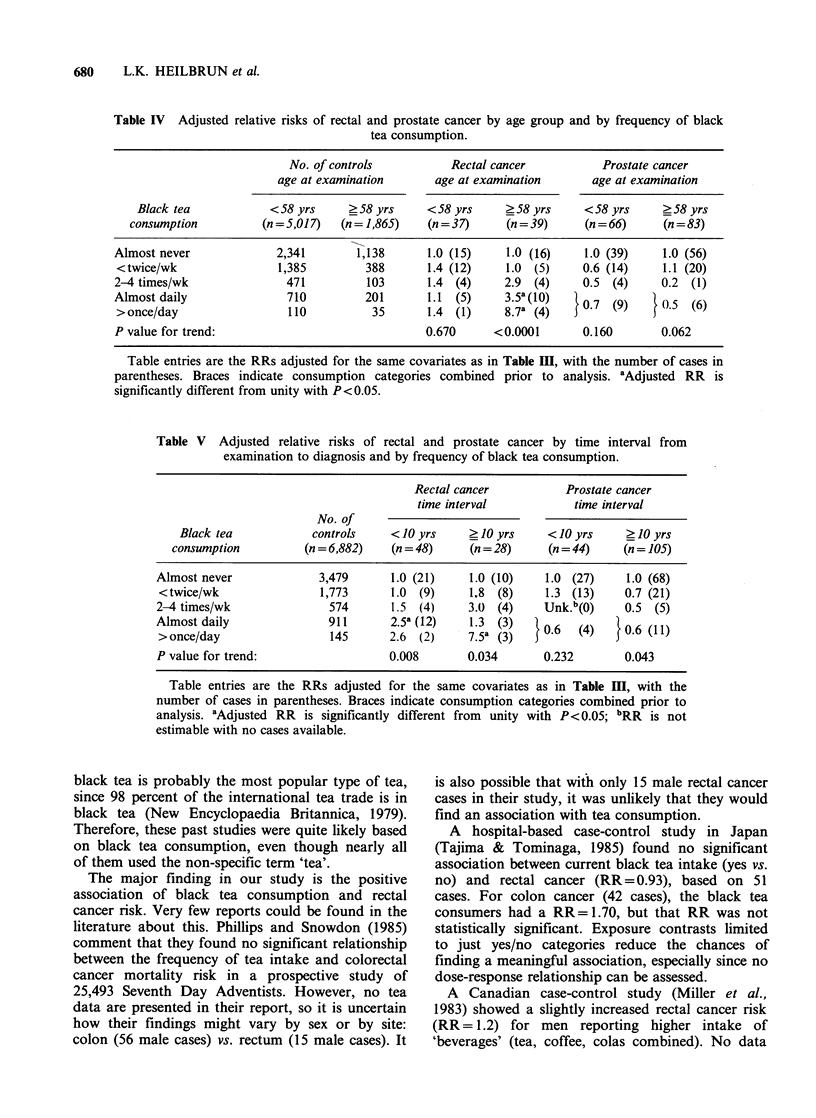
In a prospective cohort study, men of Japanese ancestry were clinically examined from 1965 to 1968. For 7,833 of these men, data on black tea consumption habits were recorded. Since 1965, newly diagnosed cancer incidence cases have been identified: 152 colon, 151 lung, 149 prostate, 136 stomach, 76 rectum, 57 bladder, 30 pancreas, 25 liver, 12 kidney and 163 at other (miscellaneous) sites. Compared to almost-never drinkers, men habitually drinking black tea more than once/day had an increased relative risk (RR) for rectal cancer (RR = 4.2). This positive association (P = 0.0007) could not be accounted for by age or alcohol intake. We also observed a weaker but significant negative association of black tea intake and prostate cancer incidence (P = 0.020). There were no significant associations between black tea consumption and cancer at any other site.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong B., Garrod A., Doll R. A retrospective study of renal cancer with special reference to coffee and animal protein consumption. Br J Cancer. 1976 Feb;33(2):127–136. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichel J., Bach A. Investigation on the toxicity of small chronic doses of tannic acid with special reference to possible carcinogenicity. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1968;26(1):41–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1967.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokuchava M. A., Skobeleva N. I. The biochemistry and technology of tea manufacture. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1980;12(4):303–370. doi: 10.1080/10408398009527280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartge P., Hoover R., West D. W., Lyon J. L. Coffee drinking and risk of bladder cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Jun;70(6):1021–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe G. R., Burch J. D., Miller A. B., Cook G. M., Esteve J., Morrison B., Gordon P., Chambers L. W., Fodor G., Winsor G. M. Tobacco use, occupation, coffee, various nutrients, and bladder cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Apr;64(4):701–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. Induction of tumours by tannin extracts. Br J Cancer. 1960 Mar;14:147–150. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1960.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORPASSY B., MOSONYI M. The carcinogenic activity of tannic acid; liver tumours induced in rats by prolonged subcutaneous administration of tannic acid solutions. Br J Cancer. 1950 Dec;4(4):411–420. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1950.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser H. E. Cancer-promoting effects of phenols in tea. Cancer. 1967 May;20(5):614–616. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(1967)20:5<614::aid-cncr2820200506>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapadia G. J., Paul B. D., Chung E. B., Ghosh B., Pradhan S. N. Carcinogenicity of Camellia sinensis (tea) and some tannin-containing folk medicinal herbs administered subcutaneously in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Jul;57(1):207–209. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.1.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinlen L. J., McPherson K. Pancreas cancer and coffee and tea consumption: a case-control study. Br J Cancer. 1984 Jan;49(1):93–96. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMahon B., Yen S., Trichopoulos D., Warren K., Nardi G. Coffee and cancer of the pancreas. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 12;304(11):630–633. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103123041102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack T. M., Yu M. C., Hanisch R., Henderson B. E. Pancreas cancer and smoking, beverage consumption, and past medical history. