Abstract
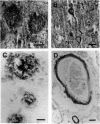
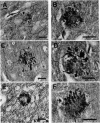
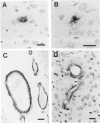
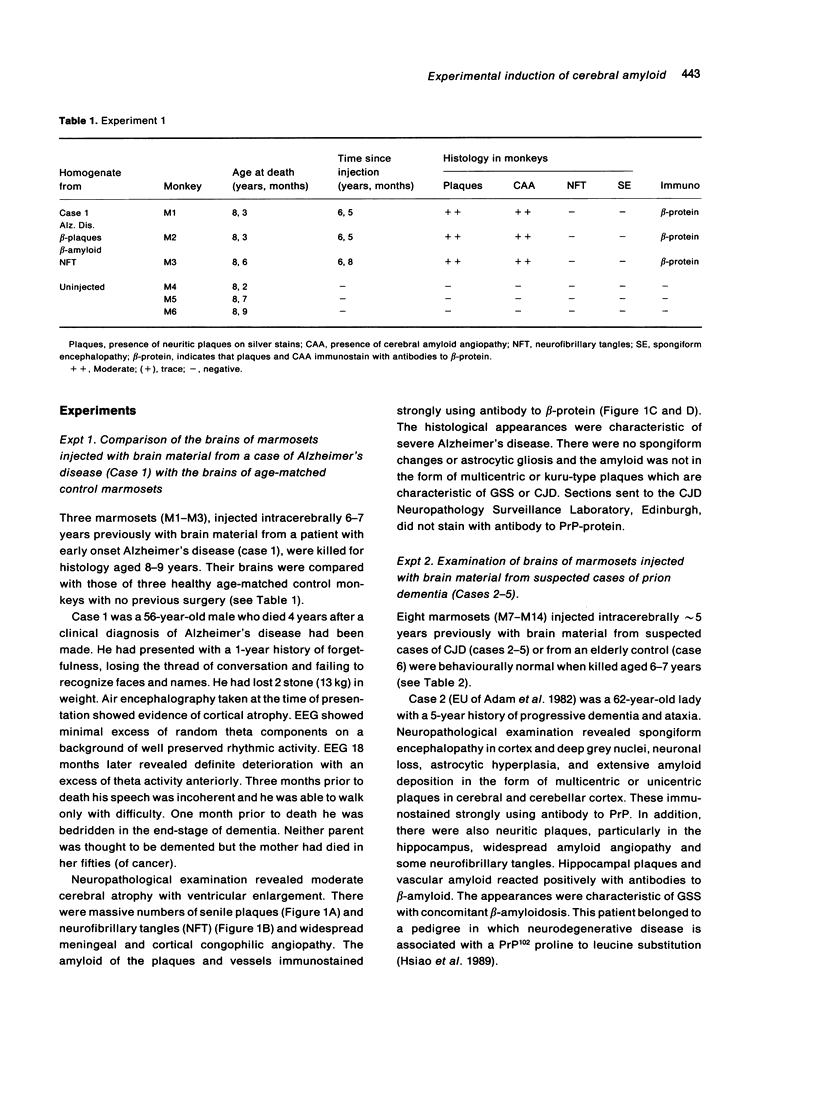
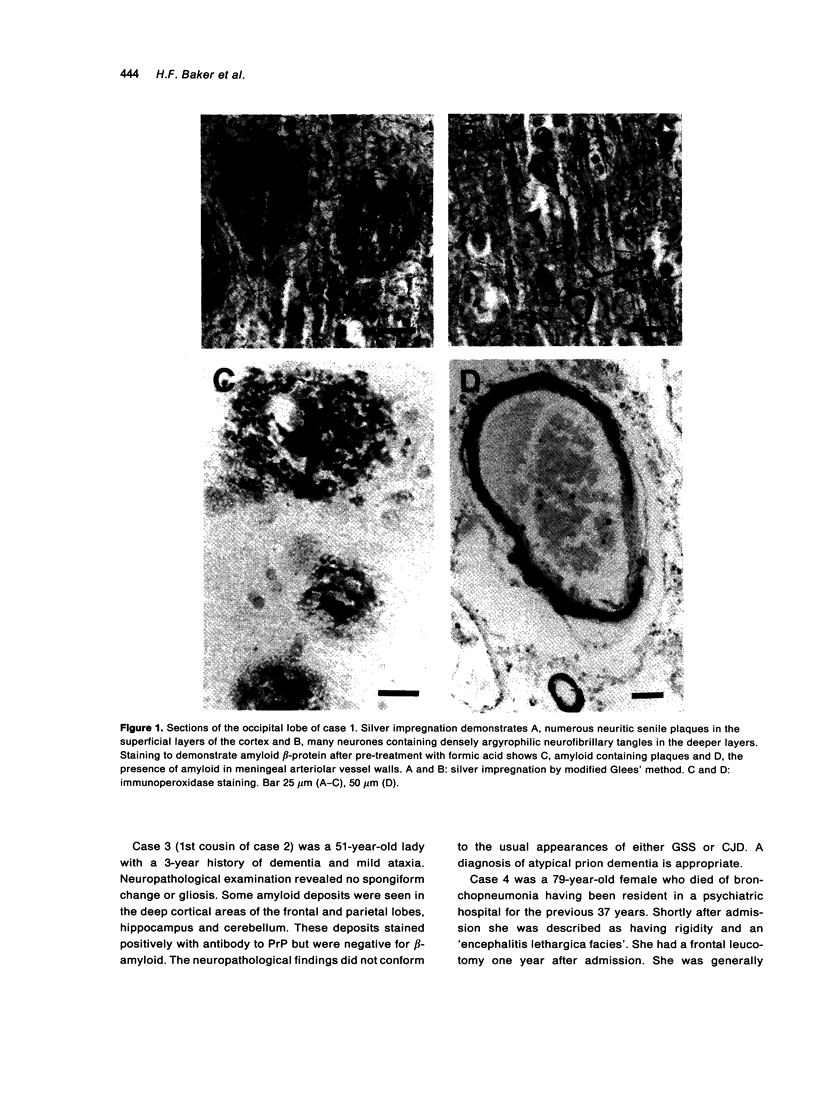
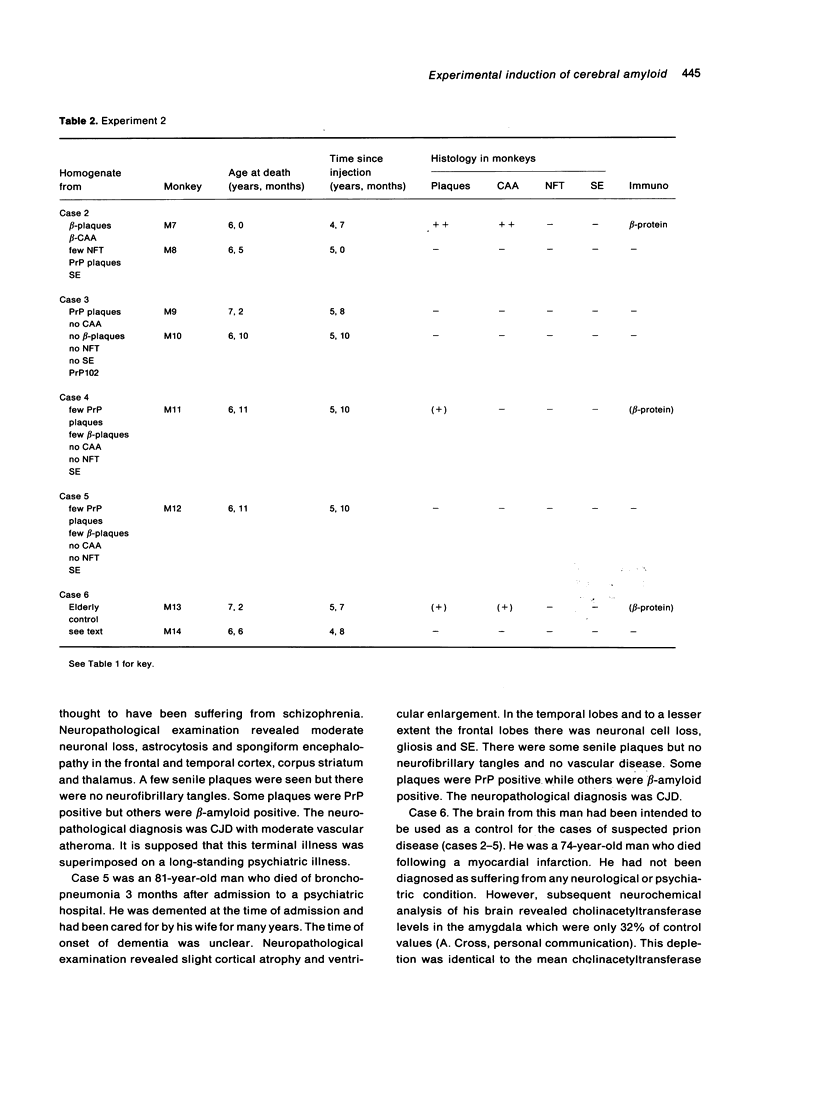
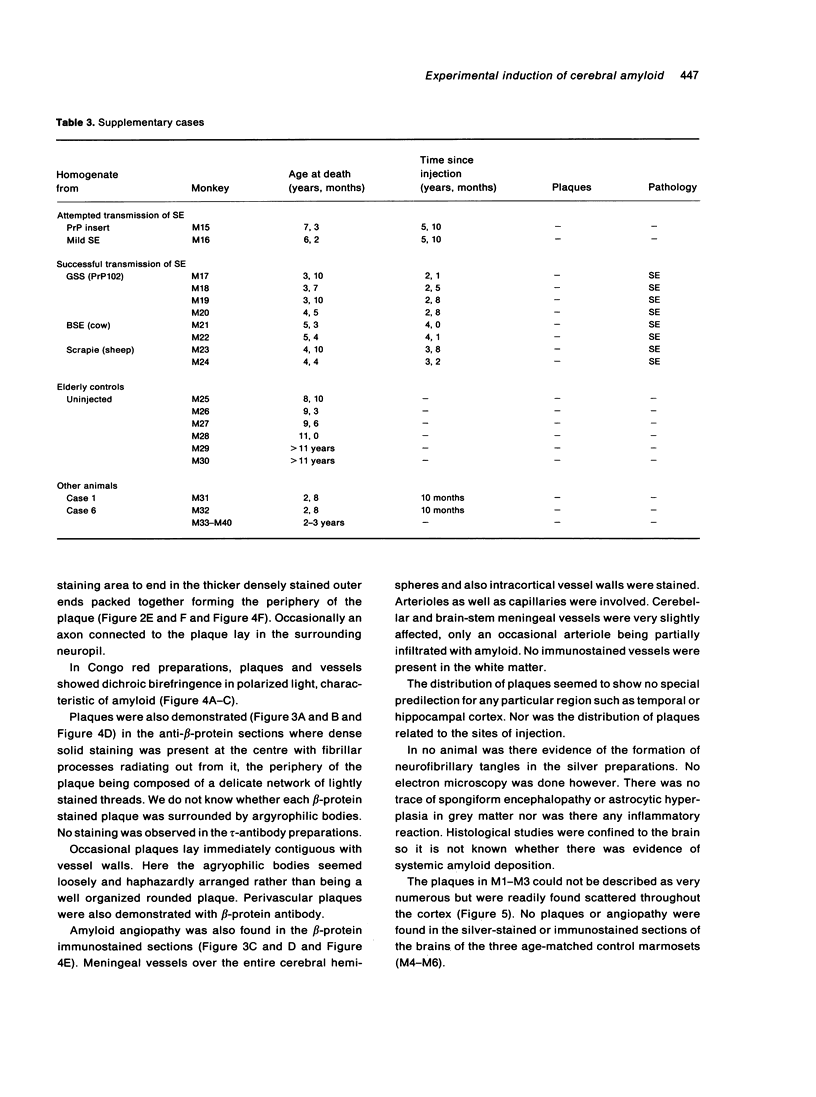
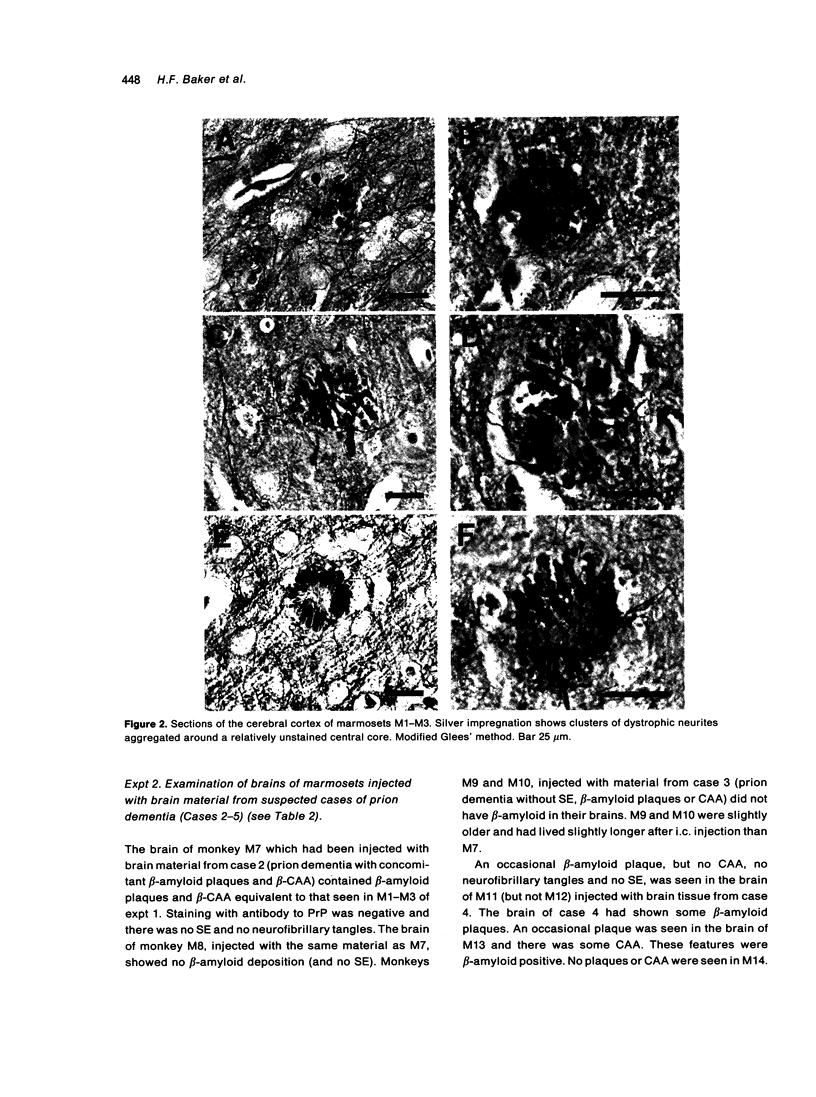
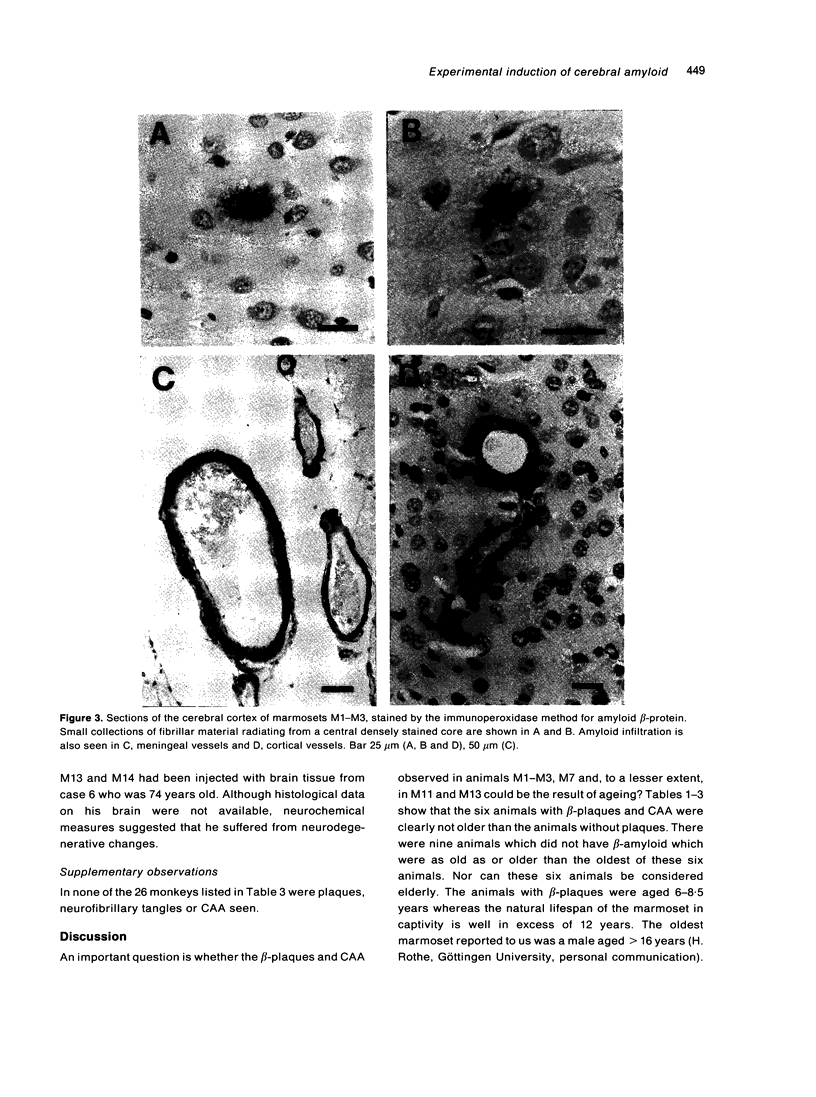
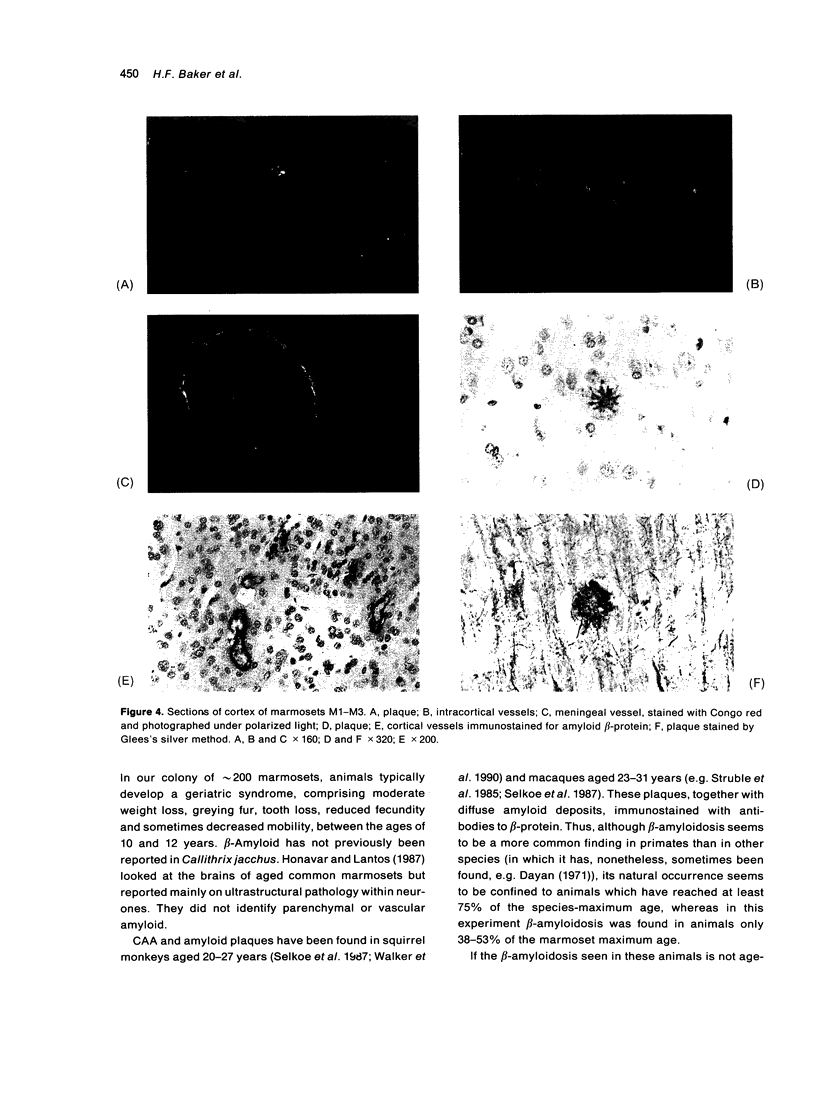
The brains of three marmosets (Callithrix jacchus) injected intracerebrally 6-7 years earlier with brain tissue from a patient with early onset Alzheimer's disease were found to contain moderate numbers of amyloid plaques with associated argyrophilic dystrophic neurites and cerebral amyloid angiopathy but no neurofibrillary tangles. The plaques and vascular amyloid stained positively with antibodies to beta (A4)-protein. The brains of three age-matched control marmosets from the same colony did not show these neuropathological features. The brain of one of two marmosets injected with brain tissue from a patient with prion disease with concomitant beta-amyloid plaques and cerebral amyloid angiopathy also showed beta-amyloid plaques and angiopathy but no spongiform encephalopathy. An occasional plaque was found in the brains of two of four marmosets injected with brain tissue from three elderly patients with age-related pathology, two of whom had an additional diagnosis of possible prion disease. Neither plaques nor cerebral amyloid angiopathy were found in six other marmosets who were older than the injected animals, in 12 further marmosets who were slightly younger but who had been injected several years previously with brain tissue which did not contain beta-amyloid, or in 10 younger marmosets who had been subjected to various neurosurgical procedures. These results suggest that cerebral beta-amyloidosis may be induced by the introduction of exogenous amyloid beta-protein.