Abstract
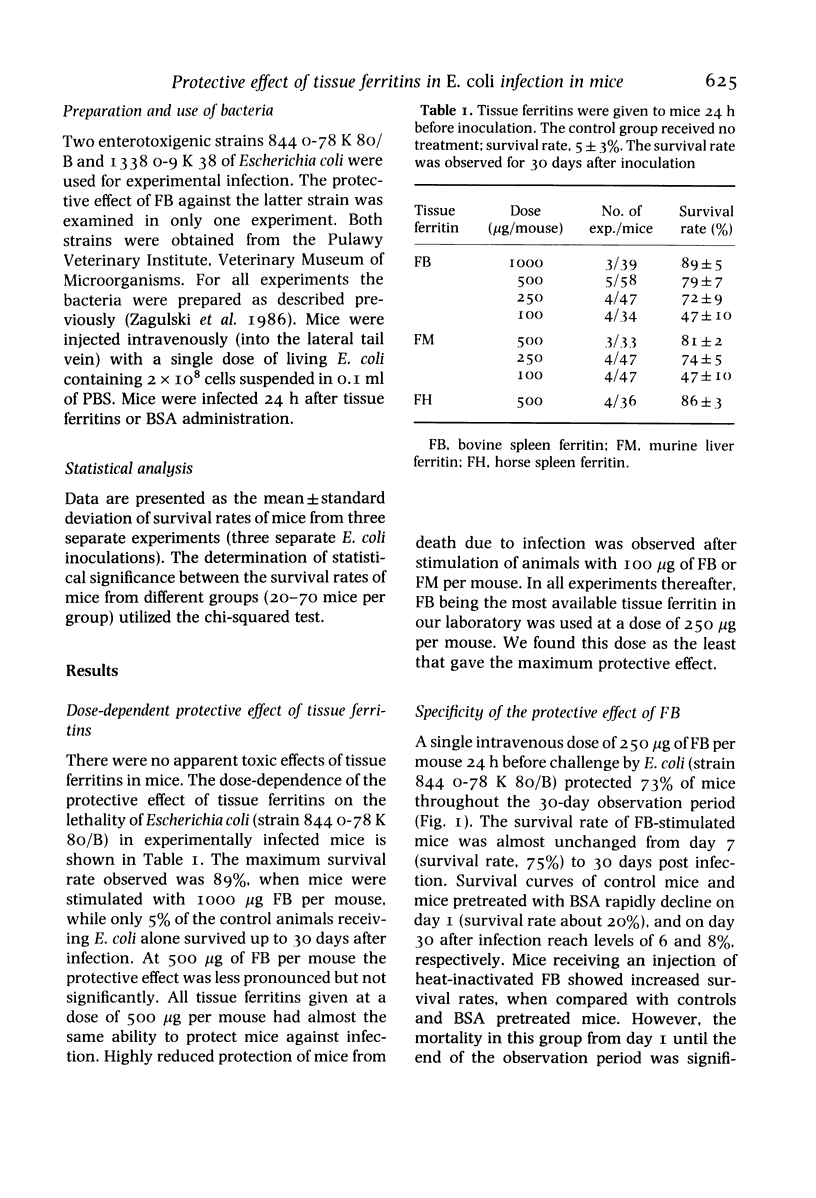
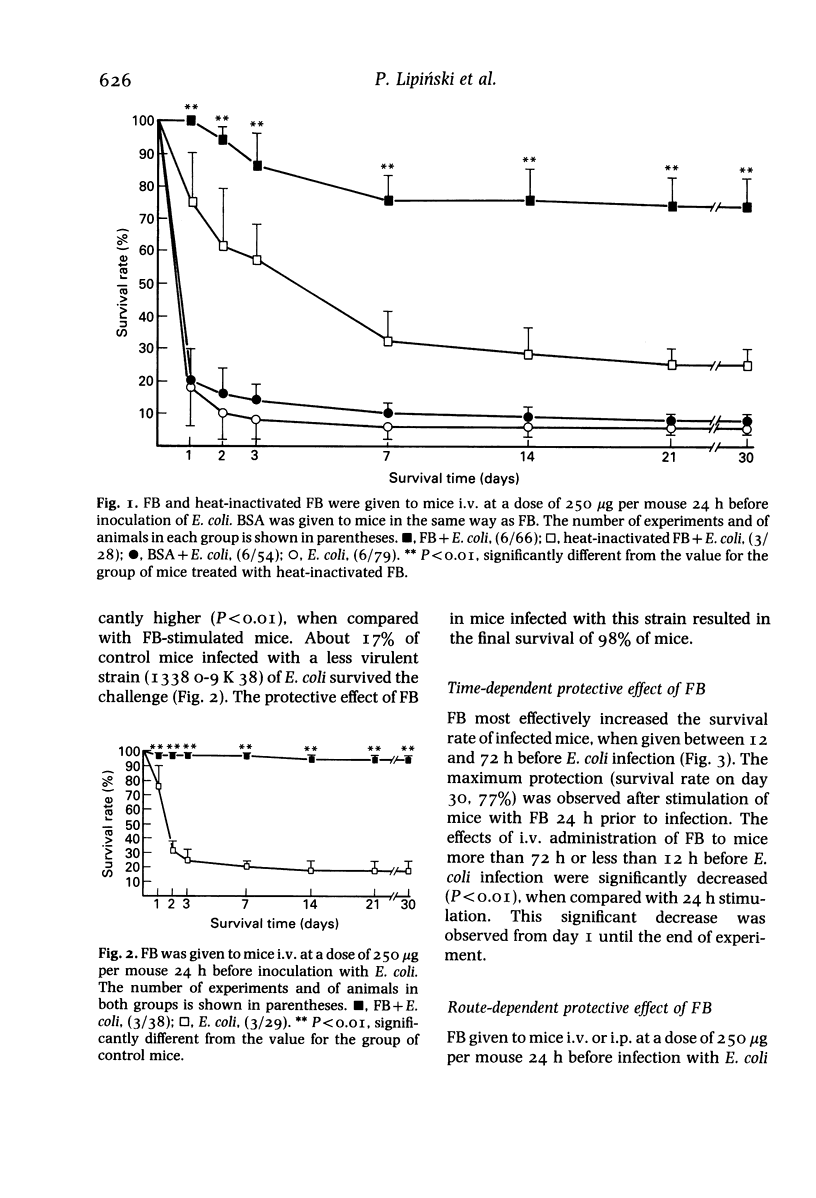
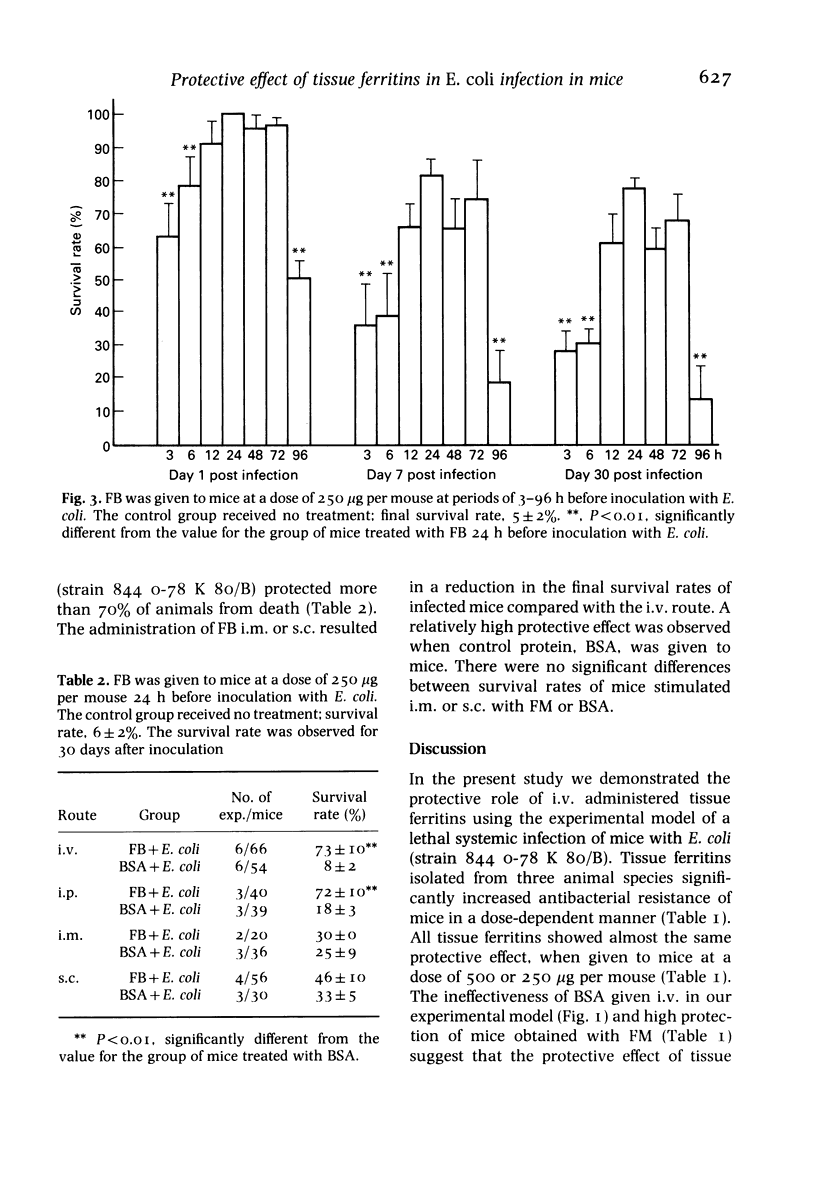
The effect of ferritins from horse (FH) and bovine (FB) spleen and murine liver (FM) on the survival rate of CFW mice lethally infected with Escherichia coli (strain 8440-78 K 80/B) was evaluated. Ferritins given intravenously 24 h before intravenous inoculation of bacteria, protected mice most effectively from death due to infection. The effect was dose dependent. At 500 micrograms of ferritin per mouse, the maximum survival rates were 86% (FH), 81% (FM) and 79% (FB), while only 5% of the control mice survived up to the 30th day. The survival rates of animals injected with bovine serum albumin (BSA) and heat-inactivated FB were 8 and 25%, respectively. Intraperitoneal injection of FB was as effective as intravenous in enhancing the resistance of mice against bacteria. These data provide evidence for the beneficial role of tissue ferritins in nonspecific antibacterial resistance.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreesen R., Osterholz J., Bodemann H., Bross K. J., Costabel U., Löhr G. W. Expression of transferrin receptors and intracellular ferritin during terminal differentiation of human monocytes. Blut. 1984 Sep;49(3):195–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00319822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birgegård G., Caro J. Increased ferritin synthesis and iron uptake in inflammatory mouse macrophages. Scand J Haematol. 1984 Jul;33(1):43–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1984.tb02208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birgegård G. The source of serum ferritin during infection. Studies with concanavalin A--Sepharose absorption. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Nov;59(5):385–387. doi: 10.1042/cs0590385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Gentile P., Bognacki J., Ralph P. Lactoferrin, transferrin and acidic isoferritins: regulatory molecules with potential therapeutic value in leukemia. Blood Cells. 