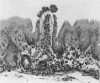Abstract
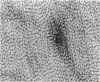
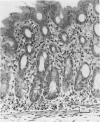
The pre-ulcerative phase of carrageenan-induced colonic ulceration was investigated in guinea-pigs supplied 3% degraded carrageenan as an aqueous solution as drinking fluid for 2 or 3 days during which no ulceration of the bowel was observed with the naked eye or dissecting microscope. Mucosal microscopic changes, from caecum to rectum, were multifocal and included cellular infiltrates, dilatation of glands, crypt abscesses, micro-ulcers and sulphated polysaccharide in the lamina propria. Sulphated polysaccharide was also demonstrated histologically for the first time within the surface epithelium and showed ultrastructural features similar to carrageenan. The results indicate that colonic epithelium in the guinea-pig is capable of macromolecular absorption. Carrageenan, a highly active polyanionic electrolyte, within the surface epithelial cells is most likely a primary factor in the breakdown of mucosal integrity. Macromolecular absorption causing enteropathy of the large bowel is a new pathophysiological concept which may have implications in man, particularly in the pathology of large bowel disease.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham R., Fabian R. J., Golberg L., Coulston F. Role of lysosomes in carrageenan-induced cecal ulceration. Gastroenterology. 1974 Dec;67(6):1169–1181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashi K. W., Inagaki T., Fujimoto Y., Fukuda Y. Induction by degraded carrageenan of colorectal tumors in rats. Cancer Lett. 1978 Mar;4(3):171–176. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(78)94237-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benitz K. F., Golberg L., Coulston F. Intestinal effects of carrageenans in the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1973 Aug;11(4):565–575. doi: 10.1016/s0015-6264(73)80327-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catanzaro P. J., Schwartz H. J., Graham R. C., Jr Spectrum and possible mechanism of carrageenan cytotoxicity. Am J Pathol. 1971 Aug;64(2):387–404. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delahunty T., Recher L., Hollander D. Intestinal permeability changes in rodents: a possible mechanism for degraded carrageenan-induced colitis. Food Chem Toxicol. 1987 Feb;25(2):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(87)90143-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engster M., Abraham R. Cecal response to different molecular weights and types of carrageenan in the guinea pig. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;38(2):265–282. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(76)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabian R. J., Abraham R., Coulston F., Golberg L. Carrageenan-induced squamous metaplasia of the rectal mucosa in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1973 Aug;65(2):265–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasso P., Sharratt M., Carpanini F. M., Gangolli S. D. Studies on carrageenan and large-bowel ulceration in mammals. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1973 Aug;11(4):555–564. doi: 10.1016/s0015-6264(73)80326-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KABACOFF B. L., WOHLMAN A., UMHEY M., AVAKIAN S. ABSORPTION OF CHYMOTRYPSIN FROM THE INTESTINAL TRACT. Nature. 1963 Aug 24;199:815–815. doi: 10.1038/199815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M., Gillund T. D., Heath D. Mast cells in the lungs of rats fed on Crotalaria spectabilis seeds. Am J Pathol. 1967 Dec;51(6):1031–1044. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling K. Y., Bhalla D., Hollander D. Mechanisms of carrageenan injury of IEC18 small intestinal epithelial cell monolayers. Gastroenterology. 1988 Dec;95(6):1487–1495. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(88)80067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maillet M., Bonfils S., Lister R. E. Carrageenan: effects in animals. Lancet. 1970 Aug 22;2(7669):414–415. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Marcus S. N., Marcus R., Watt J. Rapid production of ulcerative disease of the colon in newly-weaned guinea-pigs by degraded carrageenan. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;41(6):423–426. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1989.tb06493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus R., Watt J. Seaweeds and ulcerative colitis in laboratory animals. Lancet. 1969 Aug 30;2(7618):489–490. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottet N. K. On animal models for inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1972 Jun;62(6):1269–1271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklin S., Miller K. Intestinal uptake and immunological effects of carrageenan--current concepts. Food Addit Contam. 1989 Oct-Dec;6(4):425–436. doi: 10.1080/02652038909373801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Hermos J. A., Bartlett J. G. The role of the intestinal microflora in experimental colitis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1977 Nov;30(11):1819–1825. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/30.11.1819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Hermos J. A., Dzink J. L., Bartlett J. G. Protective effect of metronidazole in experimental ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Mar;74(3):521–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter G. D., Lester R. The developing colon and nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984 Sep;3(4):485–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharratt M., Grasso P., Carpanini F., Gangolli S. D. Carrageenan ulceration as a model for human ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 1970 Oct 31;2(7679):932–932. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Waaij D., Cohen B. J., Anver M. R. Mitigation of experimental inflammatory bowel disease in guinea pigs by selective elimination of the aerobic gram-negative intestinal microflora. Gastroenterology. 1974 Sep;67(3):460–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt J., Marcus R. Experimental ulcerative disease of the colon in animals. Gut. 1973 Jun;14(6):506–510. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.6.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt J., Marcus S. N., Marcus A. J. The comparative prophylactic effects of sulphasalazine, prednisolone and azathioprine in experimental colonic ulceration. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1980 Dec;32(12):873–874. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1980.tb13100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthington B. S., Enwonwu C. Absorption of intact protein by colonic epithelial cells of the rat. Am J Dig Dis. 1975 Aug;20(8):750–763. doi: 10.1007/BF01070833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]