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam J., Crow T. J., Duchen L. W., Scaravilli F., Spokes E. Familial cerebral amyloidosis and spongiform encephalopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Jan;45(1):37–45. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H. F., Duchen L. W., Jacobs J. M., Ridley R. M. Spongiform encephalopathy transmitted experimentally from Creutzfeldt-Jakob and familial Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker diseases. Brain. 1990 Dec;113(Pt 6):1891–1909. doi: 10.1093/brain/113.6.1891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H. F., Ridley R. M., Crow T. J. Experimental transmission of an autosomal dominant spongiform encephalopathy: does the infectious agent originate in the human genome? Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Aug 3;291(6491):299–302. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6491.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H. F., Ridley R. M., Crow T. J., Tyrrell D. A. A re-investigation of the behavioural effects of intracerebral injection in marmosets of cytopathic cerebrospinal fluid from patients with schizophrenia or neurological disease. Psychol Med. 1989 May;19(2):325–329. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700012368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H. F., Ridley R. M., Wells G. A. Experimental transmission of BSE and scrapie to the common marmoset. Vet Rec. 1993 Apr 17;132(16):403–406. doi: 10.1136/vr.132.16.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman J. M., Kingsbury D. T., McKinley M. P., Bendheim P. E., Prusiner S. B. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease prion proteins in human brains. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 10;312(2):73–78. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501103120202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P., Goldfarb L. G., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. The phenotypic expression of different mutations in transmissible familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Eur J Epidemiol. 1991 Sep;7(5):469–476. doi: 10.1007/BF00143124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P., Kaur P., Sulima M. P., Goldfarb L. G., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Real and imagined clinicopathological limits of "prion dementia". Lancet. 1993 Jan 16;341(8838):127–129. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90001-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugiani O., Giaccone G., Verga L., Pollo B., Frangione B., Farlow M. R., Tagliavini F., Ghetti B. Beta PP participates in PrP-amyloid plaques of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease, Indiana kindred. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1993 Jan;52(1):64–70. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199301000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. H., Feiner H., Jensson O., Frangione B. Amyloid fibril in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis (HCHWA) is related to the gastroentero-pancreatic neuroendocrine protein, gamma trace. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):623–628. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinge J., Brown J., Hardy J., Mullan M., Rossor M. N., Baker H., Crow T. J., Lofthouse R., Poulter M., Ridley R. Inherited prion disease with 144 base pair gene insertion. 2. Clinical and pathological features. Brain. 1992 Jun;115(Pt 3):687–710. doi: 10.1093/brain/115.3.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinge J., Brown J., Hardy J., Mullan M., Rossor M. N., Baker H., Crow T. J., Lofthouse R., Poulter M., Ridley R. Inherited prion disease with 144 base pair gene insertion. 2. Clinical and pathological features. Brain. 