Abstract
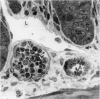
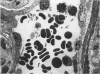
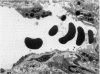
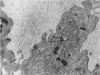
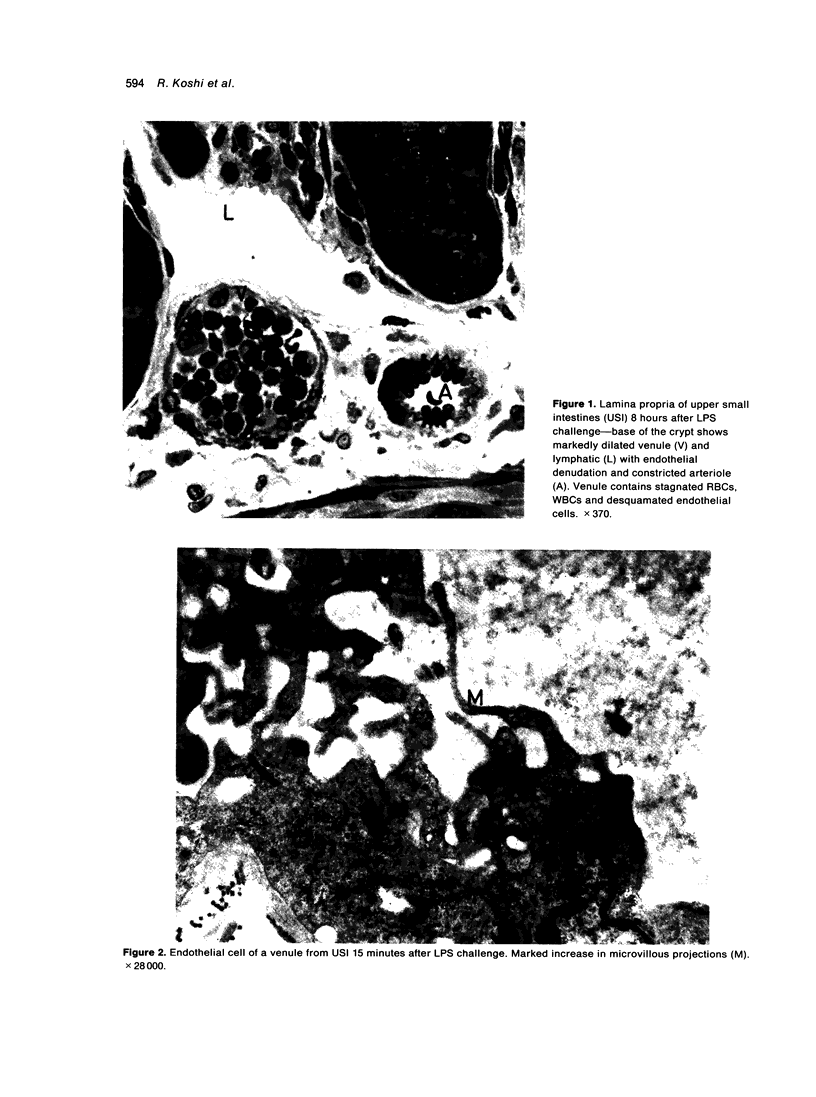
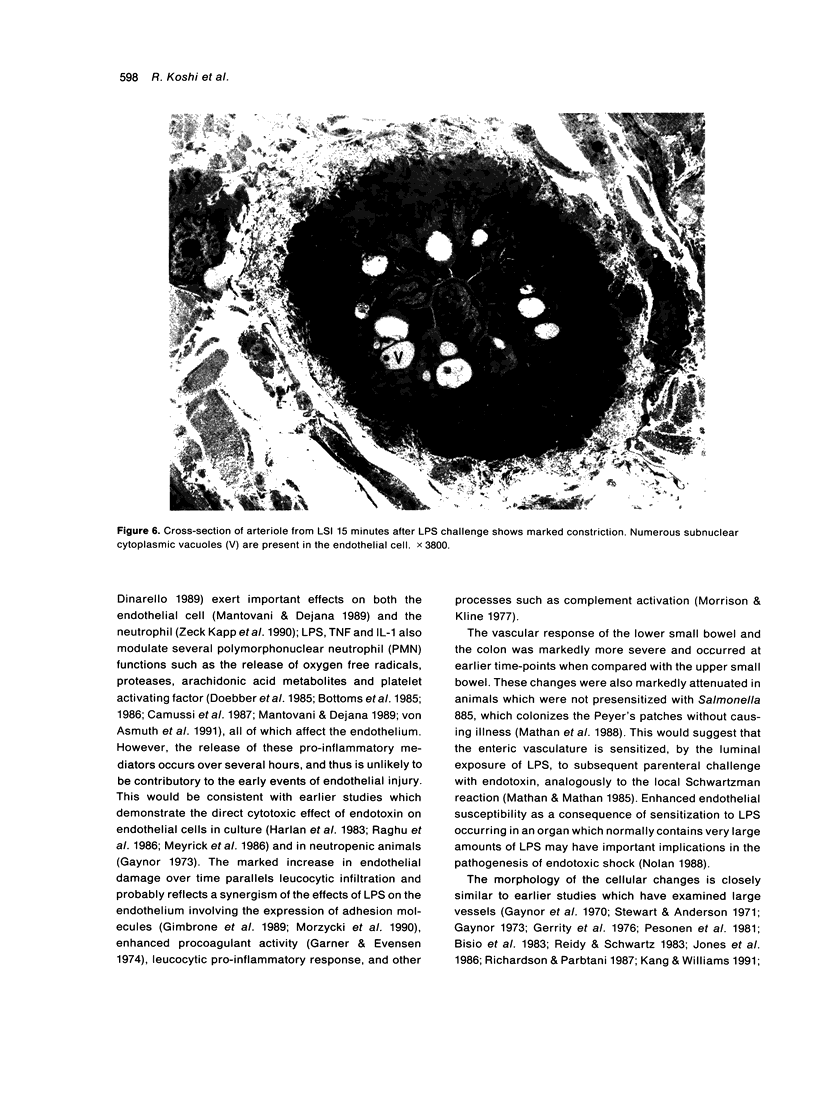
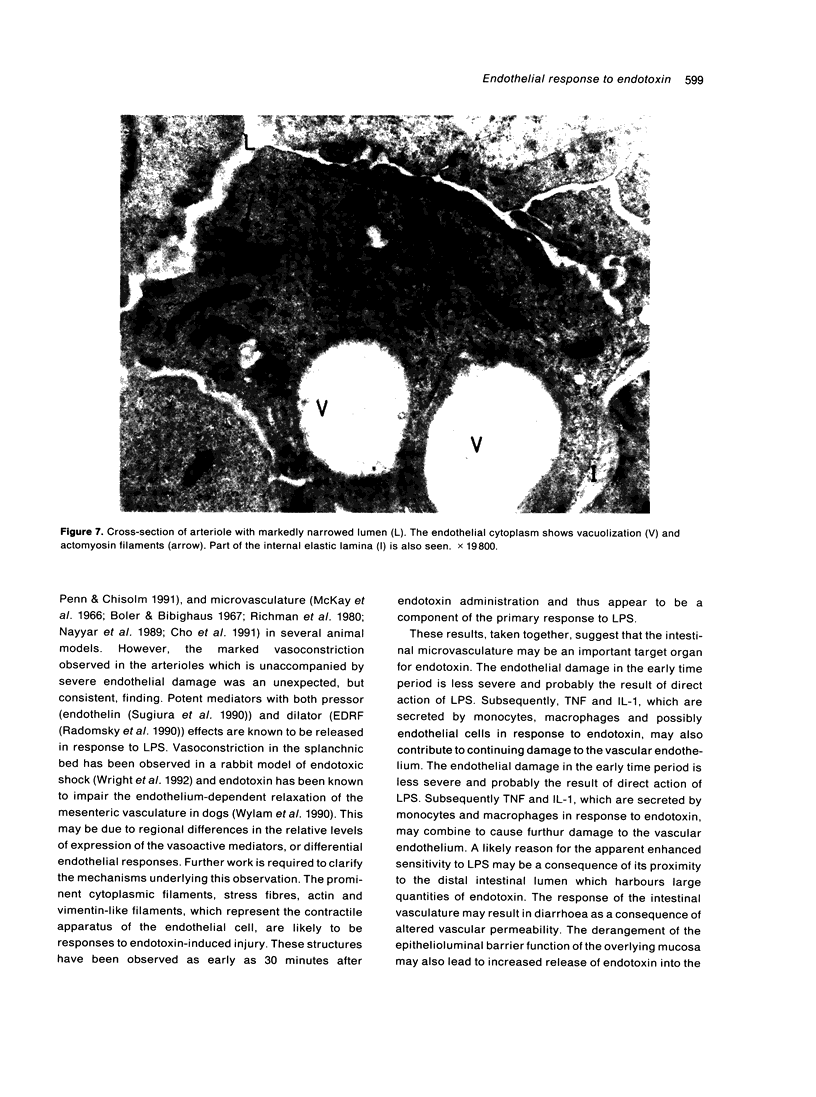
The response of enteric vasculature to endotoxin was examined at the ultrastructural level using a murine model of endotoxin-induced acute diarrhoea. Morphological changes indicative of endothelial damage were evident as early as 15 minutes following endotoxin challenge. These changes, characterized by widening of intercellular spaces, increased microvillous projections and the appearance of stress fibres, preceded the leucocytic response. Endothelial damage increased with time, being associated with progressive degenerative changes in the plasma membrane, cytoplasm and organelles, ultimately leading to desquamation. These latter changes were temporally associated with margination of neutrophils and platelet adhesion to the denuded subendothelium. The venules were the primary site of these changes while the capillaries were the least affected. The arterioles were markedly constricted with minimal endothelial damage. These changes suggest that the enteric vascular endothelium may be an important target organ, and the resultant endothelial injury may have implications in host responses to endotoxin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis, cachexia, shock, and inflammation: a common mediator. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:505–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisio J. M., Breen R. E., Connell R. S., Harrison M. W. Pulmonary capillary endothelial dysfunction in hypoxia and endotoxemia: a biochemical and electron microscope study. J Trauma. 1983 Aug;23(8):730–739. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198308000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottoms G. D., Johnson M. A., Lamar C. H., Fessler J. F., Turek J. J. Endotoxin-induced eicosanoid production by equine vascular endothelial cells and neutrophils. Circ Shock. 1985;15(3):155–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottoms G. D., Johnson M., Ward D., Fessler J., Lamar C., Turek J. Release of eicosanoids from white blood cells, platelets, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells in response to endotoxin and A23187. Circ Shock. 1986;20(1):25–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Bussolino F., Salvidio G., Baglioni C. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin stimulates peritoneal macrophages, polymorphonuclear neutrophils, and vascular endothelial cells to synthesize and release platelet-activating factor. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1390–1404. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho T. H., Kwak J. S., Sohn T. J. Effects of Escherichia coli endotoxin on structure and permeability of myocardial capillaries. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1991 Jan;41(1):12–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1991.tb03266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choudari C. P., Mathan M., Rajan D. P., Raghavan R., Mathan V. I. A correlative study of etiology, clinical features and rectal mucosal pathology in adults with acute infectious diarrhea in southern India. Pathology. 1985 Jul;17(3):443–450. doi: 10.3109/00313028509105498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and its biologically related cytokines. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:153–205. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60642-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doebber T. W., Wu M. S., Robbins J. C., Choy B. M., Chang M. N., Shen T. Y. Platelet activating factor (PAF) involvement in endotoxin-induced hypotension in rats. Studies with PAF-receptor antagonist kadsurenone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 29;127(3):799–808. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner R., Evensen S. A. Endotoxin-induced intravascular coagulation and shock in dogs: the role of factor VII. Br J Haematol. 1974 Aug;27(4):655–668. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor E., Bouvier C., Spaet T. H. Vascular lesions: possible pathogenetic basis of the generalized Shwartzman reaction. Science. 1970 Nov 27;170(3961):986–988. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3961.986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor E. The role of granulocytes in endotoxin-induced vascular injury. Blood. 1973 Jun;41(6):797–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity R. G., Richardson M., Caplan B. A., Cade J. F., Hirsh J., Schwartz C. J. Endotoxin-induced vascular endothelial injury and repair. II. Focal injury, en face morphology, (3H)thymidine uptake and circulating endothelial cells in the dog. Exp Mol Pathol. 1976 Feb;24(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(76)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Obin M. S., Brock A. F., Luis E. A., Hass P. E., Hébert C. A., Yip Y. K., Leung D. W., Lowe D. G., Kohr W. J. Endothelial interleukin-8: a novel inhibitor of leukocyte-endothelial interactions. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1601–1603. doi: 10.1126/science.2688092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Harker L. A., Reidy M. A., Gajdusek C. M., Schwartz S. M., Striker G. E. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated bovine endothelial cell injury in vitro. Lab Invest. 1983 Mar;48(3):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Kirton O. C., Zapol W. M., Reid L. Rat pulmonary artery wall injury by chronic intermittent infusions of Escherichia coli endotoxin. Obliterative vasculitis and vascular occlusion. Lab Invest. 