Abstract
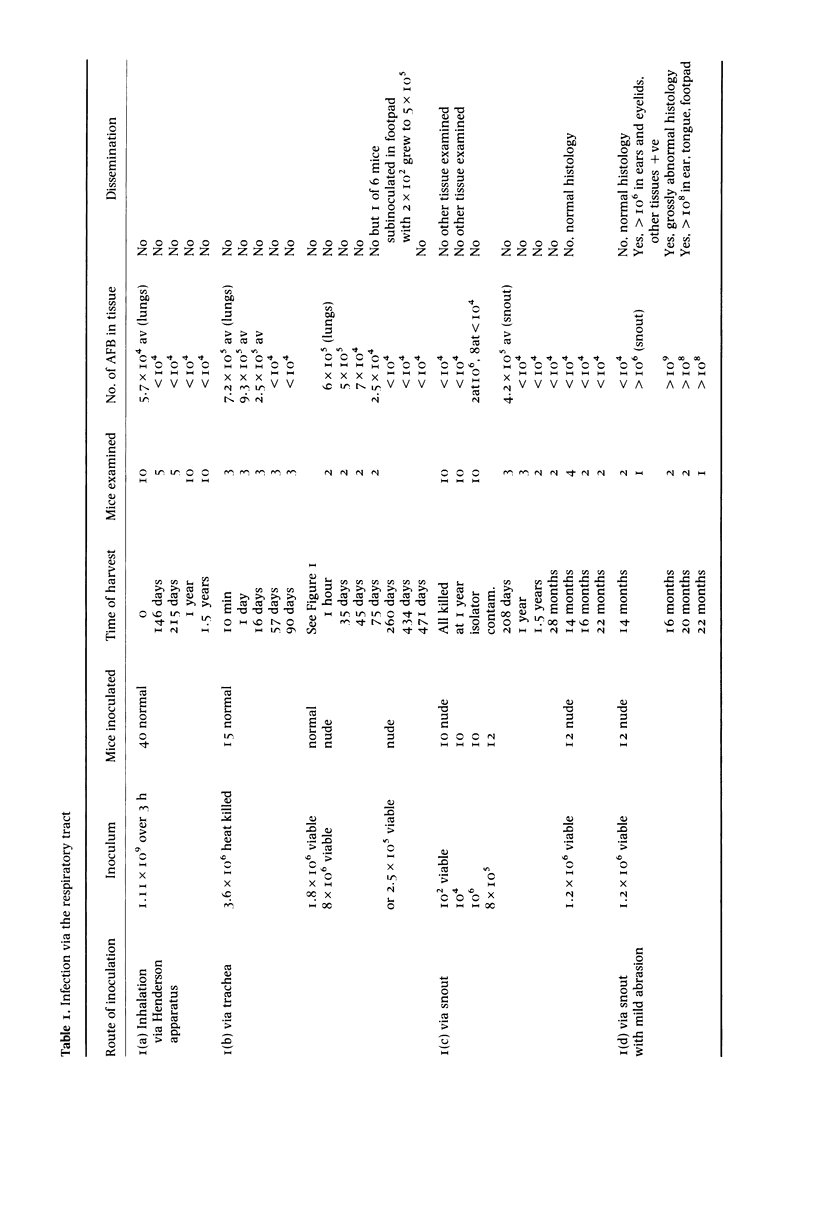
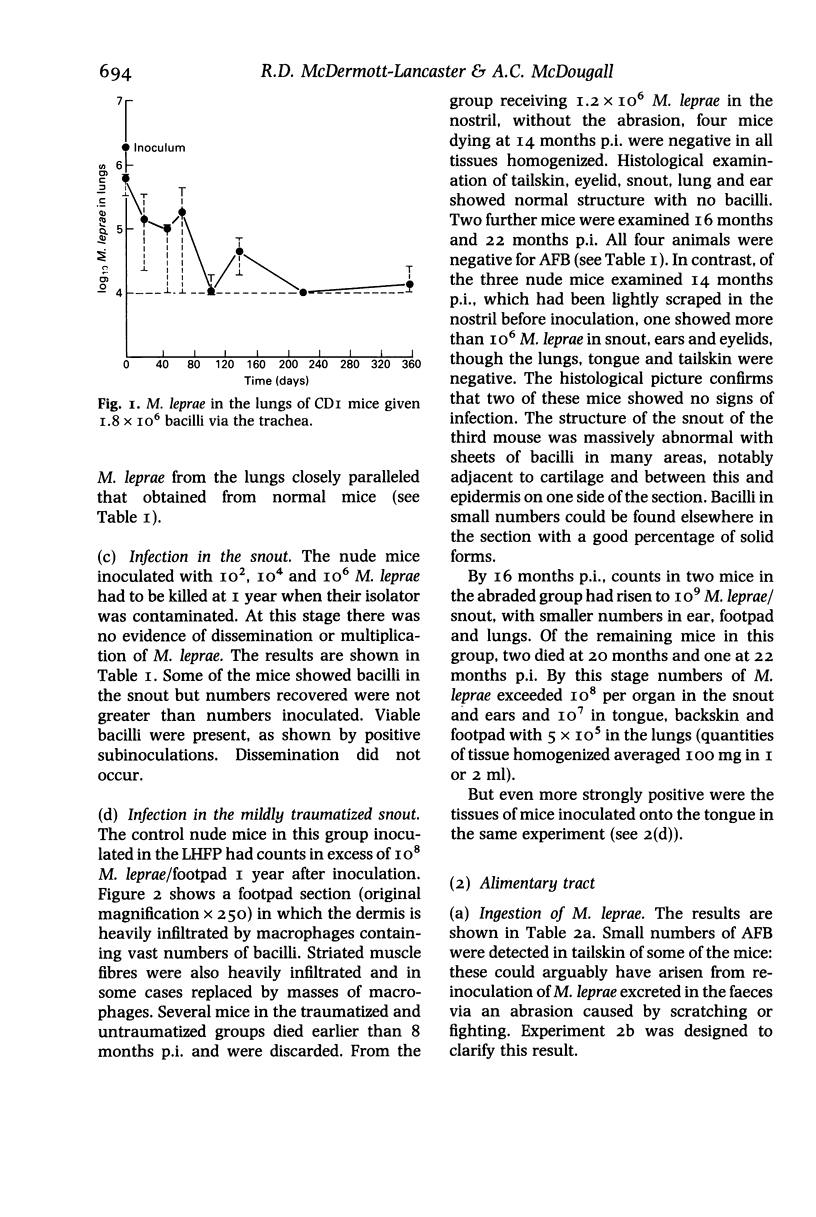
Athymic (nude) mice were experimentally infected with Mycobacterium leprae via the alimentary and respiratory tracts and through the skin. Animals were allowed to inhale aerosols of M. leprae or had bacilli instilled into the nostrils or directly into the lungs. Others were fed M. leprae by gastric tube or had bacilli placed on the tongue. Attempts were also made to transmit M. leprae from infected footpads by Aedes aegyptii mosquitoes. The most successful infections resulted from nasal instillations and from bacilli inoculated onto the tongue surface: in these cases heavy systemic infections occurred. M. leprae was also shown to survive passage through the alimentary tract and bacilli recovered from the faeces were capable of causing infection in recipient nude mice. The possible epidemiological significance of these findings for the transmission of leprosy in man is discussed.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davey T. F., Rees R. J. The nasal dicharge in leprosy: clinical and bacteriological aspects. Lepr Rev. 1974 Jun;45(2):121–134. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19740014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDERSON D. W. An apparatus for the study of airborne infection. J Hyg (Lond) 1952 Mar;50(1):53–68. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400019422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. The transmission of leprosy in man. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1980 Sep;48(3):309–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubscher S., Girdhar B. K., Desikan K. V. Discharge of Mycobacterium leprae from the mouth in lepromatous leprosy patients. Lepr Rev. 1979 Mar;50(1):45–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWY L. Processing of biopsies for leprosy bacilli. J Med Lab Technol. 1956 Oct;13(8):558–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster R. D., Hilson G. R., McDougall A. C., Colston M. J. Mycobacterium leprae infection in nude mice: bacteriological and histological responses to primary infection and large inocula. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):865–872. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.865-872.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster R. D., McDougall A. C., Hilson G. R., Colston M. J. Leprosy in the nude mouse. Exp Cell Biol. 1984;52(1-2):154–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan E., Manja K. S., Bedi B. M., Kirchheimer W. F., Balasubrahmanyan M. Arthropod feeding experiments in lepromatous leprosy. Lepr Rev. 1972 Dec;43(4):188–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallen M. J., McDermott R. D. How might Mycobacterium leprae enter the body? Lepr Rev. 1986 Dec;57(4):289–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley J. C. The presence of M. leprae in human milk. Lepr Rev. 1967 Oct;38(4):239–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley M., Jopling W. H., Ridley D. S. Acid-fast bacilli in the fingers of long-treated lepromatous patients. Lepr Rev. 1976 Jun;47(2):93–96. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19760017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPARD C. C. The nasal excretion of Mycobacterium leprae in leprosy. Int J Lepr. 1962 Jan-Mar;30:10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C., McRae D. H. A method for counting acid-fast bacteria. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1968 Jan-Mar;36(1):78–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinsnes O. K. Editorial: Coughing, sneezing and mosquitoes in the transmission of leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1975 Oct-Dec;43(4):378–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West B. C., Todd J. R., Lary C. H., Blake L. A., Fowler M. E., King J. W. Leprosy in six isolated residents of northern Louisiana. Time-clustered cases in an essentially nonendemic area. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Sep;148(9):1987–1992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






