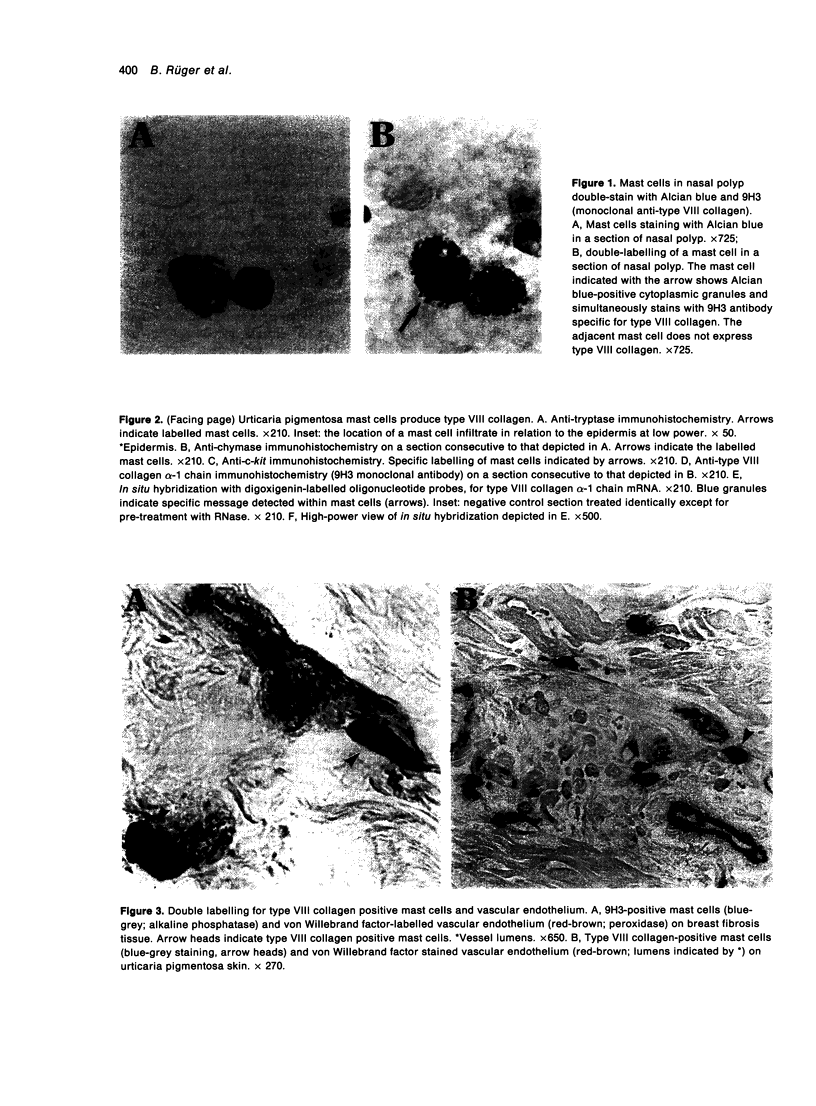
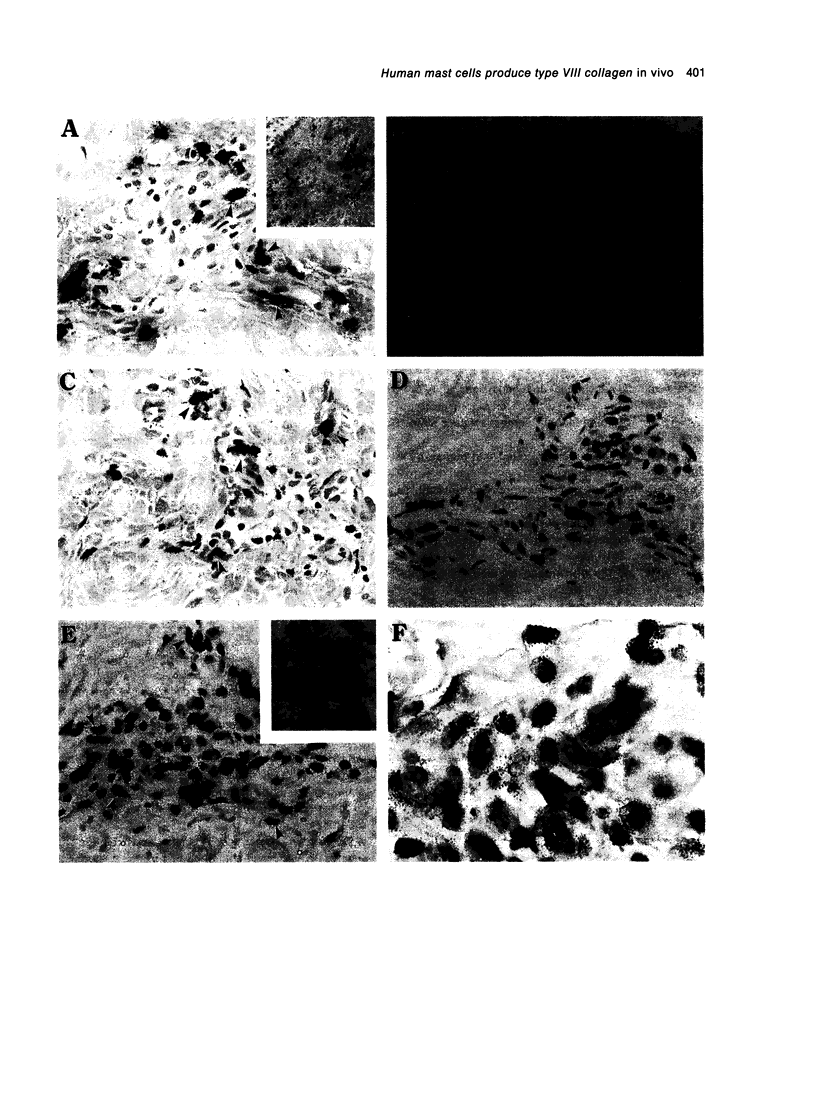
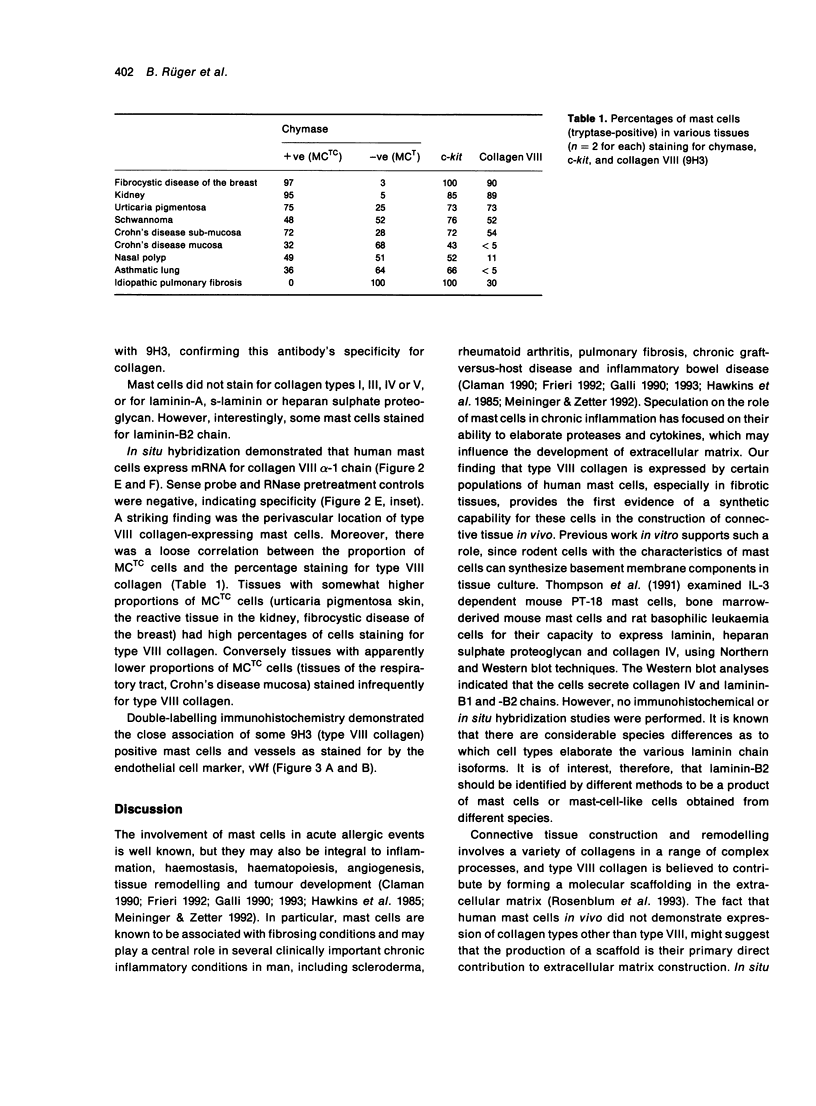
Abstract
Mast cells are assuming importance not only in their familiar role in acute allergic and parasitic diseases but also in chronic inflammatory, immunologic and fibrotic states. The processes by which human extracellular matrices are influenced by mast cells have remained obscure. We report here the production of type VIII collagen by human mast cells. Mast cells representing each of the known phenotypes were identified in a variety of tissues using histochemical techniques, and monoclonal antibodies specific for tryptase, chymase, and c-kit. Mast cells in normal and pathologic tissues expressed type VIII collagen alpha-1 chain protein and mRNA, detected by immunohistochemistry using monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, and non-isotopic oligonucleotide in situ hybridization using digoxigenin-labelled oligonucleotide probes based on the published human alpha-1 collagen VIII sequence. Perivascular location of type VIII collagen positive mast cells was a striking finding. The secretion of type VIII collagen by mast cells in vivo may contribute to angiogenesis, tissue remodelling, and fibrosis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Bornstein P., Vaheri A., Sage H. Biosynthesis of an unusual collagen type by human astrocytoma cells in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2653–2661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benya P. D. EC collagen: biosynthesis by corneal endothelial cells and separation from type IV without pepsin treatment or denaturation. Ren Physiol. 1980;3(1-6):30–35. doi: 10.1159/000172738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claman H. N. Mast cells and fibrosis. The relevance to scleroderma. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1990 Feb;16(1):141–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb I. D., Hughes S. S., Hicks D. G., Puzas J. E., Tsao G. J., Rosier R. N. Nonradioactive in situ hybridization using digoxigenin-labeled oligonucleotides. Applications to musculoskeletal tissues. Am J Pathol. 1992 Sep;141(3):579–589. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck L. Berberine sulphate binding to mast cell polyanions: a cytofluorometric method for the quantitation of heparin. Histochemistry. 1974;42(4):301–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00492678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieri M. Systemic sclerosis. The role of the mast cell and cytokines. Ann Allergy. 