1983;9(1):83–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. J. Circulating and tissue angiotensin systems. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI112768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Wolff S. M., Finch C. A. Effect of induced fever on serum iron and ferritin concentrations in man. Blood. 1977 Jan;49(1):147–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel E. J., van den Beld B., Marx J. J. Influence of subunit composition of rabbit liver ferritin on its clearance from plasma. Int J Biochem. 1987;19(12):1229–1231. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(87)90108-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardi A., Arpagaus G. R. Improved microtechnique for endotoxin assay by the Limulus amebocyte lysate test. Anal Biochem. 1980 Dec;109(2):382–385. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90664-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliday J. W., Mack U., Powell L. W. The kinetics of serum and tissue ferritins: relation to carbohydrate content. Br J Haematol. 1979 Aug;42(4):535–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb01166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs A. Serum ferritin and iron stores. Fed Proc. 1977 Jun;36(7):2024–2027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laohapand T., Smith J., Cattell V. Blood leucocyte infiltration after intravenous injection of ferritin in the rat. Br J Exp Pathol. 1985 Aug;66(4):475–482. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhyner K., Taetle R., Bering H., To D. Transferrin receptor regulation is coupled to intracellular ferritin in proliferating and differentiating HL60 leukemia cells. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Dec;125(3):608–612. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041250333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiaffonati L., Rappocciolo E., Tacchini L., Bardella L., Arosio P., Cozzi A., Cantu G. B., Cairo G. Mechanisms of regulation of ferritin synthesis in rat liver during experimental inflammation. Exp Mol Pathol. 1988 Apr;48(2):174–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(88)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., MacPhail P., Bothwell T., Lyons G., Baynes R., Torrance J. The fate of intravenously administered hepatic ferritin in normal, phenylhydrazine-treated and scorbutic guinea-pigs. Br J Haematol. 1987 Feb;65(2):239–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb02272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyberg J., Hedin U., Stenseth K. Endocytic pathways and time sequence of lysosomal transfer of macromolecules in cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. Double-labeling experiments with horseradish peroxidase and ferritin. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;241(2):299–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00217174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron withholding: a defense against infection and neoplasia. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jan;64(1):65–102. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worwood M., Aherne W., Dawkins S., Jacobs A. The characteristics of ferritin from human tissues, serum and blood cells. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1975 May;48(5):441–451. doi: 10.1042/cs0480441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagulski T., Lipiński P., Zagulska A., Broniek S., Jarzabek Z. Lactoferrin can protect mice against a lethal dose of Escherichia coli in experimental infection in vivo. Br J Exp Pathol. 1989 Dec;70(6):697–704. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zdravkovic D. Changes in serum ferritin following surgical trauma. Eur J Haematol. 1987 Jan;38(1):60–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1987.tb01425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