1986 Mar;54(3):282–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang Y. H., Williams R. Endotoxin-induced endothelial injury and subendothelial accumulation of fibronectin in rat aorta. Anat Rec. 1991 Jan;229(1):86–102. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092290110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani A., Dejana E. Cytokines as communication signals between leukocytes and endothelial cells. Immunol Today. 1989 Nov;10(11):370–375. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathan M. M., Mathan V. I. Local Shwartzman reaction in the rectal mucosa in acute diarrhoea. J Pathol. 1985 Jul;146(3):179–187. doi: 10.1002/path.1711460304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathan V. I., Penny G. R., Mathan M. M., Rowley D. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal microvascular lesions leading to acute diarrhea. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1714–1721. doi: 10.1172/JCI113785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. G., Margaretten W., Csavossy I. An electron microscope study of the effects of bacterial endotoxin on the blood-vascular system. Lab Invest. 1966 Dec;15(12):1815–1829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B. O., Ryan U. S., Brigham K. L. Direct effects of E coli endotoxin on structure and permeability of pulmonary endothelial monolayers and the endothelial layer of intimal explants. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jan;122(1):140–151. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Kline L. F. Activation of the classical and properdin pathways of complement by bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS). J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):362–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morzycki W., Sadowska J., Issekutz A. C. Interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor alpha induced polymorphonuclear leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion and transendothelial migration in vitro: the effect of apical versus basal monolayer stimulation. Immunol Lett. 1990 Sep;25(4):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(90)90204-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayyar R. P., Hurley R. M., Goto M., Zeller W. P. Microvascular endothelium: a major target site of endotoxin induced injury in 10 day old rat. J Exp Pathol. 1989;4(2):57–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn M. S., Chisolm G. M. Relation between lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial cell injury and entry of macromolecules into the rat aorta in vivo. Circ Res. 1991 May;68(5):1259–1269. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.5.1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen E., Kaprio E., Rapola J., Soveri T., Oksanen H. Endothelial cell damage in piglet coronary artery after intravenous administration of E. coli endotoxin. A scanning and transmission electron-microscopic study. Atherosclerosis. 