1992 Jun;115(Pt 3):687–710. doi: 10.1093/brain/115.3.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinge J., Owen F., Poulter M., Leach M., Crow T. J., Rossor M. N., Hardy J., Mullan M. J., Janota I., Lantos P. L. Prion dementia without characteristic pathology. Lancet. 1990 Jul 7;336(8706):7–9. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91518-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayan A. D. Comparative neuropathology of ageing. Studies on the brains of 47 species of vertebrates. Brain. 1971;94(1):31–42. doi: 10.1093/brain/94.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeArmond S. J., McKinley M. P., Barry R. A., Braunfeld M. B., McColloch J. R., Prusiner S. B. Identification of prion amyloid filaments in scrapie-infected brain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):221–235. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90076-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dlouhy S. R., Hsiao K., Farlow M. R., Foroud T., Conneally P. M., Johnson P., Prusiner S. B., Hodes M. E., Ghetti B. Linkage of the Indiana kindred of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease to the prion protein gene. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):64–67. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen L. W. Current status review: cerebral amyloid. Int J Exp Pathol. 1992 Aug;73(4):535–550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esiri M. M., Wilcock G. K. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in dementia and old age. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Nov;49(11):1221–1226. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.11.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier I. N., Cross A. J., Johnson J. A., Roberts G. W., Crow T. J., Corsellis J. A., Lee Y. C., O'Shaughnessy D., Adrian T. E., McGregor G. P. Neuropeptides in Alzheimer type dementia. