Full text
PDF




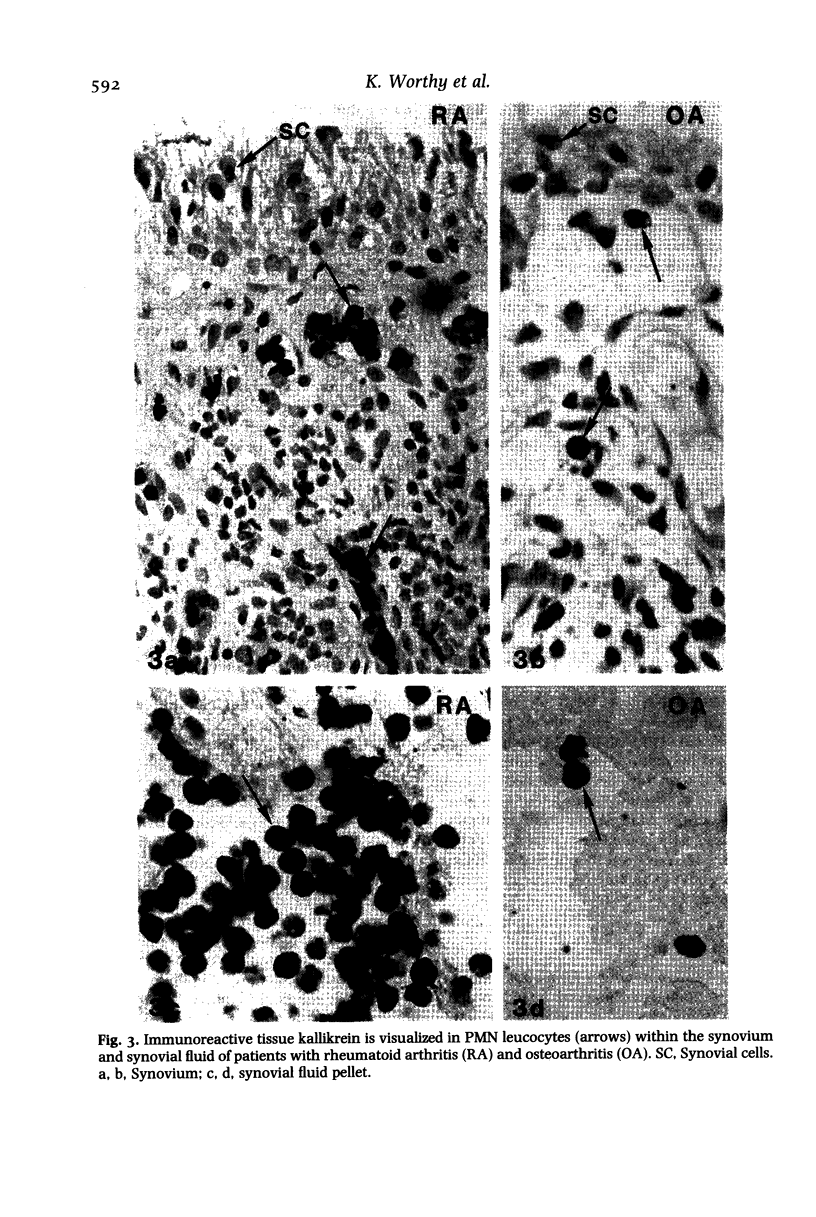









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG D., JEPSON J. B., KEELE C. A., STEWART J. W. Pain-producing substance in human inflammatory exudates and plasma. J Physiol. 1957 Feb 15;135(2):350–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Nour A. N., Elson C. J., Dieppe P. A. Proliferative responses of T-cell lines grown from joint fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other arthritides. Immunol Lett. 1986 Jun;12(5-6):329–333. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(86)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borth W., Dunky A., Kleesiek K. Alpha 2-macroglobulin-proteinase complexes as correlated with alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor-elastase complexes in synovial fluids of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Mar;29(3):319–325. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromley M., Fisher W. D., Woolley D. E. Mast cells at sites of cartilage erosion in the rheumatoid joint. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Feb;43(1):76–79. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W. Formation of human plasma kinin. N Engl J Med. 1974 Sep 5;291(10):509–515. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197409052911008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly J. C., Skidgel R. A., Schulz W. W., Johnson A. R., Erdös E. G. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11 in human neutrophils: cleavage of chemotactic peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8737–8741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crisp A. J., Chapman C. M., Kirkham S. E., Schiller A. L., Krane S. M. Articular mastocytosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Aug;27(8):845–851. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crisp A. J., Wright J. K., Hazleman B. L. Effects of heparin, histamine, and salmon calcitonin on mouse calvarial bone resorption. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 May;45(5):422–427. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.5.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieppe P. Osteoarthritis: are we asking the wrong questions? Br J Rheumatol. 1984 Aug;23(3):161–163. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/23.3.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dularay B., Dieppe P. A., Elson C. J. Depressed degranulation response of synovial fluid polymorphonuclear leucocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis to IgG aggregates. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Feb;79(2):195–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. T., Silverberg M., Kaplan A. P. The cleavage and formation of activated human Hageman factor by autodigestion and by kallikrein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1779–1784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eeckhout Y., Vaes G. Further studies on the activation of procollagenase, the latent precursor of bone collagenase. Effects of lysosomal cathepsin B, plasmin and kallikrein, and spontaneous activation. Biochem J. 1977 Jul 15;166(1):21–31. doi: 10.1042/bj1660021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen V. Plasma kinins in synovial exudates. Br J Exp Pathol. 1970 Jun;51(3):322–327. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen V. Urates and kinin formation in synovial fluid. Proc R Soc Med. 1966 Apr;59(4):302–307. doi: 10.1177/003591576605900403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H. Prostaglandins, aspirin-like drugs and analgesia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 13;240(102):200–203. doi: 10.1038/newbio240200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa C. D., MacIver A. G., Bhoola K. D. Identification of a tissue kallikrein in human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Br J Haematol. 1989 Jul;72(3):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb07711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger R., Stuckstedte U., Clausnitzer B., Fritz H. Progressive inhibition of human glandular (urinary) kallikrein by human serum and identification of the progressive antikallikrein as alpha 1-antitrypsin (alpha 1-protease inhibitor). Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Mar;362(3):317–325. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1981.362.1.