1981 Aug-Sep;40(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(81)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Glucocorticoids inhibit the expression of an inducible, but not the constitutive, nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10043–10047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghu G., Striker L. J., Striker G. E. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated injury to cultured human glomerular endothelial cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Mar;38(3):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidy M. A., Schwartz S. M. Endothelial injury and regeneration. IV. Endotoxin: a nondenuding injury to aortic endothelium. Lab Invest. 1983 Jan;48(1):25–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson M., Parbtani A. Identification of non-denuding endothelial injury by scanning electron microscopy. Scanning Microsc. 1987 Sep;1(3):1315–1326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman A. V., Gerber L. I., Balis J. U. Peritubular capillaries. A major target site of endotoxin-induced vascular injury in the primate kidney. Lab Invest. 1980 Oct;43(4):327–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. J., Anderson M. J. An ultrastructural study of endotoxin induced damage in rabbit mesenteric arteries. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Feb;52(1):75–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M., Inagami T., Kon V. Endotoxin stimulates endothelin-release in vivo and in vitro as determined by radioimmunoassay. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 30;161(3):1220–1227. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. E., Rees D. D., Moncada S. Protective and pathological roles of nitric oxide in endotoxin shock. Cardiovasc Res. 1992 Jan;26(1):48–57. doi: 10.1093/cvr/26.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wylam M. E., Samsel R. W., Umans J. G., Mitchell R. W., Leff A. R., Schumacker P. T. Endotoxin in vivo impairs endothelium-dependent relaxation of canine arteries in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Dec;142(6 Pt 1):1263–1267. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.6_Pt_1.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeck-Kapp G., Kapp A., Busse R., Riede U. N. Interaction of granulocytes and endothelial cells upon stimulation with tumor necrosis factor-alpha: an ultrastructural study. Immunobiology. 1990 Nov;181(4-5):267–275. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(11)80518-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Asmuth E. J., Leeuwenberg J. F., van der Linden C. J., Buurman W. A. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha induces neutrophil-mediated injury of cultured human endothelial cells. Scand J Immunol. 1991 Aug;34(2):197–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1991.tb01537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]