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Dec;62(1-3):159–170. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiso J., Jensson O., Frangione B. Amyloid fibrils in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis of Icelandic type is a variant of gamma-trace basic protein (cystatin C). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2974–2978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, and the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-Parkinsonism-dementia complex on Guam: a review and summary of attempts to demonstrate infection as the aetiology. J Clin Pathol Suppl (R Coll Pathol) 1972;6:132–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb L. G., Petersen R. B., Tabaton M., Brown P., LeBlanc A. C., Montagna P., Cortelli P., Julien J., Vital C., Pendelbury W. W. Fatal familial insomnia and familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: disease phenotype determined by a DNA polymorphism. Science. 1992 Oct 30;258(5083):806–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1439789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren H., Steinberg M. C., Farboody G. H. Familial oculoleptomeningeal amyloidosis. Brain. 1980 Sep;103(3):473–495. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.3.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudmundsson G., Hallgrímsson J., Jónasson T. A., Bjarnason O. Hereditary cerebral haemorrhage with amyloidosis. Brain. 1972;95(2):387–404. doi: 10.1093/brain/95.2.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy J., Allsop D. Amyloid deposition as the central event in the aetiology of Alzheimer's disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Oct;12(10):383–388. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90609-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honavar M., Lantos P. L. Ultrastructural changes in the frontal cortex and hippocampus in the ageing marmoset. Mech Ageing Dev. 1987 Nov;41(1-2):161–175. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(87)90060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao K., Baker H. F., Crow T. J., Poulter M., Owen F., Terwilliger J. D., Westaway D., Ott J., Prusiner S. B. Linkage of a prion protein missense variant to Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):342–345. doi: 10.1038/338342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Ogomori K., Tateishi J., Prusiner S. B. Formic acid pretreatment enhances immunostaining of cerebral and systemic amyloids. Lab Invest. 1987 Aug;57(2):230–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowall N. W., Beal M. F., Busciglio J., Duffy L. K., Yankner B. A. An in vivo model for the neurodegenerative effects of beta amyloid and protection by substance P. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7247–7251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSLAND T. A., GLEES P., ERIKSON L. B. Modification of the Glees silver impregnation for paraffin sections. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1954 Oct;13(4):587–591. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195410000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Jones D., South P. W., Snowden J. S., Neary D. Deposition of amyloid beta protein in non-Alzheimer dementias: evidence for a neuronal origin of parenchymal deposits of beta protein in neurodegenerative disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1992;83(4):415–419. doi: 10.1007/BF00713534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease virus isolations from the Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome with an analysis of the various forms of amyloid plaque deposition in the virus-induced spongiform encephalopathies. Brain. 1981 Sep;104(3):559–588. doi: 10.1093/brain/104.3.