Abstract
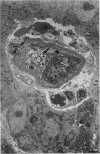
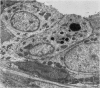
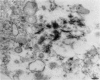
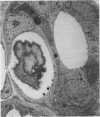
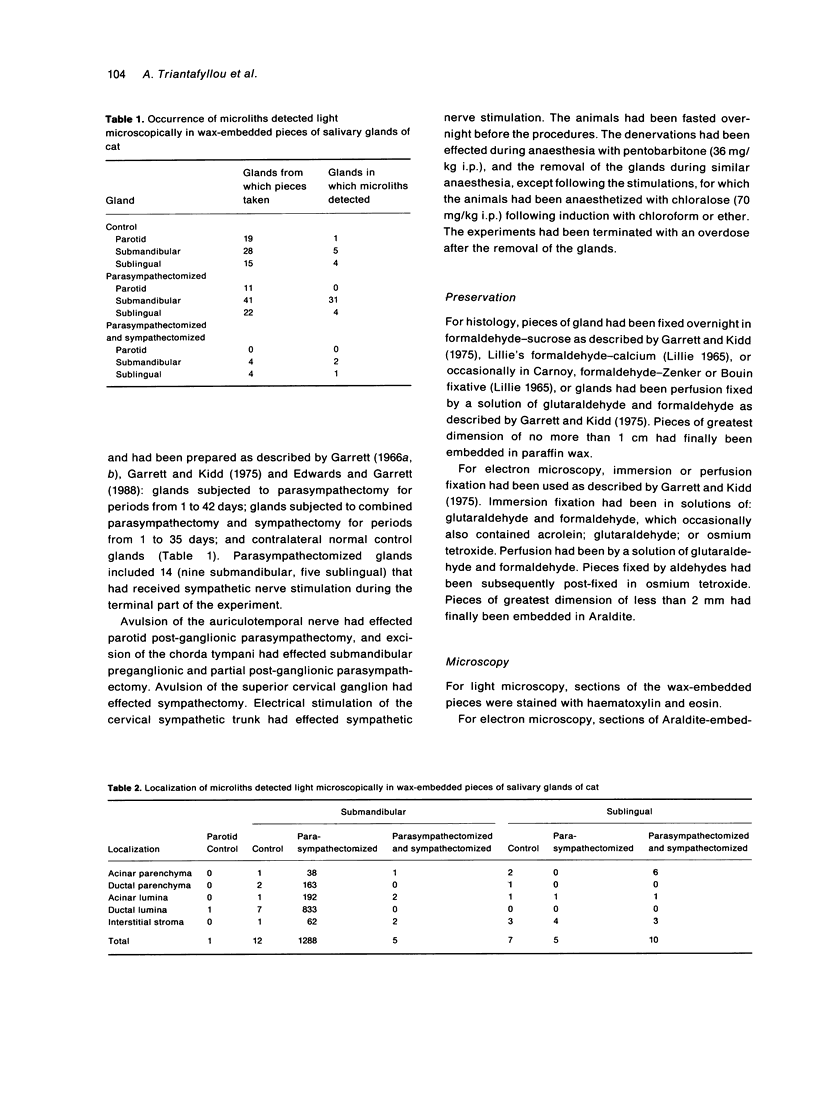
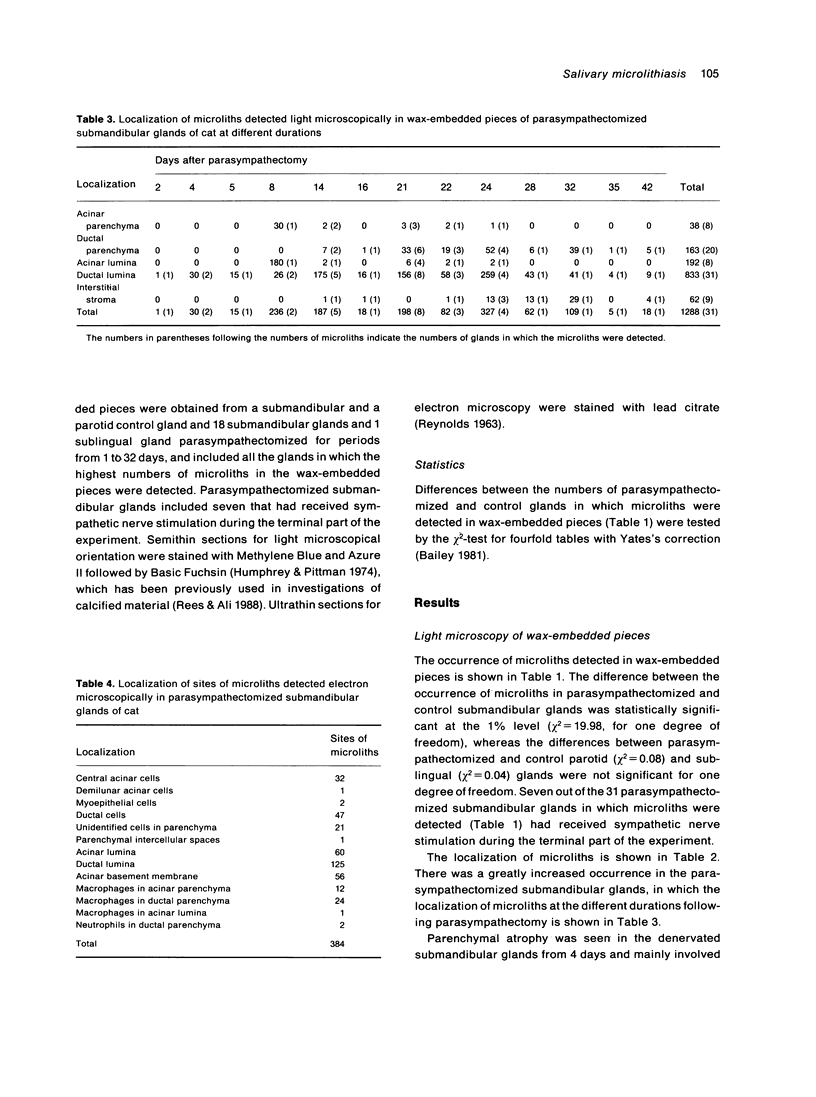
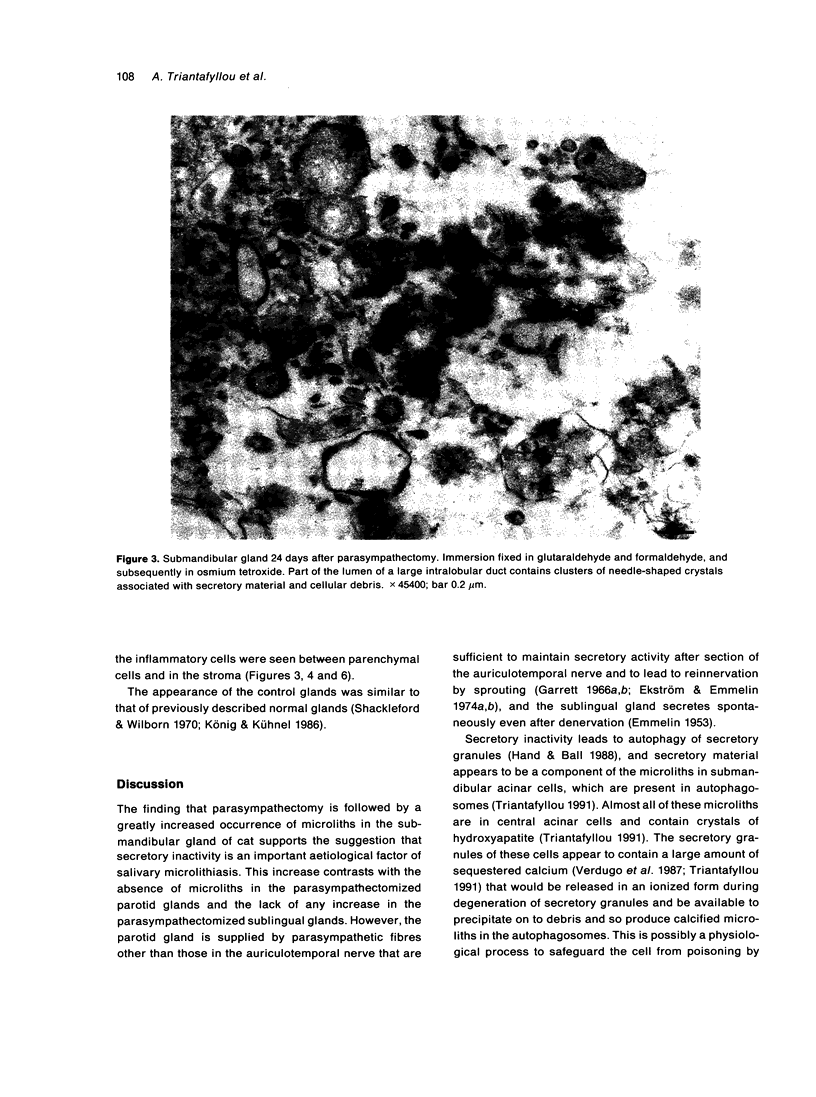
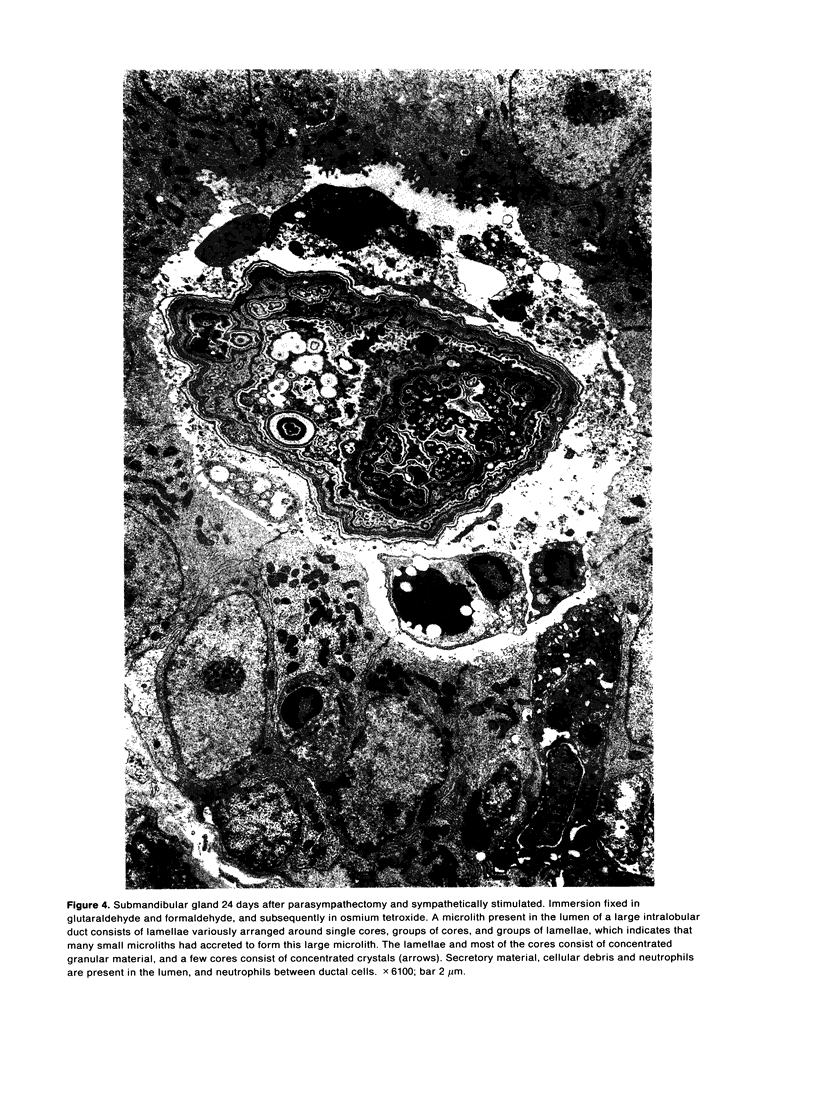
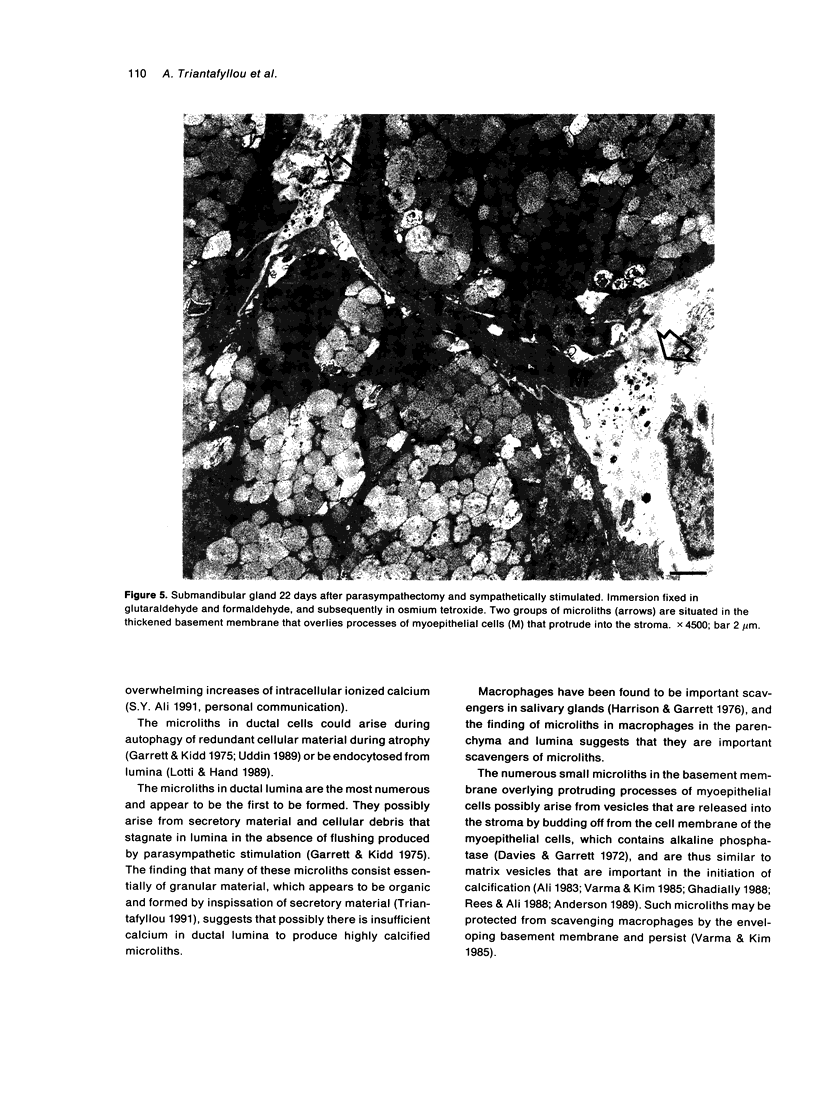
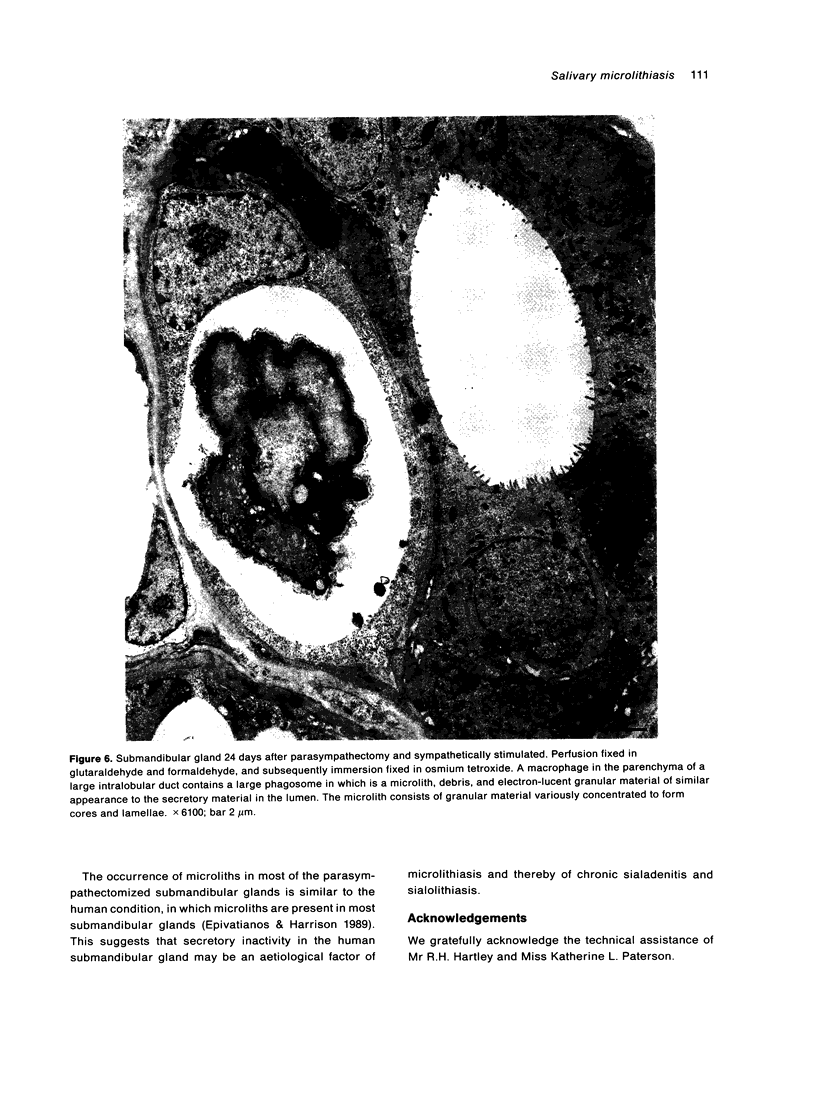
Salivary glands of cat were examined from 1 to 42 days following parasympathectomy and compared with contralateral normal control glands. Microliths were detected by light microscopy in none of 11 parotid, 31 out of 41 submandibular and four out of 22 sublingual glands following parasympathectomy, and one out of 19 parotid, five out of 28 submandibular and four out of 15 sublingual normal control glands. The greatly increased occurrence of microliths in the submandibular gland was statistically significant. Microliths in the parasympathectomized submandibular glands were detected by light microscopy most often in ductal lumina, followed by acinar lumina, ductal parenchyma, interstitial stroma, and acinar parenchyma. They were detected by electron microscopy also in the basement membrane overlying protruding processes of myoepithelial cells and in intraparenchymal macrophages. Intracellular microliths were in phagosomes. In the parasympathectomized submandibular glands, parenchymal atrophy was seen and