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Cochrane C. G. Mechanisms for the involvement of high molecular weight kininogen in surface-dependent reactions of Hageman factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães J. A., Borges D. R., Prado E. S., Prado J. L. Kinin-converting aminopeptidase from human serum. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 15;22(24):3157–3172. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson E. J., Schmaier A. H., Wachtfogel Y. T., Kaufman N., Kucich U., Colman R. W. Human neutrophils contain and bind high molecular weight kininogen. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):28–35. doi: 10.1172/JCI114151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson G. T., Lerner U. Bradykinin stimulates bone resorption and lysosomal-enzyme release in cultured mouse calvaria. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 1;219(1):329–332. doi: 10.1042/bj2190329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Human plasma alpha 2-macroglobulin. An inhibitor of plasma kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):329–352. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz M., Vignery A., Gershon R. K., Baron R. Thymus-derived lymphocytes and their interactions with macrophages are required for the production of osteoclast-activating factor in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2181–2185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasani M. K., Katori M., Lewis G. P. Intracellular enzymes and kinin enzymes in synovial fluid in joint diseases. Origin and relation to disease category. Ann Rheum Dis. 1969 Sep;28(5):497–512. doi: 10.1136/ard.28.5.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLERMEYER R. W., BRECKENRIDGE R. T. THE INFLAMMATORY PROCESS IN ACUTE GOUTY ARTHRITIS. I. ACTIVATION OF HAGEMAN FACTOR BY SODIUM URATE CRYSTALS. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Feb;65:307–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P. Kinins and bone resorption in rheumatic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 May;30(5):589–592. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Silverberg M. The coagulation-kinin pathway of human plasma. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner U. H., Jones I. L., Gustafson G. T. Bradykinin, a new potential mediator of inflammation-induced bone resorption. Studies of the effects on mouse calvarial bones and articular cartilage in vitro. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 May;30(5):530–540. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo O., Tanaka S., Kikuchi H. Effect of urinary trypsin inhibitor on osteoarthritis. Thromb Res. 1988 Nov 1;52(3):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Steinberg S. G., Habal F. M., Ranadive N. S. Demonstration of a kinin-generating enzyme in the lysosomes of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Lab Invest. 1973 Dec;29(6):669–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Esterl W. Kininogens, kinins and kinships. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Feb 28;61(1):2–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H., Cawston T. E., De Silva M., Barrett A. J. Identification of plasma kallikrein as an activator of latent collagenase in rheumatoid synovial fluid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 18;702(1):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. L., Storz J. Observations on sheep with polyarthritis produced by an agent of the psittacosis-lymphogranuloma venereum-trachoma group. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Feb;10(1):1–12. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard M. H. Synovial protease/inhibitor ratios in erosive and nonerosive arthropathies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Feb;43(1):50–55. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G. The relationship of structure and function in human Hageman factor. The association of enzymatic and binding activities with separate regions of the molecule. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):852–860. doi: 10.1172/JCI108361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. D., Boyden K. N., Hendrickson S. M., Muirden K. D. Antitrypsin activity and enzyme inhibitors in the rheumatoid joint. J Rheumatol. 