Abstract
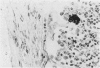
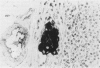
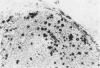
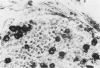
Metastases to axillary lymph nodes is an important factor in predicting prognosis and survival in primary operable carcinoma of the breast. A series of post mastectomy lymph nodes (150 cases) was selected in this retrospective study, in which the initial diagnosis had been no metastases by light microscopy and in which a long follow-up was available (average 10 years). The original H&E sections from these cases were immunostained to detect metastases which might not have been previously appreciated. The study was performed using a cocktail of 5 monoclonal antibodies directed against epithelial antigens. The object was to explore the possibility of detection of occult micrometastases by immunohistochemistry and to evaluate their prognostic significance. Micrometastases with individual cells and cell clusters were readily detected by this technique in 14% of all cases. It also became apparent towards the end of the study that micrometastases could be detected with equal sensitivity by any one of the 5 monoclonal antibodies. Positive staining of malignant cells was found to be more frequent in invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) than in invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC). However, for the IDC group a striking association was found between micrometastases and both recurrence and survival rate. The ILC sample was considered too small for meaningful interpretation. We recommend the use of immunohistochemical techniques using monoclonal antibodies for the detection of occult metastases in lymph nodes to improve the prediction of recurrence and survival in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arklie J., Taylor-Papadimitrious J., Bodmer W., Egan M., Millis R. Differentiation antigens expressed by epithelial cells in the lactating breast are also detectable in breast cancers. Int J Cancer. 1981 Jul 15;28(1):23–29. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J., Richardson T. C., Pulford K. A., Ghosh A. K., Gatter K. C., Heyderman E., Mason D. Y. Production of monoclonal antibodies against human epithelial membrane antigen for use in diagnostic immunocytochemistry. Br J Cancer. 1985 Sep;52(3):347–354. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delsol G., Gatter K. C., Stein H., Erber W. N., Pulford K. A., Zinne K., Mason D. Y. Human lymphoid cells express epithelial membrane antigen. Implications for diagnosis of human neoplasms. Lancet. 1984 Nov 17;2(8412):1124–1129. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91558-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epenetos A. A., Canti G., Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Curling M., Bodmer W. F. Use of two epithelium-specific monoclonal antibodies for diagnosis of malignancy in serous effusions. Lancet. 1982 Nov 6;2(8306):1004–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. R., Palekar A., Rockette H., Redmond C., Fisher B. Pathologic findings from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast Project (Protocol No. 4). V. Significance of axillary nodal micro- and macrometastases. Cancer. 1978 Oct;42(4):2032–2038. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197810)42:4<2032::aid-cncr2820420453>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. R., Swamidoss S., Lee C. H., Rockette H., Redmond C., Fisher B. Detection and significance of occult axillary node metastases in patients with invasive breast cancer. Cancer. 1978 Oct;42(4):2025–2031. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197810)42:4<2025::aid-cncr2820420452>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PICKREN J. W. Significance of occult metastases. A study of breast cancer. Cancer. 1961 Nov-Dec;14:1266–1271. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196111/12)14:6<1266::aid-cncr2820140617>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redding W. H., Coombes R. C., Monaghan P., Clink H. M., Imrie S. F., Dearnaley D. P., Ormerod M. G., Sloane J. P., Gazet J. C., Powles T. J. Detection of micrometastases in patients with primary breast cancer. Lancet. 1983 Dec 3;2(8362):1271–1274. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91150-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen P. P., Saigo P. E., Braun D. W., Jr, Weathers E., DePalo A. Predictors of recurrence in stage I (T1N0M0) breast carcinoma. Ann Surg. 1981 Jan;193(1):15–25. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198101000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen P. P., Saigo P. E., Braun D. W., Weathers E., Fracchia A. A., Kinne D. W. Axillary micro- and macrometastases in breast cancer: prognostic significance of tumor size. Ann Surg. 1981 Nov;194(5):585–591. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198111000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloane J. P., Ormerod M. G., Imrie S. F., Coombes R. C. The use of antisera to epithelial membrane antigen in detecting micrometastases in histological sections. Br J Cancer. 1980 Sep;42(3):392–398. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Peterson J. A., Arklie J., Burchell J., Ceriani R. L., Bodmer W. F. Monoclonal antibodies to epithelium-specific components of the human milk fat globule membrane: production and reaction with cells in culture. Int J Cancer. 1981 Jul 15;28(1):17–21. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viac J., Reano A., Brochier J., Staquet M. J., Thivolet J. Reactivity pattern of a monoclonal antikeratin antibody (KL1). J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Oct;81(4):351–354. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12519941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells C. A., Heryet A., Brochier J., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. The immunocytochemical detection of axillary micrometastases in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1984 Aug;50(2):193–197. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Mascarel I., Trojani M., Abadjian G., Durand M., Bonichon F., Coindre J. M., Meuge-Moraw C. Ganglions axillaires dans les cancers du sein. Comparaison des techniques d'analyse histologique standard et en coupes macroscopiquement sériées. Bull Cancer. 1982;69(5):451–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]