particularly involved the striated ducts; secretory material and cellular debris were seen in lumina; and macrophages and neutrophils were more apparent than normally. The great increase of microlithiasis in the submandibular gland appears to be the result of secretory inactivity, and microliths appear to form in stagnant secretory material and cellular debris in lumina and in phagosomes of parenchymal cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson H. C. Mechanism of mineral formation in bone. Lab Invest. 1989 Mar;60(3):320–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. J., Garrett J. R. Improved preservation of alkaline phosphatase in salivary glands of the cat. Histochem J. 1972 Jul;4(4):365–379. doi: 10.1007/BF01005010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMMELIN N. On spontaneous secretion of saliva. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1953;111:34–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Garrett J. R. Submandibular responses to stimulation of the sympathetic innervation following parasympathetic denervation in cats. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:421–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekström J., Emmelin N. Reinnervation of the denervated parotid gland of the cat. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1974 Jan;59(1):1–9. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1974.sp002236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekström J., Emmelin N. The secretory innervation of the parotid gland of the cat: an unexpected component. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1974 Jan;59(1):11–17. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1974.sp002237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmelin N., Garrett J. R. Nerve-induced secretion of parotid acinar granules in cats. Cell Tissue Res. 1989 Sep;257(3):549–554. doi: 10.1007/BF00221465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epivatianos A., Harrison J. D., Dimitriou T. Ultrastructural and histochemical observations on microcalculi in chronic submandibular sialadenitis. J Oral Pathol. 1987 Nov;16(10):514–517. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1987.tb00683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epivatianos A., Harrison J. D., Garrett J. R., Davies K. J., Senkus R. Ultrastructural and histochemical observations on intracellular and luminal microcalculi in the feline sublingual salivary gland. J Oral Pathol. 1986 Nov;15(10):513–517. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1986.tb00567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epivatianos A., Harrison J. D. The presence of microcalculi in normal human submandibular and parotid salivary glands. Arch Oral Biol. 1989;34(4):261–265. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(89)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett J. R., Kidd A. Effects of nerve stimulation and denervation on secretory material in submandibular striated duct cells of cats, and the possible role of these cells in the secretion of salivary kallikrein. Cell Tissue Res. 1975 Aug 1;161(1):71–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00222115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett J. R. The innervation of salivary glands. 3. The effects of certain experimental procedures on cholinesterase-positive nerves in glands of the cat. J R Microsc Soc. 1966 Oct;86(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett J. R. The innervation of salivary glands. IV. The effects of certain experimental procedures on the ultrastructure of nerves in glands of the cat. J R Microsc Soc. 1966 Oct;86(1):15–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand A. R., Ball W. D. Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of secretory proteins in autophagic vacuoles of parotid acinar cells of starved rats. J Oral Pathol. 1988 Jul;17(6):279–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1988.tb01537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. D., Epivatianos A. Production of microliths and sialadenitis in rats by a short combined course of isoprenaline and calcium gluconate. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1992 May;73(5):585–590. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(92)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. D., Garrett J. R. Inflammatory cells in duct-ligated salivary glands of the cat: a histochemical study. J Pathol. 1976 Oct;120(2):115–119. doi: 10.1002/path.1711200207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey C. D., Pittman F. E. A simple methylene blue-azure II-basic fuchsin stain for epoxy-embedded tissue sections. Stain Technol. 1974 Jan;49(1):9–14. doi: 10.3109/10520297409116929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König B., Jr, Kühnel W. Licht- und elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen and der Glandula parotis und der Glandula submandibularis der Hauskatze. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch. 1986;100(3):469–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotti L. V., Hand A. R. Endocytosis of native and glycosylated bovine serum albumin by duct cells of the rat parotid gland. Cell Tissue Res. 1989 Feb;255(2):333–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00224116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees J. A., Ali S. Y. Ultrastructural localisation of alkaline phosphatase activity in osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988 Sep;47(9):747–753. doi: 10.1136/ard.47.9.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert G., Donath K. Zur Pathogenese des Kütter-Tumors der Submandibularis. Analyse von 349 Fällen mit chronischer Sialadenitis der Submandibularis. HNO. 1977 Mar;25(3):81–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackleford J. M., Wilborn W. H. Ultrastructural aspects of cat submandibular glands. J Morphol. 1970 Jul;131(3):253–276. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051310303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandler B. Electron microscopical observations on early sialoliths in a human submaxillary gland. Arch Oral Biol. 1965 May-Jun;10(3):509–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(65)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandler B., Poulsen J. H. Ultrastructure of the cat sublingual gland. Anat Rec. 1977 Feb;187(2):153–171. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091870204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uddin M. Autonomic denervation effects on the kallikrein and striated duct cells of the rat and cat submandibular glands. Anat Anz. 1989;169(4):273–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varma V. A., Kim K. M. Placental calcification: ultrastructural and X-ray microanalytic studies. Scan Electron Microsc. 1985;(Pt 4):1567–1572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdugo P., Deyrup-Olsen I., Aitken M., Villalon M., Johnson D. Molecular mechanism of mucin secretion: I. The role of intragranular charge shielding. J Dent Res. 1987 Feb;66(2):506–508. doi: 10.1177/00220345870660022001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]