1992 Nov;69(5):385-92, 395-6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Gordon J. R., Wershil B. K. Cytokine production by mast cells and basophils. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Dec;3(6):865–872. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(05)80005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J. New concepts about the mast cell. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jan 28;328(4):257–265. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199301283280408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J. New insights into "the riddle of the mast cells": microenvironmental regulation of mast cell development and phenotypic heterogeneity. Lab Invest. 1990 Jan;62(1):5–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Tsai M., Wershil B. K. The c-kit receptor, stem cell factor, and mast cells. What each is teaching us about the others. Am J Pathol. 1993 Apr;142(4):965–974. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins R. A., Claman H. N., Clark R. A., Steigerwald J. C. Increased dermal mast cell populations in progressive systemic sclerosis: a link in chronic fibrosis? Ann Intern Med. 1985 Feb;102(2):182–186. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-2-182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani A. A., Schechter N. M., Craig S. S., DeBlois G., Schwartz L. B. Two types of human mast cells that have distinct neutral protease compositions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4464–4468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iruela-Arispe M. L., Diglio C. A., Sage E. H. Modulation of extracellular matrix proteins by endothelial cells undergoing angiogenesis in vitro. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 Jul-Aug;11(4):805–815. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.4.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor R., Sakai L. Y., Funk S., Roux E., Bornstein P., Sage E. H. Type VIII collagen has a restricted distribution in specialized extracellular matrices. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):721–730. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kittelberger R., Davis P. F., Flynn D. W., Greenhill N. S. Distribution of type VIII collagen in tissues: an immunohistochemical study. Connect Tissue Res. 1990;24(3-4):303–318. doi: 10.3109/03008209009152157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kittelberger R., Davis P. F., Greenhill N. S. Immunolocalization of type VIII collagen in vascular tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):414–419. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner N. B., Nocka K. H., Cole S. R., Qiu F. H., Strife A., Ashman L. K., Besmer P. Monoclonal antibody YB5.B8 identifies the human c-kit protein product. Blood. 1991 May 1;77(9):1876–1883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrhofer G., Gadd S. J., Spargo L. D., Ashman L. K. Specificity of a mouse monoclonal antibody raised against acute myeloid leukaemia cells for mast cells in human mucosal and connective tissues. Immunol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;65(Pt 3):241–250. doi: 10.1038/icb.1987.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meininger C. J., Zetter B. R. Mast cells and angiogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 1992 Apr;3(2):73–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muragaki Y., Mattei M. G., Yamaguchi N., Olsen B. R., Ninomiya Y. The complete primary structure of the human alpha 1 (VIII) chain and assignment of its gene (COL8A1) to chromosome 3. Eur J Biochem. 1991 May 8;197(3):615–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15951.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadel J. A. Biology of mast cell tryptase and chymase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;629:319–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb37986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulus W., Sage E. H., Liszka U., Iruela-Arispe M. L., Jellinger K. Increased levels of type VIII collagen in human brain tumours compared to normal brain tissue and non-neoplastic cerebral disorders. Br J Cancer. 1991 Mar;63(3):367–371. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. H., Primrose L., Kind C. N., Talbot I. C., Lauder I. In situ hybridization demonstration of poly-adenylated RNA sequences in formalin-fixed paraffin sections using a biotinylated oligonucleotide poly d(T) probe. J Pathol. 1989 Aug;158(4):279–286. doi: 10.1002/path.1711580403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney P., Wang M., Kumar P., Kumar S. Angiogenic oligosaccharides of hyaluronan enhance the production of collagens by endothelial cells. J Cell Sci. 1993 May;105(Pt 1):213–218. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.1.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum N. D., Briscoe D. M., Karnovsky M. J., Olsen B. R. Alpha 1-VIII collagen is expressed in the rat glomerulus and in resident glomerular cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jun;264(6 Pt 2):F1003–F1010. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.6.F1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum N. D., Karnovsky M. J., Olsen B. R. Non-fibrillar collagenous proteins synthesized by rat mesangial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1990 Nov;1(5):785–791. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V15785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Balian G., Vogel A. M., Bornstein P. Type VIII collagen. Synthesis by normal and malignant cells in culture. Lab Invest. 1984 Feb;50(2):219–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Iruela-Arispe M. L. Type VIII collagen in murine development. Association with capillary formation in vitro. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;580:17–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb17914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Pritzl P., Bornstein P. A unique, pepsin-sensitive collagen synthesized by aortic endothelial cells in culture. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 9;19(25):5747–5755. doi: 10.1021/bi00566a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada H., Konomi H., Hirosawa K. Characterization of the collagen in the hexagonal lattice of Descemet's membrane: its relation to type VIII collagen. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):219–227. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada H., Konomi H. The alpha 1 chain of type VIII collagen is associated with many but not all microfibrils of elastic fiber system. Cell Struct Funct. 1991 Dec;16(6):455–466. doi: 10.1247/csf.16.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Austen K. F. Recent advances in the cellular and molecular biology of mast cells. Immunol Today. 1989 Nov;10(11):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. L., Burbelo P. D., Gabriel G., Yamada Y., Metcalfe D. D. Murine mast cells synthesize basement membrane components. A potential role in early fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):619–623. doi: 10.1172/JCI115038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walls A. F., Jones D. B., Williams J. H., Church M. K., Holgate S. T. Immunohistochemical identification of mast cells in formaldehyde-fixed tissue using monoclonal antibodies specific for tryptase. J Pathol. 1990 Oct;162(2):119–126. doi: 10.1002/path.1711620204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi N., Mayne R., Ninomiya Y. The alpha 1 (VIII) collagen gene is homologous to the alpha 1 (X) collagen gene and contains a large exon encoding the entire triple helical and carboxyl-terminal non-triple helical domains of the alpha 1 (VIII) polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4508–4513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]