1981 Jul-Aug;8(4):547–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J., Pilsworth L. M., Sarsfield S. J., Gavrilovic J., Heath J. K. Pig catabolin is a form of interleukin 1. Cartilage and bone resorb, fibroblasts make prostaglandin and collagenase, and thymocyte proliferation is augmented in response to one protein. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):461–466. doi: 10.1042/bj2240461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter M. Kallikreins (kininogenases)--a group of serine proteases with bioregulatory actions. Pharmacol Rev. 1979 Mar;31(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn B. M., Figueroa C. D., Fink E., Swan A., Dieppe P. A., Bhoola K. D. A tissue kallikrein in the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Feb;48(2):128–133. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg M., Diehl S. V. The autoactivation of factor XII (Hageman factor) induced by low-Mr heparin and dextran sulphate. The effect of the Mr of the activating polyanion. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):715–720. doi: 10.1042/bj2480715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilberg I., Osterland C. K. Anti-inflammatory effect of the trypsin-kallikrein inhibitor in acute arthritis induced by urate crystals in rabbits. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Sep;76(3):472–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Ito A., Mori Y., Hayashi Y., Matsuta K. Kallikrein in synovial fluid with rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem Med Metab Biol. 1987 Apr;37(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0885-4505(87)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanay A., Field E. H., Hoppe R. T., Strober S. Long-term followup of rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with total lymphoid irradiation. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jan;30(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terkeltaub R., Tenner A. J., Kozin F., Ginsberg M. H. Plasma protein binding by monosodium urate crystals. Analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jun;26(6):775–783. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., West G. B. Prostaglandins, kinin and inflammation in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Feb;50(2):231–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb08566.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiffany C. W., Burch R. M. Bradykinin stimulates tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 release from macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81331-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschesche H., Michaelis J., Kohnert U., Fedrowitz J., Oberhoff R. Tissue kallikrein effectively activates latent matrix degrading metalloenzymes. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1989;247A:545–548. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9543-4_84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vahtera E., Hamberg U. Absence of binding of pancreatic and urinary kallikreins to alpha 2-macroglobulin. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):521–524. doi: 10.1042/bj1570521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M. Development of bradykinin antagonists: structure-activity relationships for new categories of antagonist sequences. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1989;247B:395–400. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9546-5_65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachtfogel Y. T., Kucich U., James H. L., Scott C. F., Schapira M., Zimmerman M., Cohen A. B., Colman R. W. Human plasma kallikrein releases neutrophil elastase during blood coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1672–1677. doi: 10.1172/JCI111126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Agnello V., Kunkel H. G. Gamma globulin complexes in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Partial characterization and relationship to lowered complement levels. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):689–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. The immunopathology of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Immunol. 1973;16(0):265–336. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Holoshitz J., Nevo Z., Frenkel A., Klajman A., Cohen I. R. Arthritis induced by a T-lymphocyte clone that responds to Mycobacterium tuberculosis and to cartilage proteoglycans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5117–5120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]