Abstract
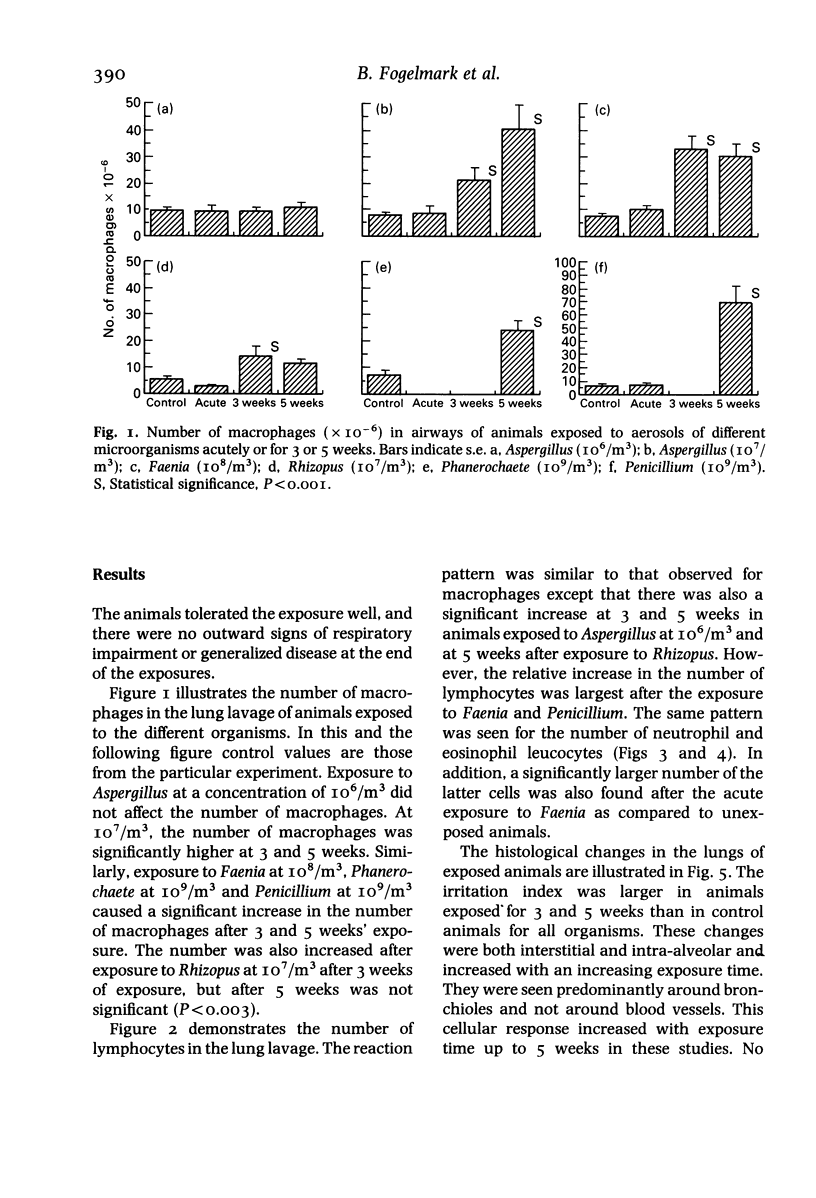
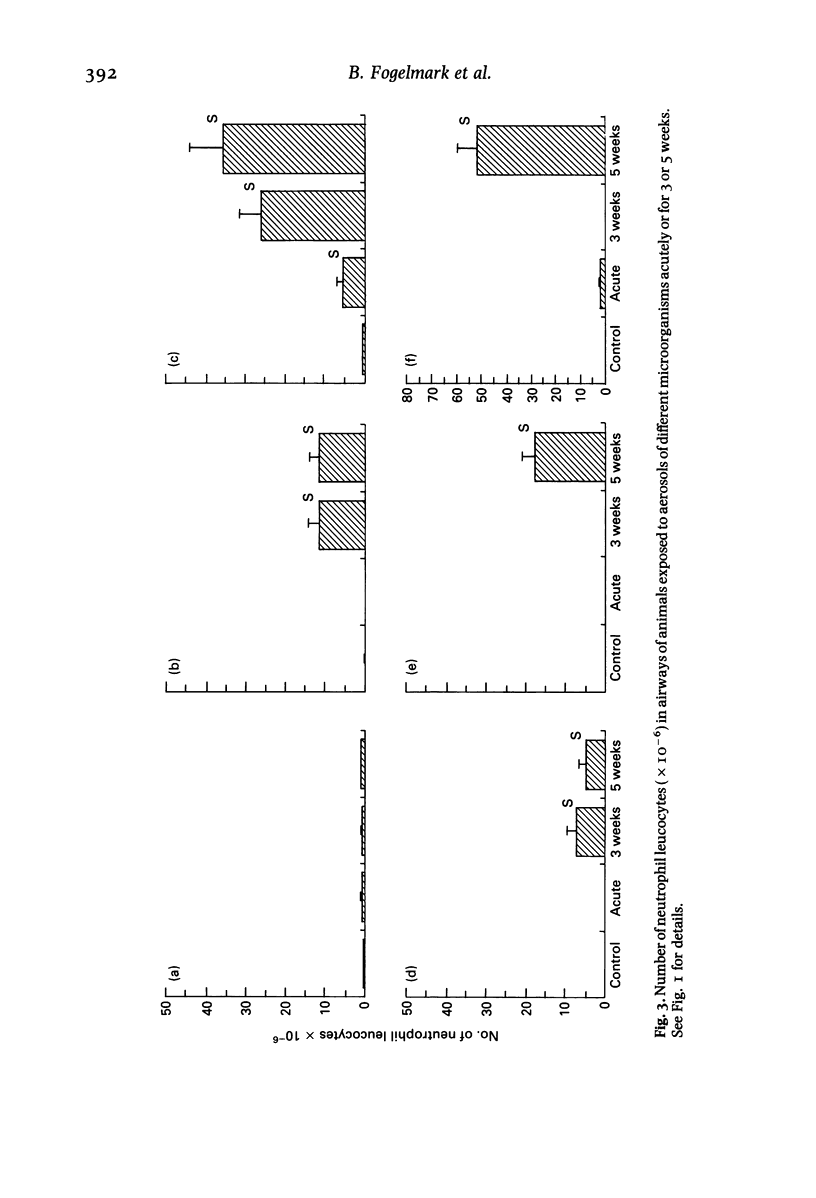
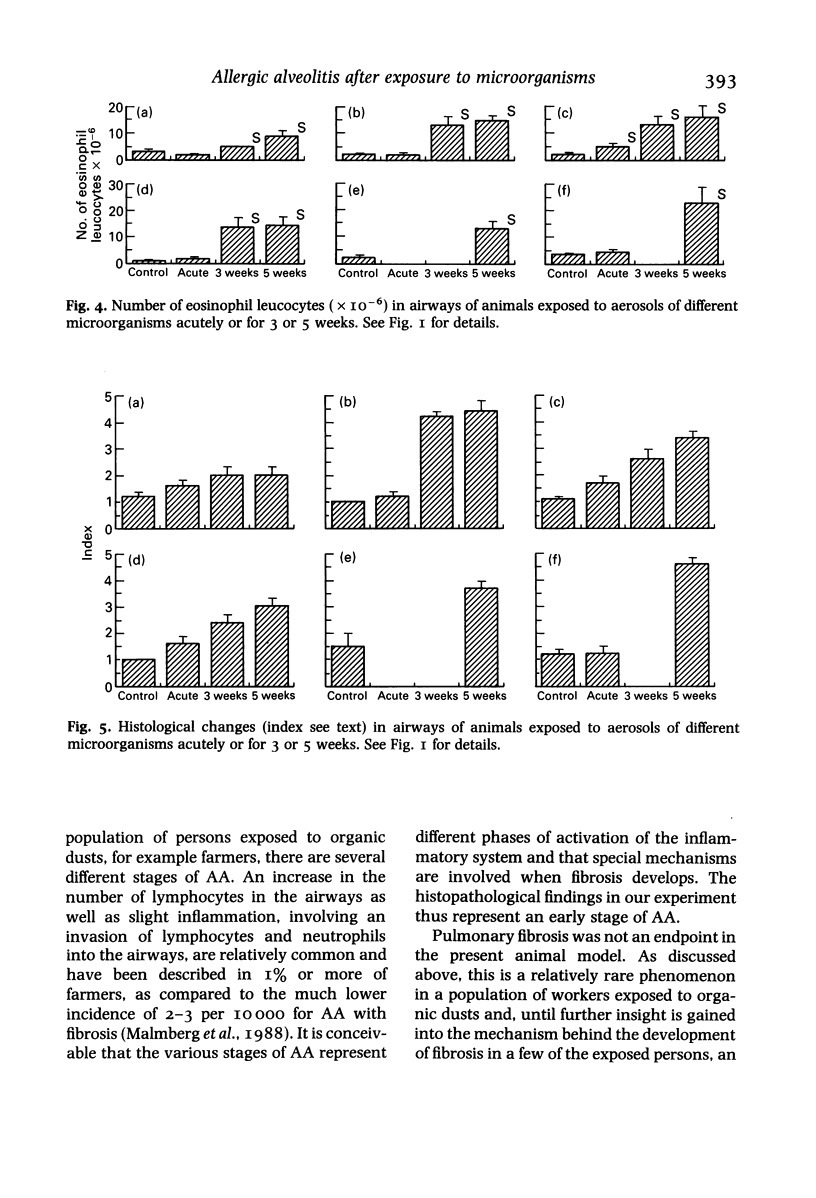
The experiments described here examined the capacity of different microorganisms to induce allergic alveolitis. Guinea-pigs were exposed to an aerosol of pure cultures of five different organisms, four of which are common in mouldy hay, without previous injection of an adjuvant. The animals were either acutely exposed or exposed for 3 to 5 weeks, after which the numbers of different inflammatory cells in the airways were counted and histological changes in the lung parenchyma were assessed. It was seen that prolonged exposures to large numbers of spores produced a cellular infiltration in the alveolar and bronchiolar region, and gave rise to lesions resembling early granulomas. The number of lymphocytes increased in the airways. The results suggest that