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant G. T., Révész T., Barnard R. O., Harding A. E., Gautier-Smith P. C. Familial cerebral amyloid angiopathy with nonneuritic amyloid plaque formation. Brain. 1990 Jun;113(Pt 3):721–747. doi: 10.1093/brain/113.3.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Molecular biology of prion diseases. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1515–1522. doi: 10.1126/science.1675487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley R. M., Baker H. F., Crow T. J. Transmissible and non-transmissible neurodegenerative disease: similarities in age of onset and genetics in relation to aetiology. Psychol Med. 1986 Feb;16(1):199–207. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700002634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley R. M., Murray T. K., Johnson J. A., Baker H. F. Learning impairment following lesion of the basal nucleus of Meynert in the marmoset: modification by cholinergic drugs. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 18;376(1):108–116. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90904-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley R. M., Samson N. A., Baker H. F., Johnson J. A. Visuospatial learning impairment following lesion of the cholinergic projection to the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1988 Jul 19;456(1):71–87. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. W., Lofthouse R., Allsop D., Landon M., Kidd M., Prusiner S. B., Crow T. J. CNS amyloid proteins in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurology. 1988 Oct;38(10):1534–1540. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.10.1534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumble B., Retallack R., Hilbich C., Simms G., Multhaup G., Martins R., Hockey A., Montgomery P., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L. Amyloid A4 protein and its precursor in Down's syndrome and Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 1;320(22):1446–1452. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906013202203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Bell D. S., Podlisny M. B., Price D. L., Cork L. C. Conservation of brain amyloid proteins in aged mammals and humans with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):873–877. doi: 10.1126/science.3544219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struble R. G., Price D. L., Jr, Cork L. C., Price D. L. Senile plaques in cortex of aged normal monkeys. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 30;361(1-2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91298-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinters H. V., Gilbert J. J. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: incidence and complications in the aging brain. II. The distribution of amyloid vascular changes. Stroke. 1983 Nov-Dec;14(6):924–928. doi: 10.1161/01.str.14.6.924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L. C., Masters C., Beyreuther K., Price D. L. Amyloid in the brains of aged squirrel monkeys. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;80(4):381–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00307691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe R., Duchen L. W. Cerebral amyloid in human prion disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1993 Jun;19(3):253–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1993.tb00435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duinen S. G., Castaño E. M., Prelli F., Bots G. T., Luyendijk W., Frangione B. Hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis in patients of Dutch origin is related to Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5991–5994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]