Abstract
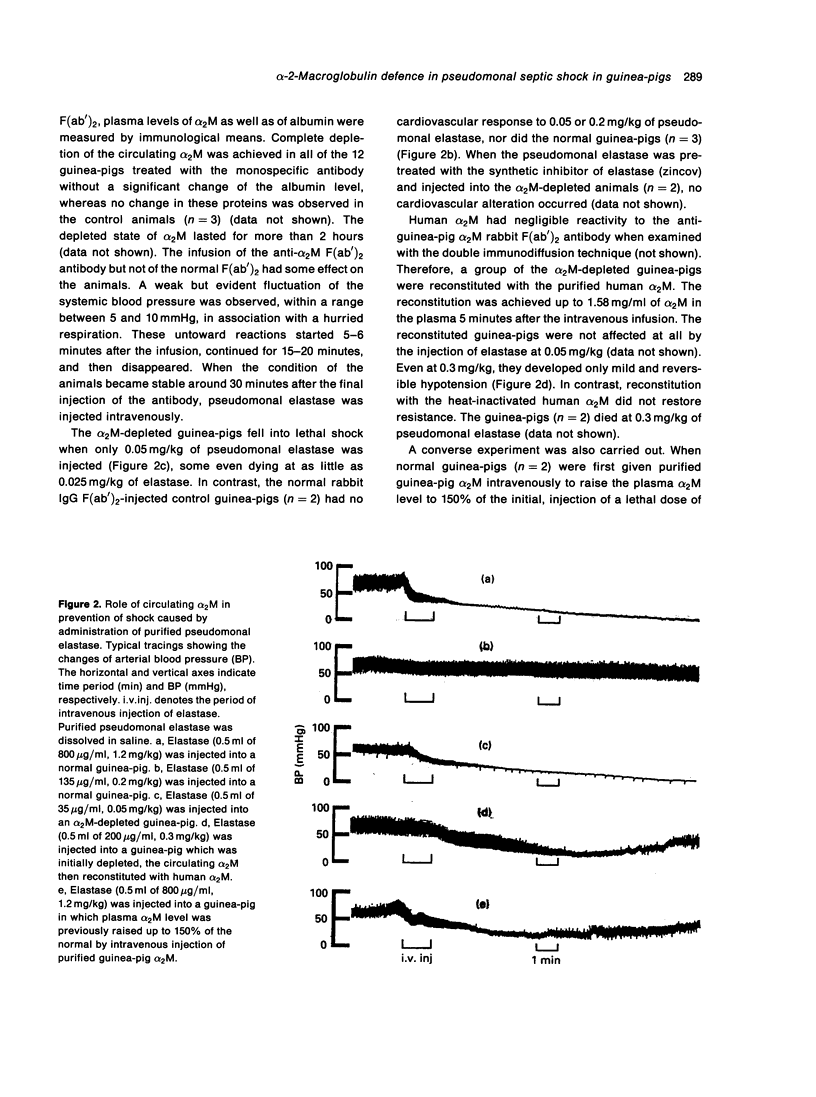
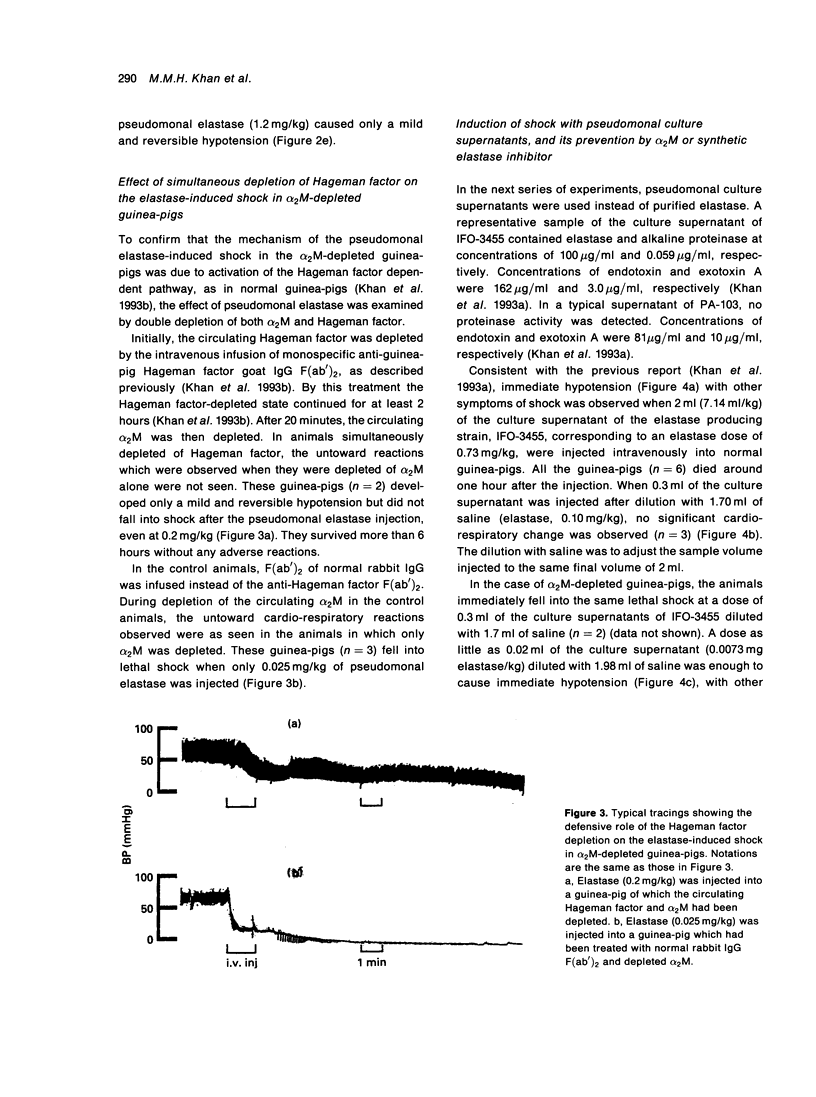
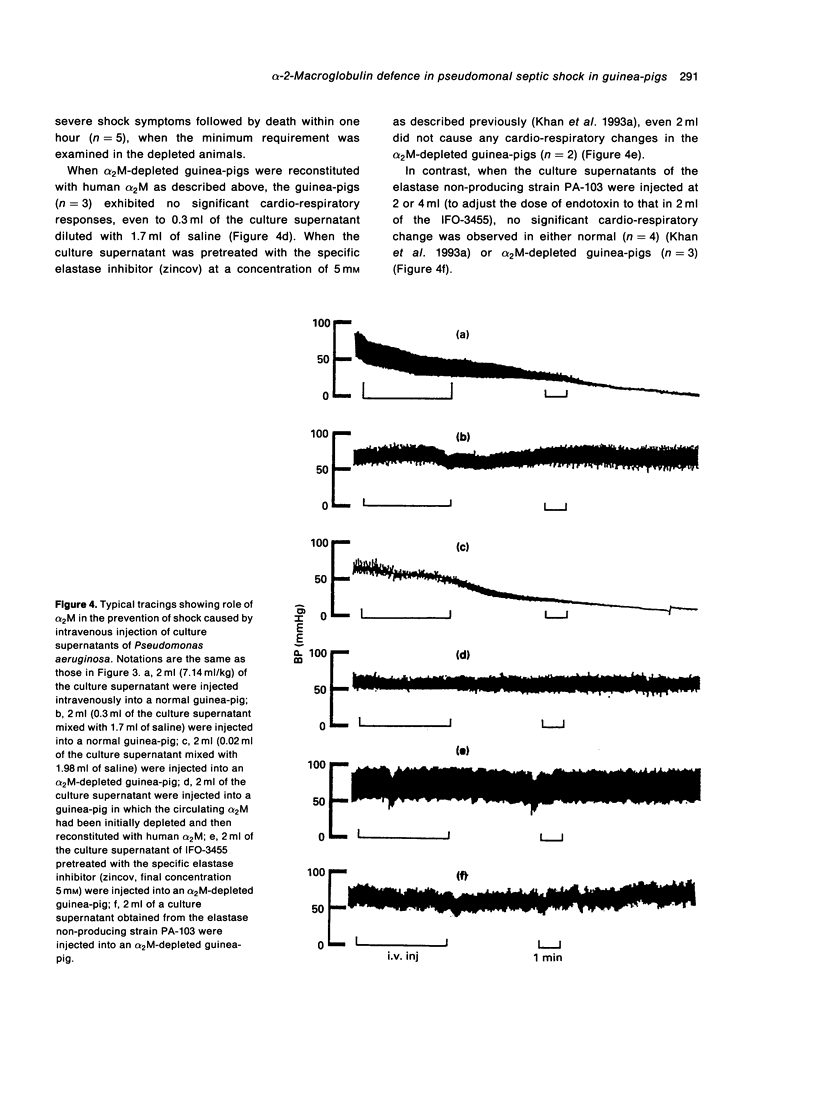
An intravenous injection of 1.2 mg/kg of Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase induces immediate lethal shock in guinea-pigs. In the present study, alpha-2-macroglobulin (alpha 2M) was shown to be the major factor in guinea-pig plasma that inhibits the enzymatic activity of elastase in vitro. Depletion of circulating alpha 2M by injecting anti-guinea-pig alpha 2M rabbit IgG F(ab')2 rendered the animals sensitive to a dose of elastase of 0.05 mg/kg. When the alpha 2M-depleted guinea-pigs were reconstituted with human alpha 2M, this sensitivity was reversed. Lethal shock did not occur in alpha 2M-depleted animals even at an elastase dose of 0.2 mg/kg when Hageman factor was simultaneously depleted, indicating that elastase induces shock through activation of the Hageman factor-dependent system. Similar results were obtained when the culture supernatants of an elastase-producing strain, IFO-3455, were used instead of the purified elastase, whereas no cardiovascular changes occurred, even in the alpha 2M-depleted guinea-pigs, when the culture supernatants were pretreated with an elastase specific inhibitor (zincov) or when the culture supernatants of an elastase non-producing strain, PA-103 were used.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham E., Shoemaker W. C., Bland R. D., Cobo J. C. Sequential cardiorespiratory patterns in septic shock. Crit Care Med. 1983 Oct;11(10):799–803. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198310000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen L. W., Baek L., Degn H., Lehd J., Krasnik M., Rasmussen J. P. Presence of circulating endotoxins during cardiac operations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1987 Jan;93(1):115–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baydoun A. R., Woodward B. Effects of bradykinin in the rat isolated perfused heart: role of kinin receptors and endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul;103(3):1829–1833. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock-Utne J. G., Gaffin S. L., Wells M. T., Gathiram P., Sohar E., James M. F., Morrell D. F., Norman R. J. Endotoxaemia in exhausted runners after a long-distance race. S Afr Med J. 1988 May 7;73(9):533–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner R. L., Natanson C., Elin R. J., Hosseini J. M., Banks S., MacVittie T. J., Parrillo J. E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa compared with Escherichia coli produces less endotoxemia but more cardiovascular dysfunction and mortality in a canine model of septic shock. Chest. 