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Jan;76(1):49–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. K., Blot W. J., Mandel J. S., Schuman L. M., Mehl E. S., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Etiology of cancer of the renal pelvis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Aug;71(2):287–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. K., Mandel J. S., Blot W. J., Schuman L. M., Mehl E. S., Fraumeni J. F., Jr A population--based case--control study of renal cell carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Feb;72(2):275–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. B., Howe G. R., Jain M., Craib K. J., Harrison L. Food items and food groups as risk factors in a case-control study of diet and colo-rectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 1983 Aug 15;32(2):155–161. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910320204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. T., Neutel C. I., Nair R. C., Marrett L. D., Last J. M., Collins W. E. Relative importance of risk factors in bladder carcinogenesis. J Chronic Dis. 1978 Jan;31(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(78)90080-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. W., Jain M. G. Bladder cancer: smoking, beverages and artificial sweeteners. Can Med Assoc J. 1974 Nov 16;111(10):1067–1070. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao M., Takahashi Y., Yamanaka H., Sugimura T. Mutagens in coffee and tea. Mutat Res. 1979 Oct;68(2):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(79)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. L., Snowdon D. A. Dietary relationships with fatal colorectal cancer among Seventh-Day Adventists. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 Feb;74(2):307–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack E. S., Nomura A. M., Heilbrun L. K., Stemmermann G. N., Green S. B. Prospective study of alcohol consumption and cancer. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 8;310(10):617–621. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403083101003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemmermann G. N., Nomura A. M., Heilbrun L. K. Dietary fat and the risk of colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1984 Oct;44(10):4633–4637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocks P. Cancer mortality in relation to national consumption of cigarettes, solid fuel, tea and coffee. Br J Cancer. 1970 Jun;24(2):215–225. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1970.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. W. Epidemiologic survey of bladder cancer in greater New Orleans. J Urol. 1982 Aug;128(2):281–283. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)52886-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima K., Tominaga S. Dietary habits and gastro-intestinal cancers: a comparative case-control study of stomach and large intestinal cancers in Nagoya, Japan. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1985 Aug;76(8):705–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson J. L., Kato H., Nichaman M. Z., Miller D. C., Gay M. L., Johnson K. G., Rhoads G. G. Epidemiology of coronary heart disease and stroke in Japanese men living in Japan, Hawaii, and California: methodology for comparison of diet. Am J Clin Nutr. 1973 Feb;26(2):177–184. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/26.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worth R. M., Kagan A. Ascertainment of men of Japanese ancestry in Hawaii through World War II Selective Service registration. J Chronic Dis. 1970 Nov;23(5):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(70)90022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