allergic alveolitis can be induced by inhalation of various kinds of microorganisms and that these may vary in their capacity to produce the disease.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cook J. A., Dougherty W. J., Holt T. M. Enhanced sensitivity to endotoxin induced by the RE stimulant, glucan. Circ Shock. 1980;7(3):225–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Luzio N. R. Lysozyme, glucan-activated macrophages and neoplasia. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Jul;26(1):67–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier E., Tonnel A. B., Gosset P., Wallaert B., Ameisen J. C., Voisin C. Early neutrophil alveolitis after antigen inhalation in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 1985 Oct;88(4):563–566. doi: 10.1378/chest.88.4.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto H., Rylander R. Kinetics of inhaled lipopolysaccharide in the guinea pig. J Lab Clin Med. 1987 Sep;110(3):287–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmberg P., Rask-Andersen A., Höglund S., Kolmodin-Hedman B., Read Guernsey J. Incidence of organic dust toxic syndrome and allergic alveolitis in Swedish farmers. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1988;87(1):47–54. doi: 10.1159/000234647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R., Morey P. Airborne endotoxin in industries processing vegetable fibers. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1982 Nov;43(11):811–812. doi: 10.1080/15298668291410611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuyler M., Subramanyan S., Hassan M. O. Prolonged exposure to M. faeni in strain II guinea-pigs: pulmonary interstitial inflammation. Br J Exp Pathol. 1987 Oct;68(5):743–754. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