1990 Dec;98(6):1480–1487. doi: 10.1378/chest.98.6.1480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Reynolds J. A., Pizzo S. V. Physical properties of human alpha 2-macroglobulin following reaction with methylamine and trypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 10;705(3):306–314. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenman R. L., Schein R. M., Martin M. A., Wenzel R. P., MacIntyre N. R., Emmanuel G., Chmel H., Kohler R. B., McCarthy M., Plouffe J. A controlled clinical trial of E5 murine monoclonal IgM antibody to endotoxin in the treatment of gram-negative sepsis. The XOMA Sepsis Study Group. JAMA. 1991 Aug 28;266(8):1097–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. B., Vermeulen M., Swenson R. P. The temperature-sensitive bond in human alpha 2-macroglobulin is the alkylamine-reactive site. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3820–3823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang B. S., Leenen F. H. Brain ouabain and central effects of dietary sodium in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Circ Res. 1992 Feb;70(2):430–437. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.2.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimatsu T., Yamamoto T., Kozono K., Kambara T. Guinea pig macroalbumin. A major inhibitor of activated Hageman factor in plasma with an alpha 2-macroglobulin-like nature. Am J Pathol. 1984 Apr;115(1):57–69. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. M., Yamamoto T., Araki H., Ijiri Y., Shibuya Y., Okamoto M., Kambara T. Pseudomonal elastase injection causes low vascular resistant shock in guinea pigs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Aug 4;1182(1):83–93. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(93)90157-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. M., Yamamoto T., Araki H., Shibuya Y., Kambara T. Role of Hageman factor/kallikrein-kinin system in pseudomonal elastase-induced shock model. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 11;1157(2):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(93)90055-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebl D. J., Koo P. H. Comparative binding of neurotrophins (NT-3, CNTF and NGF) and various cytokines to alpha 2-macroglobulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jun 30;193(3):1255–1261. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molla A., Yamamoto T., Akaike T., Miyoshi S., Maeda H. Activation of hageman factor and prekallikrein and generation of kinin by various microbial proteinases. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10589–10594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino N., Powers J. C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase. Development of a new substrate, inhibitors, and an affinity ligand. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3482–3486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northemann W., Shiels B. R., Braciak T. A., Hanson R. W., Heinrich P. C., Fey G. H. Structure and acute-phase regulation of the rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9194–9203. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. M., Shelhamer J. H., Natanson C., Alling D. W., Parrillo J. E. Serial cardiovascular variables in survivors and nonsurvivors of human septic shock: heart rate as an early predictor of prognosis. Crit Care Med. 1987 Oct;15(10):923–929. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198710000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocke D. A., Gaffin S. L., Wells M. T., Koen Y., Brock-Utine J. G. Endotoxemia associated with cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1987 Jun;93(6):832–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toossi Z., Sedor J. R., Mettler M. A., Everson B., Young T., Ratnoff O. D. Induction of expression of monocyte interleukin 1 by Hageman factor (factor XII). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11969–11972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leuven F., Cassiman J. J., Van den Berghe H. Functional modifications of alpha 2-macroglobulin by primary amines. Kinetics of inactivation of alpha 2-macroglobulin by methylamine, and formation of anomalous complexes with trypsin. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 1;201(1):119–128. doi: 10.1042/bj2010119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren H. S., Danner R. L., Munford R. S. Anti-endotoxin monoclonal antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 23;326(17):1153–1157. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204233261711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., Fisher C. J., Jr, Sprung C. L., Straube R. C., Sadoff J. C., Foulke G. E., Wortel C. H., Fink M. P., Dellinger R. P., Teng N. N. Treatment of gram-negative bacteremia and septic shock with HA-1A human monoclonal antibody against endotoxin. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The HA-1A Sepsis Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1991 Feb 14;324(7):429–436. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199102143240701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


