Abstract
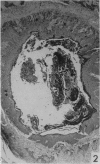
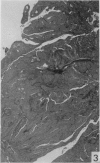
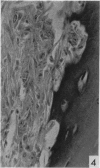
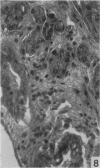
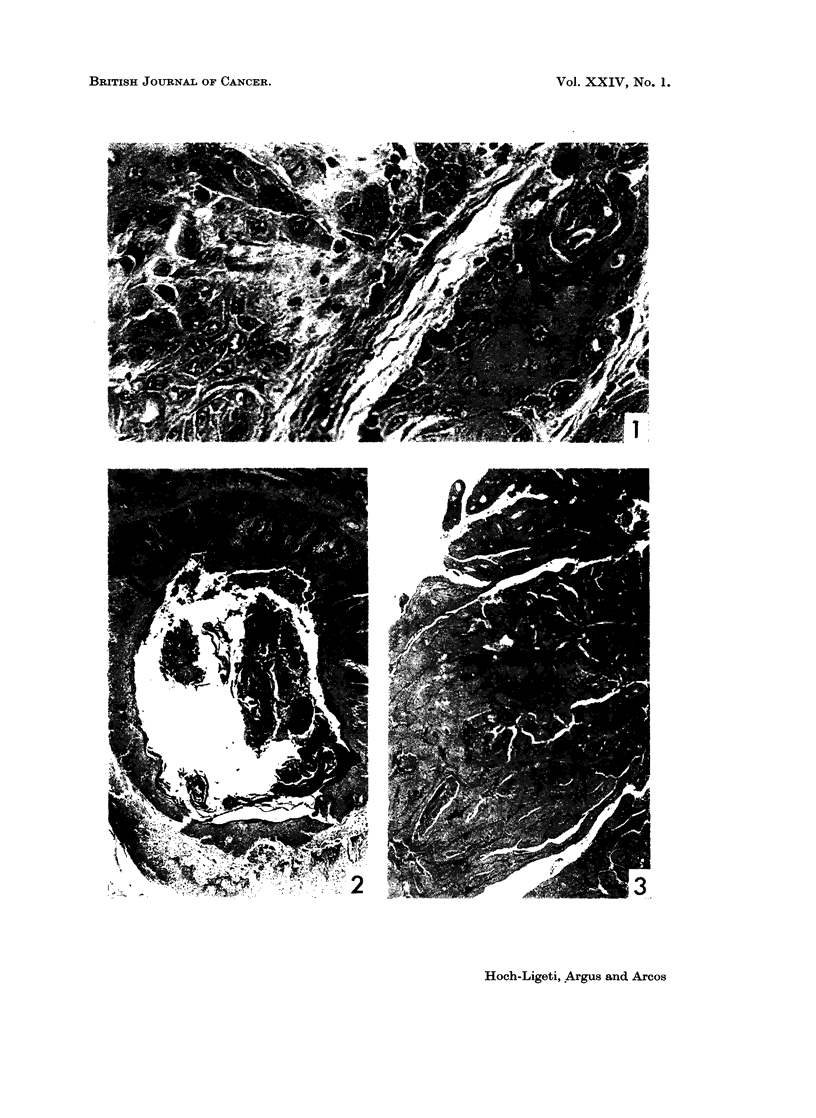
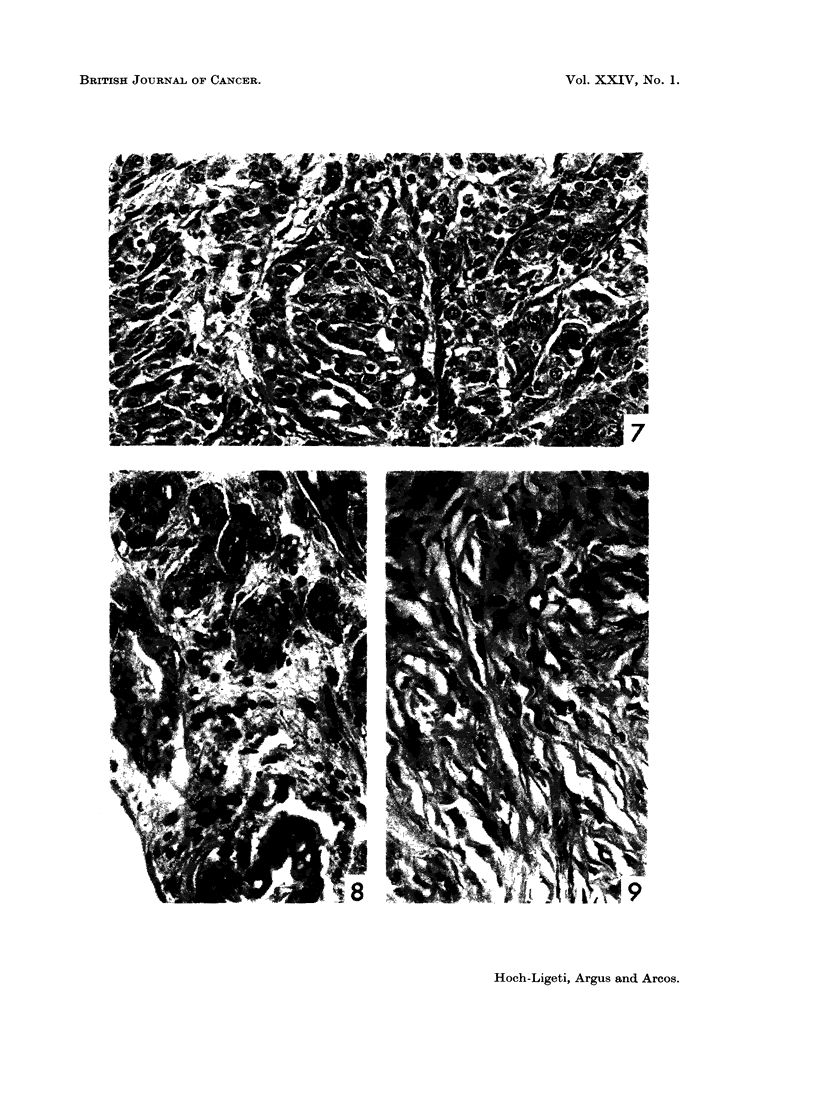
Six out of 120 rats fed dioxane in drinking water at levels of 0.75, 1.0, 1.4 or 1.8% developed carcinomas in the nasal cavity. Spontaneous tumors at this tissue localization have not been reported to occur in laboratory animals. The carcinomas were pre-eminently of epidermoid type with few adenocarcinomatous areas and epithelial papillomas. Four rats with carcinoma of the nasal cavity had hepatocellular carcinoma in addition.
Full text
PDF
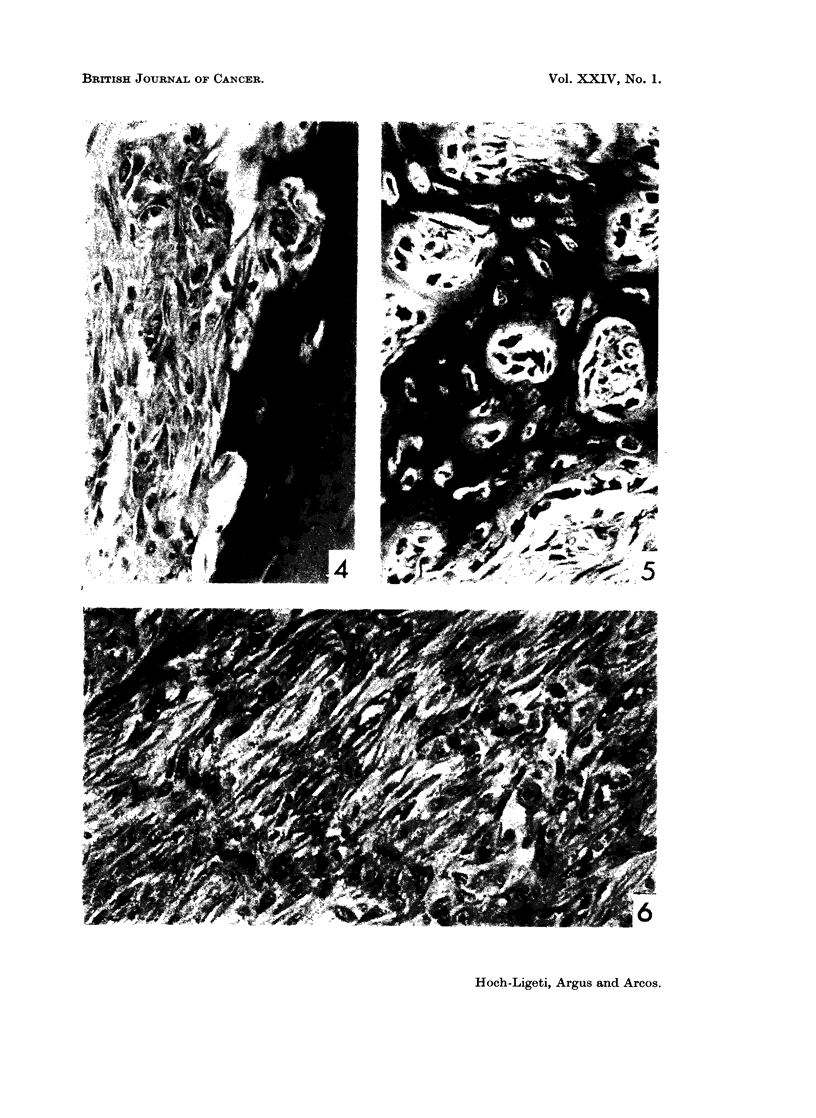




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARGUS M. F., ARCOS J. C., ALAM A., MATHISON J. H. A VISCOMETRIC STUDY OF HYDROGEN-BONDING PROPERTIES OF CARCINOGENIC NITROSAMINES AND RELATED COMPOUNDS. J Med Chem. 1964 Jul;7:460–465. doi: 10.1021/jm00334a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argus M. F., Arcos J. C., Hochligeti C. Studies on the carcinogenic activity of protein-denaturing agents: hepatocarcinogenicity of dioxane. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1965 Dec;35(6):949–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bemis J. A., Argus M. F., Arcos J. C. Studies on the denaturation of biological macromolecules by chemical carcinogens. 3. Optical rotatory dispersion and light-scattering changes of ovalbumin during denaturation and aggregation by water-soluble carcinogens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 10;126(2):274–285. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRUCKREY H., IVANKOVIC S., MENNEL H. D., PREUSSMANN R. SELEKTIVE ERZEUGUNG VON CARCINOMEN DER NASENHOEHLE BEI RATTEN DURCH N,N'-DI-NITROSOPIPERAZIN, NITROSOPIPERIDIN, NITROSOMORPHOLIN, METHYL-ALLYL-, DIMETHYL- UND METHYL-VINYL-NITROSAMIN. Z Krebsforsch. 1964 May 8;66:138–150. doi: 10.1007/BF02395339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipple A., Lawley P. D., Brookes P. Theory of tumour initiation by chemical carcinogens: dependence of activity on structure of ultimate carcinogen. Eur J Cancer. 1968 Oct;4(5):493–506. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(68)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner R. C., McLean A. E. Increased susceptibility to carbon tetrachloride poisoning in the rat after pretreatment with oral phenobarbitone. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Mar;18(3):645–650. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERROLD K. M., DUNHAM L. J. Induction of tumors in the Syrian hamster with diethylnitrosamine (N-nitrosodiethylamine). Cancer Res. 1963 Jun;23:773–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman A. D., Di Luzio N. R., Trumbull M. L. Modification of chronic carbon tetrachloride hepatic injury by N,N'-diphenyl-p-phenylenediamine. Exp Mol Pathol. 1968 Dec;9(3):349–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(68)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijinsky W., Loo J., Ross A. E. Mechanism of alkylation of nucleic acids by nitrosodimethylamine. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1174–1175. doi: 10.1038/2181174b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEWART H. L., SNELL K. C., MORRIS H. P. (THE COMBINED EFFECT OF 3-METHYLCHOLANTHRENE AND N,N'-2,7-FLUORENYLENEBISACETMIDE ON THE INDUCTION OF CANCER OF THE GLANDULAR STOMACH OF THE RAT.) J Natl Cancer Inst. 1965 Feb;34:157–174. doi: 10.1093/jnci/34.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman H. J. The spectrum of hepatotoxicity. Perspect Biol Med. 1968 Autumn;12(1):135–161. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1968.0004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]